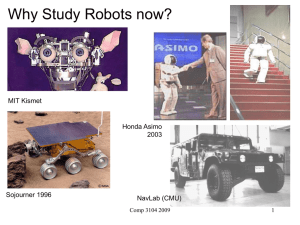
On the Implementation of MIPS
... of objects, an initial state s and set of goal states G the planning problem is to find a sequence of operators that transforms s into g in G. The algorithm is admissible if the sequence of operators is the shortest possible. The algorithm is complete if it always terminates returning a plan or with ...
... of objects, an initial state s and set of goal states G the planning problem is to find a sequence of operators that transforms s into g in G. The algorithm is admissible if the sequence of operators is the shortest possible. The algorithm is complete if it always terminates returning a plan or with ...
COMBINED ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE BEHAVIOUR SYSTEMS IN
... utilise the most appropriate methodology for any given situation. Given that it would take an AI system by itself to determine which methodology was most appropriate at any one time, it is more effective to simply split the behaviour of an Agent into categories, and assign the most appropriate AI me ...
... utilise the most appropriate methodology for any given situation. Given that it would take an AI system by itself to determine which methodology was most appropriate at any one time, it is more effective to simply split the behaviour of an Agent into categories, and assign the most appropriate AI me ...
Resume - University of Houston
... Computer and Information Science of Indiana University, Purdue University at Indianapolis. My initial research interests include the construction of stochastic models for information flows, see [53] through [57]. In [55] we study a mechanism followed by a decision maker ethically bound to pursue the ...
... Computer and Information Science of Indiana University, Purdue University at Indianapolis. My initial research interests include the construction of stochastic models for information flows, see [53] through [57]. In [55] we study a mechanism followed by a decision maker ethically bound to pursue the ...
Implementing Tools for Artificial Intelligence
... on multiple additional machines. The combination of Threads and RMI (Remote Method Invocation) would allow applications to subtask across the web. RMI enables the programmer to create distributed Javabased applications in which the methods of remote Java objects can be invoked from other Java virtua ...
... on multiple additional machines. The combination of Threads and RMI (Remote Method Invocation) would allow applications to subtask across the web. RMI enables the programmer to create distributed Javabased applications in which the methods of remote Java objects can be invoked from other Java virtua ...
Lecture 11 - Chapter 7
... Principles and Learning Objectives: Natural and Artificial Intelligence Systems • Artificial intelligence systems form a broad and diverse set of systems that can replicate human decision making for certain types of well-defined problems – List the characteristics of intelligent behavior and compar ...
... Principles and Learning Objectives: Natural and Artificial Intelligence Systems • Artificial intelligence systems form a broad and diverse set of systems that can replicate human decision making for certain types of well-defined problems – List the characteristics of intelligent behavior and compar ...
Vision-Language Integration in AI: a reality check
... such as SOCCER [3] that go from images to language, one gets involved with Natural Language Generation, while with ones going from text to images, such as WordsEye [7], one crosses over into the field of Computer Graphics. Multimedia generation systems in their turn, start from a specific format of ...
... such as SOCCER [3] that go from images to language, one gets involved with Natural Language Generation, while with ones going from text to images, such as WordsEye [7], one crosses over into the field of Computer Graphics. Multimedia generation systems in their turn, start from a specific format of ...
The Third International Conference on Case
... CBR permits problem solving even when the underlying domain theory is incomplete. This characteristic is beneficial in domains such as medicine (Porter et al. 1990) and law (Skalak and Rissland 1992; Ashley 1990) in which reasoning depends on vague or context-dependent concepts, such as reasonable c ...
... CBR permits problem solving even when the underlying domain theory is incomplete. This characteristic is beneficial in domains such as medicine (Porter et al. 1990) and law (Skalak and Rissland 1992; Ashley 1990) in which reasoning depends on vague or context-dependent concepts, such as reasonable c ...
A theory of abstraction - Computer Science and Engineering
... on, we will write " a b s t r a c t i o n " to mean this intuitive idea of abstraction, and to distinguish this notion from the various formal and informal notions of abstraction used elsewhere in this paper. The abstractions described in Examples 8.5, 8.8, 8.10, 8.14, 8.27 and 8.29 below, are examp ...
... on, we will write " a b s t r a c t i o n " to mean this intuitive idea of abstraction, and to distinguish this notion from the various formal and informal notions of abstraction used elsewhere in this paper. The abstractions described in Examples 8.5, 8.8, 8.10, 8.14, 8.27 and 8.29 below, are examp ...
Software Agents - UMBC Agent Web
... growing movement to study a much broader range of agent types, from the moronic to the moderately smart. The emphasis has subtly shifted from deliberation to doing; from reasoning to remote action. The very diversity of applications and approaches is a key sign that software agents are becoming main ...
... growing movement to study a much broader range of agent types, from the moronic to the moderately smart. The emphasis has subtly shifted from deliberation to doing; from reasoning to remote action. The very diversity of applications and approaches is a key sign that software agents are becoming main ...
What is a Knowledge Representation
... supplied by a representation can provide that guidance: In telling us what and how to see, they allow us to cope with what would otherwise be untenable complexity and detail. Hence the ontological commitment made by a representation can be one of the most important contributions it offers. There is ...
... supplied by a representation can provide that guidance: In telling us what and how to see, they allow us to cope with what would otherwise be untenable complexity and detail. Hence the ontological commitment made by a representation can be one of the most important contributions it offers. There is ...
Intelligent Agents
... In AGENTO, an agent is specified in terms of a set of capabilities (things the agent can do), a set of initial beliefs, a set of initial commitments (an agreement to perform a particular action at a particular time) and a set of commitment rules. Capabilities are used by the agent to decide whet ...
... In AGENTO, an agent is specified in terms of a set of capabilities (things the agent can do), a set of initial beliefs, a set of initial commitments (an agreement to perform a particular action at a particular time) and a set of commitment rules. Capabilities are used by the agent to decide whet ...
- PPT Topics
... (6) KBS as real-world problem solvers - Problem-solving power does not lie with smart reasoning techniques nor clever search algorithms but domain dependent real-world knowledge - Real-world problems do not have well-defined solutions - Expertise not laid down in algorithms but are domain dependent ...
... (6) KBS as real-world problem solvers - Problem-solving power does not lie with smart reasoning techniques nor clever search algorithms but domain dependent real-world knowledge - Real-world problems do not have well-defined solutions - Expertise not laid down in algorithms but are domain dependent ...
Toward Narrative Schema-Based Goal Recognition Models for Interactive Narrative Environments
... models for interactive narrative systems, we aim to leverage explicit representations of common narrative sequences in order to identify relationships between higher-level story structures and player goals. Our intention is to automatically mine interactive narrative schemas from logs of players’ in ...
... models for interactive narrative systems, we aim to leverage explicit representations of common narrative sequences in order to identify relationships between higher-level story structures and player goals. Our intention is to automatically mine interactive narrative schemas from logs of players’ in ...
The RacerPro Knowledge Representation and Reasoning System1
... via the built-in RacerPro web server/client. The language miniLisp is designed in such a way that termination of miniLisp programs is guaranteed, and miniLisp can be used to specify rather complex queries and server extensions while the reasoning server is running (see Figure 5). The functional lang ...
... via the built-in RacerPro web server/client. The language miniLisp is designed in such a way that termination of miniLisp programs is guaranteed, and miniLisp can be used to specify rather complex queries and server extensions while the reasoning server is running (see Figure 5). The functional lang ...
The RacerPro Knowledge Representation and Reasoning System
... via the built-in RacerPro web server/client. The language miniLisp is designed in such a way that termination of miniLisp programs is guaranteed, and miniLisp can be used to specify rather complex queries and server extensions while the reasoning server is running (see Figure 5). The functional lang ...
... via the built-in RacerPro web server/client. The language miniLisp is designed in such a way that termination of miniLisp programs is guaranteed, and miniLisp can be used to specify rather complex queries and server extensions while the reasoning server is running (see Figure 5). The functional lang ...
Toward Narrative Schema-Based Goal Recognition Models for
... defined by the information gained by the player throughout the course of the investigation. As each clue is uncovered, the player gets closer to solving the final mystery, which is the end of the narrative experience. Each clue is uncovered by a sequence of events. These sequences share the same str ...
... defined by the information gained by the player throughout the course of the investigation. As each clue is uncovered, the player gets closer to solving the final mystery, which is the end of the narrative experience. Each clue is uncovered by a sequence of events. These sequences share the same str ...
Solving Large Markov Decision Processes (depth paper)
... by the agent acting over some time frame. This time frame is normally measured in stages, where the occurrence of an event, such as the performance of a stochastic action, constitutes one stage. The horizon specifies how long (for how many stages) the agent will act. It can be finite or infinite. Fi ...
... by the agent acting over some time frame. This time frame is normally measured in stages, where the occurrence of an event, such as the performance of a stochastic action, constitutes one stage. The horizon specifies how long (for how many stages) the agent will act. It can be finite or infinite. Fi ...
X is A - Wiki Index
... information= capability to compute with information described in a natural language= NL-capability. ...
... information= capability to compute with information described in a natural language= NL-capability. ...
Chapter 1 ARGUMENTATION THEORY AND DECISION AIDING
... “that action” is the best one (we are not going to discuss the rationality hypotheses about “best” here). Decision Theory and Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis have focussed on such issues for a long time, but more on how this “best solution” should be established and less on how a decision maker ...
... “that action” is the best one (we are not going to discuss the rationality hypotheses about “best” here). Decision Theory and Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis have focussed on such issues for a long time, but more on how this “best solution” should be established and less on how a decision maker ...
The 2004 Mobile Robot Competition and Exhibition
... evaluate the participant robots. The Rescue Robot event requires the participants to deploy robots that demonstrate the ability to perform USAR-relevant tasks, such as dealing with cluttered, highly unstructured environments, mapping these environments, and providing a useful interface for human ope ...
... evaluate the participant robots. The Rescue Robot event requires the participants to deploy robots that demonstrate the ability to perform USAR-relevant tasks, such as dealing with cluttered, highly unstructured environments, mapping these environments, and providing a useful interface for human ope ...