click here - CAPSTONE 2011
... Analysis of binaries •The need now is to get as many stars as possible defined in terms of mass, temperature and luminosity. • Stars in the same part of the HR diagram that come from binaries are the same as other stars that fall near them in luminosity and temperature • In clusters, spectra can be ...
... Analysis of binaries •The need now is to get as many stars as possible defined in terms of mass, temperature and luminosity. • Stars in the same part of the HR diagram that come from binaries are the same as other stars that fall near them in luminosity and temperature • In clusters, spectra can be ...
Slide 1
... Milky Way Galaxy • Consists of over 200 billion stars • 16,000 light years thick (central bulge) • 100,000 light years across (long end to end) • The arm that our solar system is in (Orion Arm) is about 30,000 light years long ...
... Milky Way Galaxy • Consists of over 200 billion stars • 16,000 light years thick (central bulge) • 100,000 light years across (long end to end) • The arm that our solar system is in (Orion Arm) is about 30,000 light years long ...
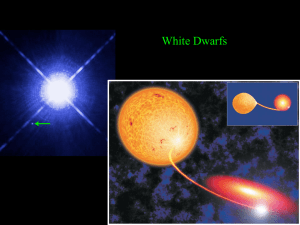
white dwarf supernova
... B) The white dwarf C) They are generally the same temperature D) Can’t answer without more information Which is more luminous, a red giant star or a white dwarf? ...
... B) The white dwarf C) They are generally the same temperature D) Can’t answer without more information Which is more luminous, a red giant star or a white dwarf? ...
The Milky Way
... It's a hundred thousand light years side to side. It bulges in the middle, sixteen thousand light years thick, But out by us, it's just three thousand light years wide. We're thirty thousand light years from galactic central point. We go 'round every two hundred million years, And our galaxy is only ...
... It's a hundred thousand light years side to side. It bulges in the middle, sixteen thousand light years thick, But out by us, it's just three thousand light years wide. We're thirty thousand light years from galactic central point. We go 'round every two hundred million years, And our galaxy is only ...
PDF version
... see a lightly glowing, almost "milky" band that stretches across the entire sky. That dim band is actually the Milky Way, full of far-away stars that can't be seen ...
... see a lightly glowing, almost "milky" band that stretches across the entire sky. That dim band is actually the Milky Way, full of far-away stars that can't be seen ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... White Dwarf • The remaining core becomes a white dwarf • White dwarfs are usually composed of carbon and oxygen (can not fuse carbon) • Oxygen-neon-magnesium white dwarfs can also form (hot enough to fuse carbon but not neon) • Helium white dwarfs can form ...
... White Dwarf • The remaining core becomes a white dwarf • White dwarfs are usually composed of carbon and oxygen (can not fuse carbon) • Oxygen-neon-magnesium white dwarfs can also form (hot enough to fuse carbon but not neon) • Helium white dwarfs can form ...
chapter 7 review questions
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? F 5. An absorption spectrum is also called a bright line spectrum. GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What kind of spectra do you see when you look at celestial objects? T. 6. Hydrogen alpha is the longest wavelength Balmer line. F ...
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? F 5. An absorption spectrum is also called a bright line spectrum. GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What kind of spectra do you see when you look at celestial objects? T. 6. Hydrogen alpha is the longest wavelength Balmer line. F ...
As two continental plates move toward each other, what landforms
... correct because 2 continental masses will push into each other and “crumple” the edges to form mountains ...
... correct because 2 continental masses will push into each other and “crumple” the edges to form mountains ...
STAR FORMATION
... • If the protostar's mass is less than about 8% of the Sun's mass it is insufficient to compress the center to temperatures and densities adequate to allow ordinary fusion -- THE LOWER MASS LIMIT • Such failed stars are called brown dwarfs. • Most astronomers make a further distinction between brown ...
... • If the protostar's mass is less than about 8% of the Sun's mass it is insufficient to compress the center to temperatures and densities adequate to allow ordinary fusion -- THE LOWER MASS LIMIT • Such failed stars are called brown dwarfs. • Most astronomers make a further distinction between brown ...
Powerpoint for today
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
The Application of Forbidden Line X-Ray Diagnostics to the Hot Star
... The strength ratio of the forbidden to intercombination line indicates the strength of the UV field.* In a strong UV field, electrons are often excited out of the long-lived upper level of the forbidden line before they spontaneously de-excite, weakening the forbidden line. * If electron densities ...
... The strength ratio of the forbidden to intercombination line indicates the strength of the UV field.* In a strong UV field, electrons are often excited out of the long-lived upper level of the forbidden line before they spontaneously de-excite, weakening the forbidden line. * If electron densities ...
Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary
... • An extremely hot ball of gas, with hydrogen (H2) fusing into helium(He)at its core. • Spend most of their lives fusing hydrogen • When the hydrogen is used up, stars fuse helium to carbon • They are always trying to achieve equilibrium ...
... • An extremely hot ball of gas, with hydrogen (H2) fusing into helium(He)at its core. • Spend most of their lives fusing hydrogen • When the hydrogen is used up, stars fuse helium to carbon • They are always trying to achieve equilibrium ...
The Bigger Picture
... only 0.01 arcseconds! • Space-based missions have taken over parallax measurements. A satellite called Hipparcos measured parallaxes for about 100,000 stars (pre-Hipparcos, this number was more like 2000 stars). ...
... only 0.01 arcseconds! • Space-based missions have taken over parallax measurements. A satellite called Hipparcos measured parallaxes for about 100,000 stars (pre-Hipparcos, this number was more like 2000 stars). ...
Measuring the Sky - Physics and Astronomy and more!
... But comets follow highly elliptical paths The little guy’s orbit was nearly circular AND its orbit was 2.7AU! ...
... But comets follow highly elliptical paths The little guy’s orbit was nearly circular AND its orbit was 2.7AU! ...
Astronomy 212 EXAM 1 2000 September 29 Answer
... Answer TRUE or FALSE (not T or F) (2 pts each) 1. If SI units (the “metric system”) are being properly used the “Megamall” is a billion times bigger than a normal mall. 2. The zenith is always directly overhead. 3. At CSB/SJU the celestial equator is an hour circle. 4. The celestial equator has zero ...
... Answer TRUE or FALSE (not T or F) (2 pts each) 1. If SI units (the “metric system”) are being properly used the “Megamall” is a billion times bigger than a normal mall. 2. The zenith is always directly overhead. 3. At CSB/SJU the celestial equator is an hour circle. 4. The celestial equator has zero ...
And a Whole Lot Farther to the Nearest Star
... So, if 10 inches equals 864,000 miles, one inch will represent 86,400 miles. And 0.0000115 inch will represent a single mile approximately. At this scale, how big is the earth? Well, the earth is 7,913 miles in diameter. 7,913 times 0.0000115 equals 0.091 inches approximately—in other words, not qu ...
... So, if 10 inches equals 864,000 miles, one inch will represent 86,400 miles. And 0.0000115 inch will represent a single mile approximately. At this scale, how big is the earth? Well, the earth is 7,913 miles in diameter. 7,913 times 0.0000115 equals 0.091 inches approximately—in other words, not qu ...
Powerpoint file
... If we leave out fi and fc (i.e. assume they are unity—all life forms develop our kind of intelligence and technology and try to communicate), we are calculating the number of life-bearing planets in our Galaxy at any given time (like now). We know there has been life on our planet for 3 billion year ...
... If we leave out fi and fc (i.e. assume they are unity—all life forms develop our kind of intelligence and technology and try to communicate), we are calculating the number of life-bearing planets in our Galaxy at any given time (like now). We know there has been life on our planet for 3 billion year ...
Year 6 Space Newsletter
... the sun is getting hotter and hotter each fastenating facts. One day on Satday and that means if it keeps getting urn is 29,447498 Earth years; hotter then in 1 billion years there will 18,755.70 days. Surprisingly, Satbe no water left and no living things of urn has only 23 rings around it! Earth s ...
... the sun is getting hotter and hotter each fastenating facts. One day on Satday and that means if it keeps getting urn is 29,447498 Earth years; hotter then in 1 billion years there will 18,755.70 days. Surprisingly, Satbe no water left and no living things of urn has only 23 rings around it! Earth s ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.