Quiz Maker - Geneva 304
... 1. From looking at Figure 24-11 in your book, draw the Lyman series and the Balmer series on the same wavelength axis, that is, on a horizontal straight line labeled in angstroms every 500 Å from 500 to 7,000 Å. ...
... 1. From looking at Figure 24-11 in your book, draw the Lyman series and the Balmer series on the same wavelength axis, that is, on a horizontal straight line labeled in angstroms every 500 Å from 500 to 7,000 Å. ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... All red giants or supergiants are NOT very massive stars. In fact, our own Sun will become a red giant and a red supergiant as it evolves through its final sequence of energy production mechanisms. Giant stars are not necessarily giants in mass, but are giants in radius. Inside all giant stars energ ...
... All red giants or supergiants are NOT very massive stars. In fact, our own Sun will become a red giant and a red supergiant as it evolves through its final sequence of energy production mechanisms. Giant stars are not necessarily giants in mass, but are giants in radius. Inside all giant stars energ ...
AST1001.ch2
... • all lie at about the same distance from Earth. • may actually be quite far away from each other. ...
... • all lie at about the same distance from Earth. • may actually be quite far away from each other. ...
Earth in the Universe Answer each in your binder or notebook. Date
... Both Earth and Jupiter follow elliptical orbits around the Sun. The orbit of Jupiter is farther from the Sun than the orbit of Earth. How does this orbit affect the motion of Jupiter compared to Earth? A. Jupiter rotates more slowly on its axis. B. Jupiter revolves more slowly in its orbit. C. The p ...
... Both Earth and Jupiter follow elliptical orbits around the Sun. The orbit of Jupiter is farther from the Sun than the orbit of Earth. How does this orbit affect the motion of Jupiter compared to Earth? A. Jupiter rotates more slowly on its axis. B. Jupiter revolves more slowly in its orbit. C. The p ...
Galileo Galilei From The Starry Messenger (1610) and The Assayer
... to the unaided vision, adding countless more which have never before been seen, exposing these plainly to the eye in numbers ten times exceeding the old and familiar stars. It is a very beautiful thing, and most gratifying to the sight, to behold the body of the moon, distant from us almost sixty ea ...
... to the unaided vision, adding countless more which have never before been seen, exposing these plainly to the eye in numbers ten times exceeding the old and familiar stars. It is a very beautiful thing, and most gratifying to the sight, to behold the body of the moon, distant from us almost sixty ea ...
Celestial Sphere Lab
... ideas they proposed have since proven to be incorrect. Some of the concepts they developed are still useful today though. One of the more useful ideas proposed by the ancient Greeks is the idea of a celestial sphere. We now know that the Earth’s rotation causes the stars to appear to move around us ...
... ideas they proposed have since proven to be incorrect. Some of the concepts they developed are still useful today though. One of the more useful ideas proposed by the ancient Greeks is the idea of a celestial sphere. We now know that the Earth’s rotation causes the stars to appear to move around us ...
Homework 12 1. How would phases change if the Moon were the
... 2. How would tides change if the Moon were the same size as Earth, but still had the same mass? The tides would be mostly unaffected because the mass of the Moon would remain the same and so the gravitational force would be nearly the same. There would be different distances of parts of the Moon fro ...
... 2. How would tides change if the Moon were the same size as Earth, but still had the same mass? The tides would be mostly unaffected because the mass of the Moon would remain the same and so the gravitational force would be nearly the same. There would be different distances of parts of the Moon fro ...
astrocoursespring2012lec1-1-5
... who search for comets they can be viewed as an inconvenience; comet discoverer Leslie Peltier called them “comet masqueraders.”. At the end of 1758, Charles Messier found a fuzzy patch around Zeta Tauri. As he studied it from hour to hour and from night to night, he found that the faint fuzzy object ...
... who search for comets they can be viewed as an inconvenience; comet discoverer Leslie Peltier called them “comet masqueraders.”. At the end of 1758, Charles Messier found a fuzzy patch around Zeta Tauri. As he studied it from hour to hour and from night to night, he found that the faint fuzzy object ...
Astronomy 15 - Problem Set Number 4 1) Suppose one were to
... results in an easily detectable pulse of electric current corresponding to the original photon. Photomultipliers therefore make it practical to count individual photons. In practice only about 20-30 per cent of the original photons create electrons (for visible wavelength photons); the Si in CCDs ha ...
... results in an easily detectable pulse of electric current corresponding to the original photon. Photomultipliers therefore make it practical to count individual photons. In practice only about 20-30 per cent of the original photons create electrons (for visible wavelength photons); the Si in CCDs ha ...
Origins of the Universe
... – called a protostar (a hot & condensed object) • Particles began to gather in the centre of the spinning cloud (analogy: stirring a glass of water with salt or sand in it) • Spinning nebula began to contract and tiny grains started to ...
... – called a protostar (a hot & condensed object) • Particles began to gather in the centre of the spinning cloud (analogy: stirring a glass of water with salt or sand in it) • Spinning nebula began to contract and tiny grains started to ...
Explorations of the Universe
... Number of Stars in the Galaxy (400 billion) x Fraction of Stars with Planets (1/4?) x Number of suitable planets per star (2?) x Fraction of planets where life appears (1/2??) x Fraction of planets with intelligence (???) x Fraction of planets with technology (???) x Fraction of planet’s life with t ...
... Number of Stars in the Galaxy (400 billion) x Fraction of Stars with Planets (1/4?) x Number of suitable planets per star (2?) x Fraction of planets where life appears (1/2??) x Fraction of planets with intelligence (???) x Fraction of planets with technology (???) x Fraction of planet’s life with t ...
distant stars nearby star parallax angle The principle of geometrical
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
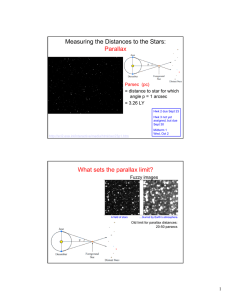
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... A nebula is an enormous cloud of gas and dust in which stars are born. Most nebulae produce an emission spectrum, which is characterized by bright lines of color against a dark background. The bright lines in an emission spectrum correspond to the dark lines in an absorption spectrum. ...
... A nebula is an enormous cloud of gas and dust in which stars are born. Most nebulae produce an emission spectrum, which is characterized by bright lines of color against a dark background. The bright lines in an emission spectrum correspond to the dark lines in an absorption spectrum. ...
The Sun and the Origin of the Solar System
... – Contraction of core, raises the temperature – Ignites He shell around the core – Eventually the core stabilizes – Envelope is ejected as a "planetary nebula" – The core remains as a "white dwarf" ...
... – Contraction of core, raises the temperature – Ignites He shell around the core – Eventually the core stabilizes – Envelope is ejected as a "planetary nebula" – The core remains as a "white dwarf" ...
Jun - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... The Planets that (probably) Never Were Brian Mills This follows on from Brian’s informative talks for beginners introducing the planets in the Solar System, but having described all the planets, the asteroid belt and Dwarf Planets he now looks at theoretical ‘planets’ that probably never existed. As ...
... The Planets that (probably) Never Were Brian Mills This follows on from Brian’s informative talks for beginners introducing the planets in the Solar System, but having described all the planets, the asteroid belt and Dwarf Planets he now looks at theoretical ‘planets’ that probably never existed. As ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... lab is designed to help you understand how the software works and what its capabilities are. Obtain a laptop computer from the cart (remember to leave the AC adapter in the cart), turn on the computer and, once the Windows desktop is displayed, click on “the Sky” icon along the bottom row or else th ...
... lab is designed to help you understand how the software works and what its capabilities are. Obtain a laptop computer from the cart (remember to leave the AC adapter in the cart), turn on the computer and, once the Windows desktop is displayed, click on “the Sky” icon along the bottom row or else th ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.