The eleventh annual AST poster session - Home
... map or GPS system. The facts and knowledge we have today concerning the movement of stars in the sky, allow us to use tools such as a sextant to find the true altitude, mathematics, logical thinking and nautical or other almanacs (to know the positions of the heavenly bodies). Therefore, it is possi ...
... map or GPS system. The facts and knowledge we have today concerning the movement of stars in the sky, allow us to use tools such as a sextant to find the true altitude, mathematics, logical thinking and nautical or other almanacs (to know the positions of the heavenly bodies). Therefore, it is possi ...
Nov - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... month it rises three hours before the Sun and is so bright it is impossible to confuse it with any other astronomical body. Mars still lies in a difficult position for observation from these latitudes. It is in the constellation of Ophiuchus at magnitude +1.2. As I described last month, the shallow ...
... month it rises three hours before the Sun and is so bright it is impossible to confuse it with any other astronomical body. Mars still lies in a difficult position for observation from these latitudes. It is in the constellation of Ophiuchus at magnitude +1.2. As I described last month, the shallow ...
Hot-plate model of stars Test 2 & grades • Public viewing sessions
... (companion of Sirius A) have about the same temperature. How can Sirius B be 10,000 times fainter? ...
... (companion of Sirius A) have about the same temperature. How can Sirius B be 10,000 times fainter? ...
Star - Uplift Education
... roughly uniformly in all directions. The Big Bang predicts an expanding universe that had a very high temperature at the beginning; during the expansion the universe is cooling down and the temperature of the radiation should fall to its present low value of about 2.7 K. • That radiation corresponds ...
... roughly uniformly in all directions. The Big Bang predicts an expanding universe that had a very high temperature at the beginning; during the expansion the universe is cooling down and the temperature of the radiation should fall to its present low value of about 2.7 K. • That radiation corresponds ...
Mr. Traeger`s Light and Stars PowerPoint
... radius in meters, σ is Stefan-Boltzmann’s constant (5.6703 x 10-8 (W/m2K4), and T is Temperature in Kelvin ...
... radius in meters, σ is Stefan-Boltzmann’s constant (5.6703 x 10-8 (W/m2K4), and T is Temperature in Kelvin ...
Chapter 21 notes - Clinton Public Schools
... Section 5: The Expanding Universe: How the universe was formed: Astronomers believe the universe was incredibly hot and dense, exploded in what astronomers called the Big Bang. According to the big bang theory, the universe formed in an instant, billion of years ago, in an enormous explosion. Since ...
... Section 5: The Expanding Universe: How the universe was formed: Astronomers believe the universe was incredibly hot and dense, exploded in what astronomers called the Big Bang. According to the big bang theory, the universe formed in an instant, billion of years ago, in an enormous explosion. Since ...
AST 341 Final Exam and Solutions
... q and R is the distance to the object. Equating 2K = mv to -U = -GM/R gives v = GM/R. QED 11. Write the equation of detailed balance. Define all the terms. (10 points) What comes up must come down. Consider a two level atom with an upper state U and a lower state L. There are nL and nU electrons in ...
... q and R is the distance to the object. Equating 2K = mv to -U = -GM/R gives v = GM/R. QED 11. Write the equation of detailed balance. Define all the terms. (10 points) What comes up must come down. Consider a two level atom with an upper state U and a lower state L. There are nL and nU electrons in ...
Comet Lulin - indstate.edu
... Since Comet Lulin will be moving opposite the motion of the Earth, it will appear to approach us and move away especially fast. Beginning in February 2009, Comet Lulin will rise at about midnight local time, and will be about 6th or 7th magnitude. This won't be bright enough to go out and look at ...
... Since Comet Lulin will be moving opposite the motion of the Earth, it will appear to approach us and move away especially fast. Beginning in February 2009, Comet Lulin will rise at about midnight local time, and will be about 6th or 7th magnitude. This won't be bright enough to go out and look at ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... Slide 7: More detailed information about the H-R diagram will be presented further along. Since the presentation of the deep sky objects includes their spectral class and luminosity classes, the H-R diagram terminology is given here for those unfamiliar with H-R diagrams. The H-R diagram is a plot ...
... Slide 7: More detailed information about the H-R diagram will be presented further along. Since the presentation of the deep sky objects includes their spectral class and luminosity classes, the H-R diagram terminology is given here for those unfamiliar with H-R diagrams. The H-R diagram is a plot ...
Helium Fusion What Will Happen When There Is No More Helium in
... Electron degeneracy pressure balances inward crush of its own gravity Very high density and hence gravity Maximum mass=1.4 Msun (Chandrasekar limit) ...
... Electron degeneracy pressure balances inward crush of its own gravity Very high density and hence gravity Maximum mass=1.4 Msun (Chandrasekar limit) ...
galaxy_physics
... • Accretion requires AM loss : MHD torques • Energy liberated as photons & bulk flow – Luminous across the EM spectrum – Powerful outflows, some at relativistic speeds ...
... • Accretion requires AM loss : MHD torques • Energy liberated as photons & bulk flow – Luminous across the EM spectrum – Powerful outflows, some at relativistic speeds ...
Stellar Evolution - University of California, Santa Cruz
... • We can use the H-R Diagram of the stars in a cluster to determine the age of the cluster. • A cluster starts off with stars along the full main sequence. • Because stars with larger mass evolve more quickly, the hot, luminous end of the main sequence becomes depleted with time. • The `main-sequenc ...
... • We can use the H-R Diagram of the stars in a cluster to determine the age of the cluster. • A cluster starts off with stars along the full main sequence. • Because stars with larger mass evolve more quickly, the hot, luminous end of the main sequence becomes depleted with time. • The `main-sequenc ...
Fingerprints in Starlight: Spectroscopy of Stars Inquiry Questions
... 6. Why is information about many stars contained in absorption rather than emission spectra? If there is a cloud of gas at a cooler temperature directly between a denser source producing a continuous spectrum (i.e. a star) and a telescope, the gas will absorb light at specific wavelengths that are c ...
... 6. Why is information about many stars contained in absorption rather than emission spectra? If there is a cloud of gas at a cooler temperature directly between a denser source producing a continuous spectrum (i.e. a star) and a telescope, the gas will absorb light at specific wavelengths that are c ...
Document
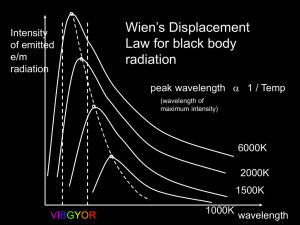
... Estimate the intensity of the radiation emitted per unit area from a star if it’s effective surface Temp is 6000K Estimate the energy emitted from a star if its peak wavelength is 600nm. Total power radiated Power output = E x surface area of star Surface area of a star = 4 R 2 Where R is the rad ...
... Estimate the intensity of the radiation emitted per unit area from a star if it’s effective surface Temp is 6000K Estimate the energy emitted from a star if its peak wavelength is 600nm. Total power radiated Power output = E x surface area of star Surface area of a star = 4 R 2 Where R is the rad ...
Colour - Magnitude Diagram for M 45
... Colour - Magnitude Diagram for M 45 (Pleiades) Introduction The Pleiades is a relatively close open cluster. The six or seven stars visible to the naked eye form a tight grouping of stars (an asterism) near the even closer Hyades cluster. They are easily visible in the winter sky in the northern hem ...
... Colour - Magnitude Diagram for M 45 (Pleiades) Introduction The Pleiades is a relatively close open cluster. The six or seven stars visible to the naked eye form a tight grouping of stars (an asterism) near the even closer Hyades cluster. They are easily visible in the winter sky in the northern hem ...
Evolution of our Sun
... About how long does our star live as a main sequence star? Explain why a massive star only lives a short time? What elements are created in a sun-like star? What elements are created in a massive star? Evolution of the Sun – Part 2 Name and briefly describe the stages that our sun will go through as ...
... About how long does our star live as a main sequence star? Explain why a massive star only lives a short time? What elements are created in a sun-like star? What elements are created in a massive star? Evolution of the Sun – Part 2 Name and briefly describe the stages that our sun will go through as ...
Instrumentation for Cosmology
... Suppose the age of the galaxy is 10 billion years. Its inner regions rotate once in 200 million years… Therefore, we’d expect about 50 turns. The galaxy would look like a clock spring. ...
... Suppose the age of the galaxy is 10 billion years. Its inner regions rotate once in 200 million years… Therefore, we’d expect about 50 turns. The galaxy would look like a clock spring. ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.