Distance Measurement in Astronomy
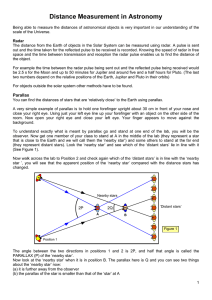
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
Slide 1
... • The man is pointing up to the pole star. • The pole star was Thuban in 1300 BC just above in the handle of the Big Dipper. • However, the other man is measuring a shift. • The shift may simply be the Bull of heaven shifting direction 180 degrees the night following a sun miracle. ...
... • The man is pointing up to the pole star. • The pole star was Thuban in 1300 BC just above in the handle of the Big Dipper. • However, the other man is measuring a shift. • The shift may simply be the Bull of heaven shifting direction 180 degrees the night following a sun miracle. ...
Star Birth
... if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change B. Its mass would increase C. Its internal pressure would increase ...
... if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change B. Its mass would increase C. Its internal pressure would increase ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint - Istituto Nazionale di Fisica
... the condition is no longer satisfied: STRONG FIELD EFFECTS ...
... the condition is no longer satisfied: STRONG FIELD EFFECTS ...
How do the most massive galaxies constrain theories of
... with thanks to the GOODS & GEMS teams, S. Faber, B. Allgood, J. ...
... with thanks to the GOODS & GEMS teams, S. Faber, B. Allgood, J. ...
but restricted to nearby large stars
... • It expressed the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum. • It has been shown that this feature is a general measure of the size of the star, and thus of the total luminosity output from the star. ...
... • It expressed the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum. • It has been shown that this feature is a general measure of the size of the star, and thus of the total luminosity output from the star. ...
The Universe Section 1
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
The Sky is Our Laboratory
... • A galaxy is a body of stars, gas, and dark matter kept together by gravity; • The `cosmos’ is a loose definition to indicate the Universe, or components of it. It comes from Greek, to indicate an harmonious whole, opposed to chaos. ...
... • A galaxy is a body of stars, gas, and dark matter kept together by gravity; • The `cosmos’ is a loose definition to indicate the Universe, or components of it. It comes from Greek, to indicate an harmonious whole, opposed to chaos. ...
Read the information on Hertzsprung
... Once you have answered the Interactive Lab and have checked that your answers are correct, take a screenshot of the Lab and paste it in the space below. ...
... Once you have answered the Interactive Lab and have checked that your answers are correct, take a screenshot of the Lab and paste it in the space below. ...
Interactive Tutorial Activities in ASTR 310
... To assess the impact on student learning of interactive tutorial activities in ASTR 310, we conducted a pre-test in January and incorporated an isomorphic post-test into the Final Exam in April. We compare the student scores on the Final Exam questions to the pre-test questions for each of the stude ...
... To assess the impact on student learning of interactive tutorial activities in ASTR 310, we conducted a pre-test in January and incorporated an isomorphic post-test into the Final Exam in April. We compare the student scores on the Final Exam questions to the pre-test questions for each of the stude ...
PH709-assn-answers
... Assignment 5 : SMITH 1. Suppose that two exoplanets are observed to transit the same star. They are both in circular orbits with an inclination of 90 degrees. One produces periodic dips with a period of 4 days and the other produces periodic dips with a period of 108 days. The decrease in luminosity ...
... Assignment 5 : SMITH 1. Suppose that two exoplanets are observed to transit the same star. They are both in circular orbits with an inclination of 90 degrees. One produces periodic dips with a period of 4 days and the other produces periodic dips with a period of 108 days. The decrease in luminosity ...
Upsilon Andromedae
... Standard error: 0.004 Mean Vt magnitude: 4.159 Standard error: 0.003 Source of photometric data: The Bt,Vt data are median values, rather than de-censored mean values (mainly relevant for bright stars with Bt<=8.5 mag and Vt<=8.0 mag). Johnson B-V colour index: 0.541 Standard error: 0.004 Number of ...
... Standard error: 0.004 Mean Vt magnitude: 4.159 Standard error: 0.003 Source of photometric data: The Bt,Vt data are median values, rather than de-censored mean values (mainly relevant for bright stars with Bt<=8.5 mag and Vt<=8.0 mag). Johnson B-V colour index: 0.541 Standard error: 0.004 Number of ...
29:52 Characteristics and Origins of the Solar System January 25
... 29:52 Characteristics and Origins of the Solar System January 25, 2004 Addendum to Lecture 2 ...
... 29:52 Characteristics and Origins of the Solar System January 25, 2004 Addendum to Lecture 2 ...
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife
... point where further fusion – and evolution – were possible. Second, at about this mass a process called “neutronization” becomes possible: the most energetic electrons in the gas would have enough energy to bind with protons and form neutrons and neutron-rich nuclei. The loss of free electrons means ...
... point where further fusion – and evolution – were possible. Second, at about this mass a process called “neutronization” becomes possible: the most energetic electrons in the gas would have enough energy to bind with protons and form neutrons and neutron-rich nuclei. The loss of free electrons means ...
white dwarfs, neutron stars, black hole
... fuse (because of iron's nuclear structure, it does not permit its atoms to fuse into heavier elements) and fusion ceases. In less than a second, the star begins the final phase of its gravitational collapse. The core temperature rises to over 100 billion degrees as the iron atoms are crushed togethe ...
... fuse (because of iron's nuclear structure, it does not permit its atoms to fuse into heavier elements) and fusion ceases. In less than a second, the star begins the final phase of its gravitational collapse. The core temperature rises to over 100 billion degrees as the iron atoms are crushed togethe ...
Section 1.1 Version 1 - Columbus State University
... dollars if the APR is r as a decimal and we make monthly payments of m dollars. Use functional notation to indicate the time required to pay off a $10000 automobile loan at an APR of 6% if the monthly payment is $430. A) ...
... dollars if the APR is r as a decimal and we make monthly payments of m dollars. Use functional notation to indicate the time required to pay off a $10000 automobile loan at an APR of 6% if the monthly payment is $430. A) ...
Wednesday, Oct. 22
... When helium fusion starts generating energy in the core of a red giant, the core expands and hydrogen fusion in the shell around the core slows down. As a result, less total energy is being generated, and the envelope contracts and warms up some. But pretty soon all of the helium in the core is conv ...
... When helium fusion starts generating energy in the core of a red giant, the core expands and hydrogen fusion in the shell around the core slows down. As a result, less total energy is being generated, and the envelope contracts and warms up some. But pretty soon all of the helium in the core is conv ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.























