A Decade in the Life of the Massive Black-Hole Binary... Silas Laycock !
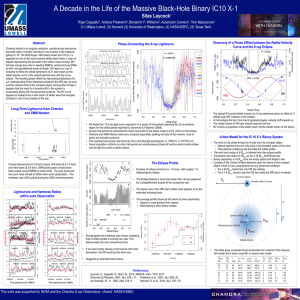
... and the radiation field of the compact object. Among other things it appears that the need for a massive BH in the system is evaporating along with the dynamical evidence. The RV curve appears to instead trace a slim sector of stellar wind that escapes ionization in the X-ray shadow of the star. ...
... and the radiation field of the compact object. Among other things it appears that the need for a massive BH in the system is evaporating along with the dynamical evidence. The RV curve appears to instead trace a slim sector of stellar wind that escapes ionization in the X-ray shadow of the star. ...
mars, antares, the sting and more
... JAMES: NOW THAT WEVE INVESTIGATED THE HEART OF THE SCORPION, HOW ABOUT HIS TAIL? AT THE END OF THE FISHHOOK SHAPE, LOOK FOR TWO STARS THAT ARE VERY CLOSE TOGETHER. THESE ARE THE STARS SHAULA AND LESATH AND TOGETHER THEY ARE KNOWN AS, THE STING. DEAN: MAKES SENSE. ALTHOUGH THESE TWO STARS LOOK CLOSE ...
... JAMES: NOW THAT WEVE INVESTIGATED THE HEART OF THE SCORPION, HOW ABOUT HIS TAIL? AT THE END OF THE FISHHOOK SHAPE, LOOK FOR TWO STARS THAT ARE VERY CLOSE TOGETHER. THESE ARE THE STARS SHAULA AND LESATH AND TOGETHER THEY ARE KNOWN AS, THE STING. DEAN: MAKES SENSE. ALTHOUGH THESE TWO STARS LOOK CLOSE ...
Black Hole Sun: A Total Eclipse Free Public Lecture about Eclipses
... We are interpreting E. C. Pickering’s (A. J. Cannon’s boss) spectra of Mizar (a star in the Big Dipper) in 1889. How can the spectral line of hydrogen appear at different wavelengths? A. The star is moving. B. Hydrogen emits at different wavelengths at different times. C. There was something wrong w ...
... We are interpreting E. C. Pickering’s (A. J. Cannon’s boss) spectra of Mizar (a star in the Big Dipper) in 1889. How can the spectral line of hydrogen appear at different wavelengths? A. The star is moving. B. Hydrogen emits at different wavelengths at different times. C. There was something wrong w ...
Lecture 10 - University of Minnesota
... tremendous amounts of energy • Star explodes in a supernova – Might form a neutron star held together by neutron degeneracy pressure – Might be so massive that it forms a black hole ...
... tremendous amounts of energy • Star explodes in a supernova – Might form a neutron star held together by neutron degeneracy pressure – Might be so massive that it forms a black hole ...
2014 State Test
... Use the images provided to answer the questions. For all questions about parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, choose from the following list: Gamma ray, Infrared, Microwave, Radio, Ultraviolet, Visible, X-ray All questions at this station are worth one (1) point. ...
... Use the images provided to answer the questions. For all questions about parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, choose from the following list: Gamma ray, Infrared, Microwave, Radio, Ultraviolet, Visible, X-ray All questions at this station are worth one (1) point. ...
4th Grade Earth Science Unit Guide:
... The SUN looks the largest because it is the closest star to Earth. All stars are hot. The hottest star is blue, then white, then yellow, then orange, then red. So blue stars are the hottest, and red stars are the coolest. Stars can be seen on a clear, dark night Sizes of stars: Supergiants a ...
... The SUN looks the largest because it is the closest star to Earth. All stars are hot. The hottest star is blue, then white, then yellow, then orange, then red. So blue stars are the hottest, and red stars are the coolest. Stars can be seen on a clear, dark night Sizes of stars: Supergiants a ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
... Hot blue stars have low, and even negative B-V. Cooler red stars have B-V values somewhat over 1. Create an H-R diagram of your data, as explained in the Introduction section. Use regular graph paper. Then complete the following items: 1. Identify the main sequence. Sketch a line through it, and lab ...
... Hot blue stars have low, and even negative B-V. Cooler red stars have B-V values somewhat over 1. Create an H-R diagram of your data, as explained in the Introduction section. Use regular graph paper. Then complete the following items: 1. Identify the main sequence. Sketch a line through it, and lab ...
Stellar Structure - McMurry University
... the flashes (“pulses”) of light happen many times a second. When observed with telescopes, these rapidly flashing (“pulsing”) objects were originally called pulsars. Pulsars are just neutron stars that are easy to observe because the pulsing makes them stand out. ...
... the flashes (“pulses”) of light happen many times a second. When observed with telescopes, these rapidly flashing (“pulsing”) objects were originally called pulsars. Pulsars are just neutron stars that are easy to observe because the pulsing makes them stand out. ...
chapter 14 - Astronomy
... (b) Type Ia result from white dwarfs. 6. A Type Ia supernova reaches maximum brightness in a few days, fades quickly for about a month, and then declines in brightness more gradually until it dissipates in about a year. 7. Models indicate that the energy of a Type Ia supernova (following the explosi ...
... (b) Type Ia result from white dwarfs. 6. A Type Ia supernova reaches maximum brightness in a few days, fades quickly for about a month, and then declines in brightness more gradually until it dissipates in about a year. 7. Models indicate that the energy of a Type Ia supernova (following the explosi ...
Review for Exam I PHYS 1050
... • circumference of circle = 2 x radius • area of circle = r2 • astronomical unit = 1 AU = 150 x 106 km = average distance from Earth to Sun • speed of light = 300,000 km/sec • light year = 1 LY = distance light travels in one year • distance = speed x time ...
... • circumference of circle = 2 x radius • area of circle = r2 • astronomical unit = 1 AU = 150 x 106 km = average distance from Earth to Sun • speed of light = 300,000 km/sec • light year = 1 LY = distance light travels in one year • distance = speed x time ...
What is light?
... In 1905 Einstein calculated the energy of a particle of light (a photon) and proposed the photoelectric effect. (Confirmed the particle nature of light.) Ephoton = hc/l or Ephoton = hf Which light is higher energy: A) Radio waves ...
... In 1905 Einstein calculated the energy of a particle of light (a photon) and proposed the photoelectric effect. (Confirmed the particle nature of light.) Ephoton = hc/l or Ephoton = hf Which light is higher energy: A) Radio waves ...
physics_cosmic_engine - HSC Guru
... Friedmann proved mathematically that the universe is expanding. However he made some assumptions in order to prove it. Hubble showed that the universe was expanding, by showing that almost all the galaxies are red-shifted, meaning that they are moving away from us. ...
... Friedmann proved mathematically that the universe is expanding. However he made some assumptions in order to prove it. Hubble showed that the universe was expanding, by showing that almost all the galaxies are red-shifted, meaning that they are moving away from us. ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... stars composition and temperature. When an element emits light only certain colors show up. The colors are called emission lines----kind of like fingerprints. ...
... stars composition and temperature. When an element emits light only certain colors show up. The colors are called emission lines----kind of like fingerprints. ...
Introduction to Basic Stargazing Part II - Naples Free-Net
... Comets as a group are not rare. At any given time, there are perhaps a half dozen or more comets in the sky, but these are telescopic objects only. About once every two years or so a comet does appear visible to the naked eye in the west after sunset or in the east before dawn. It is a peculiarity o ...
... Comets as a group are not rare. At any given time, there are perhaps a half dozen or more comets in the sky, but these are telescopic objects only. About once every two years or so a comet does appear visible to the naked eye in the west after sunset or in the east before dawn. It is a peculiarity o ...
Stages 12 to 14
... Isolated white dwarfs are hard to observe, and most are still in the planetary nebula phase. However, if they are part of a binary system, the expanding shells can be sucked into the companion star, leaving an isolate white dwarf in orbit around the companion star. If the white dwarf is bright enoug ...
... Isolated white dwarfs are hard to observe, and most are still in the planetary nebula phase. However, if they are part of a binary system, the expanding shells can be sucked into the companion star, leaving an isolate white dwarf in orbit around the companion star. If the white dwarf is bright enoug ...
Related Handout - Orange County Astronomers
... Mars is the last of the terrestrial planets. Its diameter is 4,116 miles, its mass 11% of Earth’s, and it circles the Sun in 1.88 years at an average distance of 1.5 AU. The planet is cratered, has a thin atmosphere of carbon dioxide, and has two small moons, Deimos and Phobos, beyond the reach of t ...
... Mars is the last of the terrestrial planets. Its diameter is 4,116 miles, its mass 11% of Earth’s, and it circles the Sun in 1.88 years at an average distance of 1.5 AU. The planet is cratered, has a thin atmosphere of carbon dioxide, and has two small moons, Deimos and Phobos, beyond the reach of t ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.























