Studying Variable stars using Small Telescopes Observational
... Types of Variable Star 1. Intrinsic variables – Stars which vary their light output, hence their brightness, by some change within the star itself. Provide a wealth of information about the internal structure of stars, models of stellar evolution and distance determination. Further classified as: P ...
... Types of Variable Star 1. Intrinsic variables – Stars which vary their light output, hence their brightness, by some change within the star itself. Provide a wealth of information about the internal structure of stars, models of stellar evolution and distance determination. Further classified as: P ...
Final Review - PCHS SCIENCE
... solar system. – In a Sun-centered, or heliocentric, model, the inner planets move faster in their orbits than the outer planets do. – As Earth bypasses a slower-moving outer planet, it appears that the outer planet temporarily moves backward in the sky. ...
... solar system. – In a Sun-centered, or heliocentric, model, the inner planets move faster in their orbits than the outer planets do. – As Earth bypasses a slower-moving outer planet, it appears that the outer planet temporarily moves backward in the sky. ...
File - 5th Grade Science Almost done!!!!!!!!!
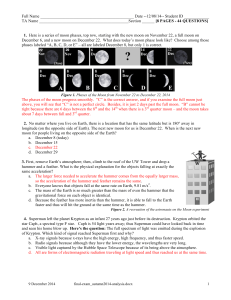
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
Lecture 10: Stellar Evolution
... Energy and neutrons released in supernova explosion enable elements heavier than iron to form, including Au and U ...
... Energy and neutrons released in supernova explosion enable elements heavier than iron to form, including Au and U ...
White Dwarfs and the age of the Universe
... • if we know the temperature and luminosity of a white dwarf, we know its size • if we know temperature, luminosity, and size now, we know the rate at which it is cooling today ...
... • if we know the temperature and luminosity of a white dwarf, we know its size • if we know temperature, luminosity, and size now, we know the rate at which it is cooling today ...
Lecture 24, PPT version
... • Pulsars (rapidly-rotating neutron stars left over after a high-mass star supernova) • Hypernova gives rise to a few-second burst of gamma rays and leaves behind a black hole (progenitor star would have had a main sequence mass > 40 Msun) • Introduction to the Milky Way • Face-on vs. edge-on perspe ...
... • Pulsars (rapidly-rotating neutron stars left over after a high-mass star supernova) • Hypernova gives rise to a few-second burst of gamma rays and leaves behind a black hole (progenitor star would have had a main sequence mass > 40 Msun) • Introduction to the Milky Way • Face-on vs. edge-on perspe ...
Planet Hunters
... exception, not the rule. The majority of giant planets are located far from their parent stars, just as in our own solar system. Yet there were other surprises in store: Unlike the stately circular orbits of our own planets, the vast majority of exoplanets have highly elliptical orbits. Some worlds ...
... exception, not the rule. The majority of giant planets are located far from their parent stars, just as in our own solar system. Yet there were other surprises in store: Unlike the stately circular orbits of our own planets, the vast majority of exoplanets have highly elliptical orbits. Some worlds ...
Adapting Materials for ELL Students - title
... hydrogen and dust come together to form stars. What pulls them together? Astronomers think that gravity does. As you know, gravity acts like a magnet. For example, if you throw a ball into the air, gravity will pull it back to earth. In the same way, gravity pulls hydrogen and dust together. If ther ...
... hydrogen and dust come together to form stars. What pulls them together? Astronomers think that gravity does. As you know, gravity acts like a magnet. For example, if you throw a ball into the air, gravity will pull it back to earth. In the same way, gravity pulls hydrogen and dust together. If ther ...
Dark Matter Burners
... Could any of the “paradoxically young” stars near Sgr A* be white dwarfs burning dark matter? Answer: yes How can we demonstrate that any of these stars are white dwarfs burning dark matter? Answer: by measuring the gravitational redshift and temperature (or luminosity) If found, a population ...
... Could any of the “paradoxically young” stars near Sgr A* be white dwarfs burning dark matter? Answer: yes How can we demonstrate that any of these stars are white dwarfs burning dark matter? Answer: by measuring the gravitational redshift and temperature (or luminosity) If found, a population ...
Binary star formation
... part of binary systems: Solar mass stars: about 2 / 3 are part of binaries Separations from: • < 0.1 au • > 103 au ...
... part of binary systems: Solar mass stars: about 2 / 3 are part of binaries Separations from: • < 0.1 au • > 103 au ...
Note - Overflow Education
... Luminosity is the total energy radiated by an object per second. This can also be called power output and its SI units are joules per second, or watts (W). The Sun’s estimated luminosity is 3.83 x 1026 W. This value is designated as L0 and is often used as a unit to express the luminosity of other s ...
... Luminosity is the total energy radiated by an object per second. This can also be called power output and its SI units are joules per second, or watts (W). The Sun’s estimated luminosity is 3.83 x 1026 W. This value is designated as L0 and is often used as a unit to express the luminosity of other s ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... • Even a long lifetime of 100 years is insignificant compared to the lifetime of the Sun (about 10 billion years) ...
... • Even a long lifetime of 100 years is insignificant compared to the lifetime of the Sun (about 10 billion years) ...
This Book of Hours calculation is a possible
... The Talisman for Aldebaran used by Agrippa is the cross (shown left) and forms the two angles for each St Michael Ley line and is shown here on the left. Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim was born in Cologne on September 14 th 1486 and was a German Magician, occult writer, astrologer and al ...
... The Talisman for Aldebaran used by Agrippa is the cross (shown left) and forms the two angles for each St Michael Ley line and is shown here on the left. Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim was born in Cologne on September 14 th 1486 and was a German Magician, occult writer, astrologer and al ...
Properties of stars: temperature, colour index and equivalent width
... Liceo Scientifico “G.Galilei” Caselle di Selvazzano (Pd) ...
... Liceo Scientifico “G.Galilei” Caselle di Selvazzano (Pd) ...
Extra-Solar Life: Habitable Zones
... • If planet is close in, orbit will be unstable and chaotic • Moving in/out of HZ is probably hard on life development • If planet is far away (orbiting BOTH stars), orbit is stable, but typically outside the HZ (!) ...
... • If planet is close in, orbit will be unstable and chaotic • Moving in/out of HZ is probably hard on life development • If planet is far away (orbiting BOTH stars), orbit is stable, but typically outside the HZ (!) ...
Spectroscopy in stellar astrophysics
... ASTROPHYSICS : studies the physics of stars, stellar systems and interstellar material. ...
... ASTROPHYSICS : studies the physics of stars, stellar systems and interstellar material. ...
pptx
... Luminosity of main sequence stars is determined by mass Main sequence is a mass sequence (bright hot stars are more massive, cool faint stars are less massive) 10 times as massive 10000 times brighter! ...
... Luminosity of main sequence stars is determined by mass Main sequence is a mass sequence (bright hot stars are more massive, cool faint stars are less massive) 10 times as massive 10000 times brighter! ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.