Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
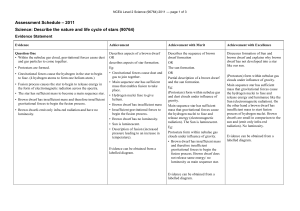
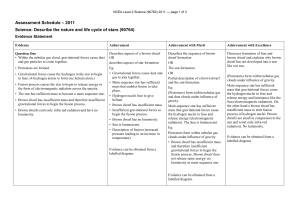
... Sun (electromagnetic radiation). On the other hand a brown dwarf has insufficient mass to start fusion process of hydrogen nuclei. Brown dwarfs are small in comparison to the sun and (emit only infra-red radiation). No luminosity. Evidence can be obtained from a labelled diagram. ...
... Sun (electromagnetic radiation). On the other hand a brown dwarf has insufficient mass to start fusion process of hydrogen nuclei. Brown dwarfs are small in comparison to the sun and (emit only infra-red radiation). No luminosity. Evidence can be obtained from a labelled diagram. ...
Name
... 35. While looking through a telescope, you see a galaxy with lots of main sequence stars in the outer regions and lots of white dwarfs and red giants near the center. What kind of galaxy do you think it is and why? Explain. ...
... 35. While looking through a telescope, you see a galaxy with lots of main sequence stars in the outer regions and lots of white dwarfs and red giants near the center. What kind of galaxy do you think it is and why? Explain. ...
same
... origin (e.g., Orion, Hercules and Andromeda), while others are more contemporary in nature (e.g., Microscopium and Telescopium). The Stars are named using several different systems. The brighter stars all have ancient names, while fainter ones are known by “number” only (although you can name those ...
... origin (e.g., Orion, Hercules and Andromeda), while others are more contemporary in nature (e.g., Microscopium and Telescopium). The Stars are named using several different systems. The brighter stars all have ancient names, while fainter ones are known by “number” only (although you can name those ...
July 2013 - Skyscrapers, Inc.
... M39 contains about 20 bright stars. A lowpower eyepiece on a small telescope will allow the object to fill the entire field of view. Just south from Sadr, the center star of the cross, one can find another open cluster called M29. This cluster is more compact than M39 and only contains about eight b ...
... M39 contains about 20 bright stars. A lowpower eyepiece on a small telescope will allow the object to fill the entire field of view. Just south from Sadr, the center star of the cross, one can find another open cluster called M29. This cluster is more compact than M39 and only contains about eight b ...
Slide 1
... This reduces the electron degeneracy pressure further and accelerates the collapse. In less than a second, the core collapses into a ball of neutrons only about 10 km in radius -- a neutron star. A neutron star is supported by gravity against a different kind of pressure, neutron degeneracy pressure ...
... This reduces the electron degeneracy pressure further and accelerates the collapse. In less than a second, the core collapses into a ball of neutrons only about 10 km in radius -- a neutron star. A neutron star is supported by gravity against a different kind of pressure, neutron degeneracy pressure ...
File
... fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of nuclear fusion marks the birth of a star. Once this process begins, it can continue for billions of years. ...
... fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of nuclear fusion marks the birth of a star. Once this process begins, it can continue for billions of years. ...
Multiple Choice, continued
... fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of nuclear fusion marks the birth of a star. Once this process begins, it can continue for billions of years. ...
... fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of nuclear fusion marks the birth of a star. Once this process begins, it can continue for billions of years. ...
Stars and Galaxies - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... from all directions at once radiation left over from the Big Bang In June 1995, scientists detected helium in the far reaches of the universe - consistent with an important aspect of the Big Bang theory that a mixture of hydrogen (75%) and helium (25%) was created at the beginning of the universe ...
... from all directions at once radiation left over from the Big Bang In June 1995, scientists detected helium in the far reaches of the universe - consistent with an important aspect of the Big Bang theory that a mixture of hydrogen (75%) and helium (25%) was created at the beginning of the universe ...
of the Sun
... STELLIFEROUS ERA – the current era • Electrons combined with existing nuclei to form atoms, mostly hydrogen and helium • Atoms condensed into the first generation of stars during the first 200 million years • Galaxies formed • Sun, solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago • Life appeared on Earth ...
... STELLIFEROUS ERA – the current era • Electrons combined with existing nuclei to form atoms, mostly hydrogen and helium • Atoms condensed into the first generation of stars during the first 200 million years • Galaxies formed • Sun, solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago • Life appeared on Earth ...
PowerPoint File
... the shape of the Milky Way. Characteristics to go on are: • Sprinkling of stars everywhere • Thick band of light across the sky (the Milky Way) • Band brightest in the direction of Sagittarius • Band faintest in the direction of TaurusAuriga What’s the answer? ...
... the shape of the Milky Way. Characteristics to go on are: • Sprinkling of stars everywhere • Thick band of light across the sky (the Milky Way) • Band brightest in the direction of Sagittarius • Band faintest in the direction of TaurusAuriga What’s the answer? ...
Supercomputer simulation provides missing link between turbulence, hypernovae and gamma-ray bursts
... “The breakthrough here is that Philipp’s team starts from a relatively weak magnetic field and shows it building up to be a very strong and large-scale coherent magnetic field of the kind that is usually assumed to be there when people make models of gamma-ray bursts,” Quataert said. Brightest even ...
... “The breakthrough here is that Philipp’s team starts from a relatively weak magnetic field and shows it building up to be a very strong and large-scale coherent magnetic field of the kind that is usually assumed to be there when people make models of gamma-ray bursts,” Quataert said. Brightest even ...
Final Exam from 2004 - Onondaga Community College
... 17. The statements that appear below are all related to the nature of gravity. Which of them is NOT true? A. The force of gravity around a star never vanishes no matter how far away you are. B. The force of gravity is an attractive force between any two objects with mass. C. The force of gravity is ...
... 17. The statements that appear below are all related to the nature of gravity. Which of them is NOT true? A. The force of gravity around a star never vanishes no matter how far away you are. B. The force of gravity is an attractive force between any two objects with mass. C. The force of gravity is ...
Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect—28 Oct Outline • Announcements
... • Eg, in the visible part of the spectrum, hydrogen emits and absorbs light at 656.2, 486.1, 434.0, 410.1nm. ...
... • Eg, in the visible part of the spectrum, hydrogen emits and absorbs light at 656.2, 486.1, 434.0, 410.1nm. ...
black hole
... This wobble may be caused by the combined gravitational pull of two planets with 67 and 98 day orbital periods. ...
... This wobble may be caused by the combined gravitational pull of two planets with 67 and 98 day orbital periods. ...
astrocoursespring2012lec5-1-1
... appear smaller and fainter. When a telescope probes about 5 billion light years into look-back time, it can detect only the brightest galaxies, giant, elliptical galaxies – because spiral galaxies similar to the Milky Way are too dim to be seen at that distance ...
... appear smaller and fainter. When a telescope probes about 5 billion light years into look-back time, it can detect only the brightest galaxies, giant, elliptical galaxies – because spiral galaxies similar to the Milky Way are too dim to be seen at that distance ...
Document
... • Begin to understand how we will constrain stellar models with hard observational evidence ...
... • Begin to understand how we will constrain stellar models with hard observational evidence ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.