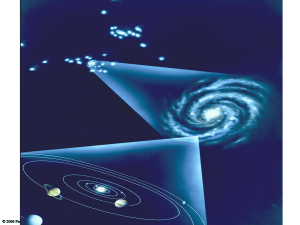
astronomy timeline
... Descartes develops concept of inertial motion. Descartes believed that all motion resulted from collision with particles called "corpuscles". In the absence of such collisions, a body remains at rest. An object in motion continues to move in the same direction at the same speed. p. 80-81, F 2.1 ...
... Descartes develops concept of inertial motion. Descartes believed that all motion resulted from collision with particles called "corpuscles". In the absence of such collisions, a body remains at rest. An object in motion continues to move in the same direction at the same speed. p. 80-81, F 2.1 ...
Lec12
... Gravitational lensing, the bending of light rays by gravity, can also tell us a cluster’s mass ...
... Gravitational lensing, the bending of light rays by gravity, can also tell us a cluster’s mass ...
Birth of Stars
... Each second in the Sun, about 600 million tons of hydrogen undergo fusion into helium, with about 4 million tons turning to energy in the process This rate of hydrogen use implies that eventually the Sun (and all other stars) will run out of central fuel ...
... Each second in the Sun, about 600 million tons of hydrogen undergo fusion into helium, with about 4 million tons turning to energy in the process This rate of hydrogen use implies that eventually the Sun (and all other stars) will run out of central fuel ...
Three Media Reports by Carole Gallagher
... sustaining life similar to life on Earth. Such a planet would have to be large enough to have an atmosphere but small enough to have continents and oceans. It would need to orbit an energy-giving star (like our sun) at a suitable distance, so as to be warmed by the star without becoming too hot. The ...
... sustaining life similar to life on Earth. Such a planet would have to be large enough to have an atmosphere but small enough to have continents and oceans. It would need to orbit an energy-giving star (like our sun) at a suitable distance, so as to be warmed by the star without becoming too hot. The ...
Stars (Ch. 13)
... almost always appear just as points of light. • But as we already know we can learn a lot from light! • Light can tell us about a star’s: ...
... almost always appear just as points of light. • But as we already know we can learn a lot from light! • Light can tell us about a star’s: ...
The First Stars - Amazon Web Services
... Exploding stars In the century that followed, astronomers measured the masses of many stars, typically by using the orbits in binary systems, and confirmed Eddington’s reasoning. The smaller balls of gas make the planets. The massive stars explode, after exhausting their nuclear fuel, because their ...
... Exploding stars In the century that followed, astronomers measured the masses of many stars, typically by using the orbits in binary systems, and confirmed Eddington’s reasoning. The smaller balls of gas make the planets. The massive stars explode, after exhausting their nuclear fuel, because their ...
Unit XII Study Guide
... 36. The length of a planet’s day is determined by its _________________________. 37. Icy objects that mostly travel in long, elliptical orbits around the sun are ____________________. 38. The ____________________ belt contains perhaps tens of thousands of objects orbiting within about 100 AU of the ...
... 36. The length of a planet’s day is determined by its _________________________. 37. Icy objects that mostly travel in long, elliptical orbits around the sun are ____________________. 38. The ____________________ belt contains perhaps tens of thousands of objects orbiting within about 100 AU of the ...
Equivalent Widths and Chemical abundances Equivalent
... The reference point for abundance determinations is generally taken to be the “solar nebula”, i.e. the composition of the gas cloud out of which the sun and solar system formed. That is because we can get the most detailed and precise information about this cloud from spectral analysis of the Sun an ...
... The reference point for abundance determinations is generally taken to be the “solar nebula”, i.e. the composition of the gas cloud out of which the sun and solar system formed. That is because we can get the most detailed and precise information about this cloud from spectral analysis of the Sun an ...
Astrophysics
... a) (3 points) Calculate the orbital semi-major axis (asun ) of the Sun’s orbit about the barycenter of the Solar System, in AU, in response to Jupiter’s orbital motion. Since Jupiter constitutes ∼70% of the non-solar mass of our Solar System, you can ignore Solar System bodies less massive than Jupi ...
... a) (3 points) Calculate the orbital semi-major axis (asun ) of the Sun’s orbit about the barycenter of the Solar System, in AU, in response to Jupiter’s orbital motion. Since Jupiter constitutes ∼70% of the non-solar mass of our Solar System, you can ignore Solar System bodies less massive than Jupi ...
Naked-eye astronomy
... useful tool of positional astronomy • Landmarks on the celestial sphere are projections of those on the Earth ...
... useful tool of positional astronomy • Landmarks on the celestial sphere are projections of those on the Earth ...
Honors Physics – Ch 7 Practice Problems
... 4. The passenger liners Carnival Destiny and Grand Princess, built recently, have a mass of about 1.0 × 108 kg each. How far apart must these two ships be to exert a gravitational attraction of 1.0 × 10-3 N on each other? 5. Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, has a mass 318 times that ...
... 4. The passenger liners Carnival Destiny and Grand Princess, built recently, have a mass of about 1.0 × 108 kg each. How far apart must these two ships be to exert a gravitational attraction of 1.0 × 10-3 N on each other? 5. Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, has a mass 318 times that ...
Virgo constellation
... about 5,900.There is strong evidence for a stellar mass black hole through observations made over a span of a few years. M49 was the first member of the Virgo clusters discovered. RA12h 29m 46.7s . DEC+08° 00′ 02″. (wikipedia.com) Then we have the M58 it was discovered in 1779 which is a barred spir ...
... about 5,900.There is strong evidence for a stellar mass black hole through observations made over a span of a few years. M49 was the first member of the Virgo clusters discovered. RA12h 29m 46.7s . DEC+08° 00′ 02″. (wikipedia.com) Then we have the M58 it was discovered in 1779 which is a barred spir ...
HR DIAGRAM (Page 1) - McDonald Observatory
... Which stars “stick out” in the distribution of nearby stars? Compare and contrast the nearby stars and bright stars. Which stars do you think are giant stars? Which types of stars do you think are most common in the night sky? Which types of stars do you think are most common in our solar neighborho ...
... Which stars “stick out” in the distribution of nearby stars? Compare and contrast the nearby stars and bright stars. Which stars do you think are giant stars? Which types of stars do you think are most common in the night sky? Which types of stars do you think are most common in our solar neighborho ...
3.1 Introduction
... presumably born out of the same interstellar cloud) allows us to consider evolutionary effects on the HR diagram. The Pleiades (Figure 3.7) are a famous stellar cluster visible from northern skies in the winter. At a distance of only 120 pc, it is one of the closest open star cluster. It consists of ...
... presumably born out of the same interstellar cloud) allows us to consider evolutionary effects on the HR diagram. The Pleiades (Figure 3.7) are a famous stellar cluster visible from northern skies in the winter. At a distance of only 120 pc, it is one of the closest open star cluster. It consists of ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.