Chapter 8 powerpoint presentation
... The name of this method is a bit deceiving as it incorrectly implies some measure of stellar parallax. Actually, what happens is we obtain a spectrum for a star of unknown distance. We use the spectrum to determine the spectral type, which locates it on the x-axis of the H-R diagram. Now draw a line ...
... The name of this method is a bit deceiving as it incorrectly implies some measure of stellar parallax. Actually, what happens is we obtain a spectrum for a star of unknown distance. We use the spectrum to determine the spectral type, which locates it on the x-axis of the H-R diagram. Now draw a line ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... nebula and its surrounding companions. Then he has presented it well, leaving some darker area around it to set off the nebula. ...
... nebula and its surrounding companions. Then he has presented it well, leaving some darker area around it to set off the nebula. ...
Galaxies - schoolphysics
... Galaxies are huge things. Our supersonic jet flying at twice the speed of sound would take 25,000 million years to fly from one side to the other. Even light takes 100,000 years to make the trip across our galaxy. This means that the light that we see from the stars on the other side of the galaxy s ...
... Galaxies are huge things. Our supersonic jet flying at twice the speed of sound would take 25,000 million years to fly from one side to the other. Even light takes 100,000 years to make the trip across our galaxy. This means that the light that we see from the stars on the other side of the galaxy s ...
- EPJ Web of Conferences
... observations that are of higher precision and spatial resolution than the discovery observations (e.g. a neighboring eclipsing binary may be blended with the target on the survey images, but not blended when observed with a 1-m telescope), some non-trivial false positives produce both radial velocit ...
... observations that are of higher precision and spatial resolution than the discovery observations (e.g. a neighboring eclipsing binary may be blended with the target on the survey images, but not blended when observed with a 1-m telescope), some non-trivial false positives produce both radial velocit ...
Altitude and Azimuth 4 page
... ALTITUDE: The angle of an object above the horizon. Altitude is measured in degrees along a line perpendicular to the horizon, to the object of interest. An object on the horizon has an Altitude of 0 o, an object directly overhead has an Altitude of 90o. AZIMUTH: The angle from North clockwise along ...
... ALTITUDE: The angle of an object above the horizon. Altitude is measured in degrees along a line perpendicular to the horizon, to the object of interest. An object on the horizon has an Altitude of 0 o, an object directly overhead has an Altitude of 90o. AZIMUTH: The angle from North clockwise along ...
PHYS3380_102615_bw
... Computer simulations can reproduce most of the observed motions We have observed disks around other stars. These could be new planetary systems in formation. ...
... Computer simulations can reproduce most of the observed motions We have observed disks around other stars. These could be new planetary systems in formation. ...
october 2008 - Mahoning Valley Astronomical Society
... expected time frames. The new sunspot was a good sign that the 11-year solar cycle is indeed progressing, albeit slowly. Earlier, on January 4, 2008, the first reverse polarity sunspot (AR10981) was seen- indicating the start of Cycle 24. But things have been quiet since then. Cycle 24 is expected t ...
... expected time frames. The new sunspot was a good sign that the 11-year solar cycle is indeed progressing, albeit slowly. Earlier, on January 4, 2008, the first reverse polarity sunspot (AR10981) was seen- indicating the start of Cycle 24. But things have been quiet since then. Cycle 24 is expected t ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radius, the smaller the temperature – Theref ...
... understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radius, the smaller the temperature – Theref ...
29_worlds_unnumbered..
... Question when is a “giant” gas giant big enough to be a “star”? Brown dwarfs: in between objects neither fish nor fowl. More massive then planets but less massive then stars. Stars: objects more massive then 0.08 the mass of the Sun. Cores get hot enough for nuclear ...
... Question when is a “giant” gas giant big enough to be a “star”? Brown dwarfs: in between objects neither fish nor fowl. More massive then planets but less massive then stars. Stars: objects more massive then 0.08 the mass of the Sun. Cores get hot enough for nuclear ...
Announcements - Lick Observatory
... Galaxy, but for the vast majority, the separation of the stars is large enough that one star doesn’t affect the evolution of the other(s). ...
... Galaxy, but for the vast majority, the separation of the stars is large enough that one star doesn’t affect the evolution of the other(s). ...
1/20/09 301 Physics Chapter 12 The Family of Stars Triangulation
... – Star classification example: The Sun is G2V ...
... – Star classification example: The Sun is G2V ...
Groups of Stars
... Galaxies Irregular Galaxies A small fraction of all galaxies are known as irregular galaxies. Irregular galaxies have a disorganized appearance. They have many young stars and large amounts of gas and ...
... Galaxies Irregular Galaxies A small fraction of all galaxies are known as irregular galaxies. Irregular galaxies have a disorganized appearance. They have many young stars and large amounts of gas and ...
Document
... • 4H He + Energy in shell • Extra energy results in extra pressure. Star expands. • The star gets bigger while its outside gets cooler. ...
... • 4H He + Energy in shell • Extra energy results in extra pressure. Star expands. • The star gets bigger while its outside gets cooler. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 9” and the earth’s radius is 4000 miles. 15. Prove that equation of time vanishes four times a year. 16. Define sidereal month and synodic month of the moon and find the relation between them. 17. Compare lunar and solar eclipses. 18. Prove that among any two planets, the inner planet moves faster t ...
... 9” and the earth’s radius is 4000 miles. 15. Prove that equation of time vanishes four times a year. 16. Define sidereal month and synodic month of the moon and find the relation between them. 17. Compare lunar and solar eclipses. 18. Prove that among any two planets, the inner planet moves faster t ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
... equator means that at some times of the year the Sun is in front of stars north of the equator and at some times it is south. Stars on the equator rise due east, pass 30o south of overhead (seen from Austin), and set due west. Stars north of the equator rise north of east, pass closer to overhead, a ...
... equator means that at some times of the year the Sun is in front of stars north of the equator and at some times it is south. Stars on the equator rise due east, pass 30o south of overhead (seen from Austin), and set due west. Stars north of the equator rise north of east, pass closer to overhead, a ...
Preview Sample 2
... second-magnitude stars, which are brighter than third-magnitude stars, and so on. The magnitude you see when you look at a star in the sky is its apparent visual magnitude, which does not take into account its distance form Earth. Apparent visual magnitude, mv, includes only the light that human eye ...
... second-magnitude stars, which are brighter than third-magnitude stars, and so on. The magnitude you see when you look at a star in the sky is its apparent visual magnitude, which does not take into account its distance form Earth. Apparent visual magnitude, mv, includes only the light that human eye ...
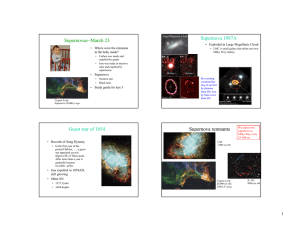
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... • Gas expelled in 1054AD, still glowing • Other SN • 1572 Tycho • 1604 Kepler ...
... • Gas expelled in 1054AD, still glowing • Other SN • 1572 Tycho • 1604 Kepler ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.