Distance measurement in Astronomy
... You can find the distances of stars that are ‘relatively close’ to the Earth using parallax. A very simple example of parallax is to hold one forefinger upright about 30 cm in front of your nose and close your right eye. Using just your left eye line up your forefinger with an object on the other si ...
... You can find the distances of stars that are ‘relatively close’ to the Earth using parallax. A very simple example of parallax is to hold one forefinger upright about 30 cm in front of your nose and close your right eye. Using just your left eye line up your forefinger with an object on the other si ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 8
... hypothesis of dark matter that does not interact with the electromagnetic force, but whose presence can be inferred from gravitational effect on visible matter. ...
... hypothesis of dark matter that does not interact with the electromagnetic force, but whose presence can be inferred from gravitational effect on visible matter. ...
How Stars Evolve
... thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change B. Its mass would increase C. Its internal temperature would increase D. It would be happy ...
... thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change B. Its mass would increase C. Its internal temperature would increase D. It would be happy ...
Document
... The Helium burning phase The helium burning phase is much shorter than the hydrogen burning phase. Helium burning produces about 1/10 the energy per unit mass compared to Hydrogen burning. Also, the star’s luminosity is higher by about an order of magnitude compared to the MS Low mass stars (0.7-2. ...
... The Helium burning phase The helium burning phase is much shorter than the hydrogen burning phase. Helium burning produces about 1/10 the energy per unit mass compared to Hydrogen burning. Also, the star’s luminosity is higher by about an order of magnitude compared to the MS Low mass stars (0.7-2. ...
Deaths of Stars - Chabot College
... Collapses until neutron degeneracy pressure holds up the corpse (neutron star) ...
... Collapses until neutron degeneracy pressure holds up the corpse (neutron star) ...
AST 207 7 Homew
... m sequencce because theey all already used up theirr There are no hotter stars on the main gen cores and d left the main n sequence. H Hotter stars usse up their fuel faster. hydrog c. Stars with w a color B-V=0.6 span a range of 5 m magnitudes. (22 pts.) What pproperty of thee stars accoun nts for ...
... m sequencce because theey all already used up theirr There are no hotter stars on the main gen cores and d left the main n sequence. H Hotter stars usse up their fuel faster. hydrog c. Stars with w a color B-V=0.6 span a range of 5 m magnitudes. (22 pts.) What pproperty of thee stars accoun nts for ...
Space Exploration
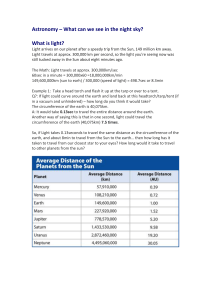
... • 1Light year = 300 000km/s x 60s/min x60min/hr x 24hr/day x 365days/yr or 9.46 x 1015 meters • The distance that light travels in one year. • The nearest star, Alpha Centari is 4 light years away ...
... • 1Light year = 300 000km/s x 60s/min x60min/hr x 24hr/day x 365days/yr or 9.46 x 1015 meters • The distance that light travels in one year. • The nearest star, Alpha Centari is 4 light years away ...
Constellations
... The first on the list of Heracles' jobs was the task of killing the Nemean Lion, a giant beast that roamed the hills and the streets of the Peloponnesian villages, devouring whomever it met. The animal's skin was immune to iron, bronze, and stone and Heracles' arrows bounced off the lion. So Heracle ...
... The first on the list of Heracles' jobs was the task of killing the Nemean Lion, a giant beast that roamed the hills and the streets of the Peloponnesian villages, devouring whomever it met. The animal's skin was immune to iron, bronze, and stone and Heracles' arrows bounced off the lion. So Heracle ...
What is your real star sign - teacher notes
... thought that the Earth was the centre of the Universe and that the things that appeared in the night sky were to do with supernatural beings that could affect their everyday life. They thought there must be a connection between where the celestial objects were in the sky and what would happen in the ...
... thought that the Earth was the centre of the Universe and that the things that appeared in the night sky were to do with supernatural beings that could affect their everyday life. They thought there must be a connection between where the celestial objects were in the sky and what would happen in the ...
Section 7.3 - CPO Science
... group of stars, dust, gas, and other objects bound together by gravitational forces. • The sun, along with an estimated 200 billion other stars, belongs to the Milky Way galaxy. ...
... group of stars, dust, gas, and other objects bound together by gravitational forces. • The sun, along with an estimated 200 billion other stars, belongs to the Milky Way galaxy. ...
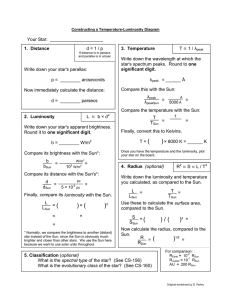
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... F. The distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arcsecond, equal to about 3.26 light-years G. The four largest moons of Jupiter—Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto H. A region of the solar system beyond the orbit of Neptune, believed to contain many comets, asteroids, and othe ...
Problems in Chapter 13
... . Alpha Centauri has its peak radiation at 500 nm. Applying Wien’s Law, T = 3 × 106 K nm / 500 nm = 6000 K. The temperature of this star is approximately the same as our Sun’s, so Alpha Centauri has a similar spectral type to the Sun (G2). ...
... . Alpha Centauri has its peak radiation at 500 nm. Applying Wien’s Law, T = 3 × 106 K nm / 500 nm = 6000 K. The temperature of this star is approximately the same as our Sun’s, so Alpha Centauri has a similar spectral type to the Sun (G2). ...
7.4 Evolution on the Main-Sequence Main-sequence (m
... Main-sequence (m-s) stars evolve on the nuclear time-scale which is very slow in contrast to the Kelvin-Helmholtz time-scale which governs the length of the pre-main-sequence phase. For the Sun, the contraction time to the m-s τK−H ∼ 30 × 106 yr and τm−s ∼ 1010 yr. For a 9 M star, the corresponding ...
... Main-sequence (m-s) stars evolve on the nuclear time-scale which is very slow in contrast to the Kelvin-Helmholtz time-scale which governs the length of the pre-main-sequence phase. For the Sun, the contraction time to the m-s τK−H ∼ 30 × 106 yr and τm−s ∼ 1010 yr. For a 9 M star, the corresponding ...
Lec11_2D
... Accretion Disks and Black Holes The accretion disk around a black hole can extend very close to the event horizon. The gas speed there is very close to the speed of light, so the friction in the disk is extremely intense. This type of disk will produce the most-energetic x-rays. ...
... Accretion Disks and Black Holes The accretion disk around a black hole can extend very close to the event horizon. The gas speed there is very close to the speed of light, so the friction in the disk is extremely intense. This type of disk will produce the most-energetic x-rays. ...
Ordering_The_Universe
... Planet Sun’s Neighbors Local Group/Cluster Star Natural Satellite Solar System Galaxy Universe Super Cluster ...
... Planet Sun’s Neighbors Local Group/Cluster Star Natural Satellite Solar System Galaxy Universe Super Cluster ...
Star Constellations
... http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 ...
... http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 ...
PPTX
... During the day, the Sun moves from east to west across the sky. In which direction do the stars move after the Sun has set? (A) The stars are stationary; they don't move (B) West (C) East ...
... During the day, the Sun moves from east to west across the sky. In which direction do the stars move after the Sun has set? (A) The stars are stationary; they don't move (B) West (C) East ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.