Review 1 - AST 1002 - FSU Physics Department
... Assuming Viking 1 is 90 AU away from Earth, how long would a radio signal from it take to reach us? ...
... Assuming Viking 1 is 90 AU away from Earth, how long would a radio signal from it take to reach us? ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 5
... I. the latitude at which sunspots are visible at a given time. II. the number of sunspots that are visible at a given time. III. the rotation rate of the sun's equator at a given time. ...
... I. the latitude at which sunspots are visible at a given time. II. the number of sunspots that are visible at a given time. III. the rotation rate of the sun's equator at a given time. ...
Chapter 20 The Universe
... North Star (POLARIS) doesn’t move! TRUE NORTH Others move around it depending on time of day and year. Brightness Apparent magnitude- brightness as it appears from Earth. Depends on 1. how much light is emitted. 2. Distance from Earth Absolute magnitude= luminosity How much light is really emitted. ...
... North Star (POLARIS) doesn’t move! TRUE NORTH Others move around it depending on time of day and year. Brightness Apparent magnitude- brightness as it appears from Earth. Depends on 1. how much light is emitted. 2. Distance from Earth Absolute magnitude= luminosity How much light is really emitted. ...
Slide 1
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
Monday, October 27
... star, cf. 100 W lightbulb • Apparent brightness B is how bright it appears from Earth – Determined by the amount of light per unit area reaching Earth – B L / d2 ...
... star, cf. 100 W lightbulb • Apparent brightness B is how bright it appears from Earth – Determined by the amount of light per unit area reaching Earth – B L / d2 ...
Name
... The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnitude. Third magnitude stars we ...
... The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnitude. Third magnitude stars we ...
Homework Problems for Quiz 1 – AY 5 – Spring 2013
... 1. If the Earth’s spin axis was not tilted with respect to the Earth’s orbital plane (around the Sun), which of the following would be true, which false?: The number of daylight hours in a day would not change through the year. The length of a day would increase from 24 hours to 365 days The change ...
... 1. If the Earth’s spin axis was not tilted with respect to the Earth’s orbital plane (around the Sun), which of the following would be true, which false?: The number of daylight hours in a day would not change through the year. The length of a day would increase from 24 hours to 365 days The change ...
Unit 1: Earth History 1. Distinguish among eons
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
Document
... Mars is home to the tallest mountain in the solar system Only 18 missions to Mars have been successful ...
... Mars is home to the tallest mountain in the solar system Only 18 missions to Mars have been successful ...
friends of the planetarium newsletter - june 2010
... has transformed the appearance of the solar system's largest planet, one of Jupiter's two main cloud belts has completely disappeared. "This is a big event," says planetary scientist Glenn Orton of NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab. "We're monitoring the situation closely and do not yet fully understand wha ...
... has transformed the appearance of the solar system's largest planet, one of Jupiter's two main cloud belts has completely disappeared. "This is a big event," says planetary scientist Glenn Orton of NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab. "We're monitoring the situation closely and do not yet fully understand wha ...
Solar System
... Largest planet in the Solar System Has the most moons in the Solar System Gas giant, composed primarily of gas & liquid Giant Red Spot Ȃ storm ...
... Largest planet in the Solar System Has the most moons in the Solar System Gas giant, composed primarily of gas & liquid Giant Red Spot Ȃ storm ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Galaxies Reading Guide
... 16. We are not able to visit distant stars, yet we can determine how far away they are. How do parallax and math help us do this? A nearby star's apparent movement against the background of more distant stars as the Earth revolves around the Sun is referred to as stellar parallax. Nearby objects hav ...
... 16. We are not able to visit distant stars, yet we can determine how far away they are. How do parallax and math help us do this? A nearby star's apparent movement against the background of more distant stars as the Earth revolves around the Sun is referred to as stellar parallax. Nearby objects hav ...
1. Star A has a distance of 3 parsecs. What is its parallax angle? 1a
... Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the following stars is the most massive: a) G2V b) K8V c) O1V? c) because its the hottest and hence brightest and hence most luminous. What do all the stars in question 13) have in common? They a ...
... Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the following stars is the most massive: a) G2V b) K8V c) O1V? c) because its the hottest and hence brightest and hence most luminous. What do all the stars in question 13) have in common? They a ...
Astronomy Lecture Notes: Stellar Nomenclature I Introduction
... c. Apparent Magnitudes i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. Established visually by Hipparcos around 140 B.C.E. iii. Now measured using solid state photometers iv. A backward scale with the brightest star represented by the lowest number v. The brightest star in the entire sky is Siriu ...
... c. Apparent Magnitudes i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. Established visually by Hipparcos around 140 B.C.E. iii. Now measured using solid state photometers iv. A backward scale with the brightest star represented by the lowest number v. The brightest star in the entire sky is Siriu ...
Sun: The Nearest Star
... be for 4.6 billion years and has enough fuel to go on for another five billion years or so. At the end of its life, the Sun will start to fuse helium into heavier elements and swell to form a red giant. After a billion years as a red giant, it will suddenly collapse into a white dwarf. It may take a ...
... be for 4.6 billion years and has enough fuel to go on for another five billion years or so. At the end of its life, the Sun will start to fuse helium into heavier elements and swell to form a red giant. After a billion years as a red giant, it will suddenly collapse into a white dwarf. It may take a ...
Table Number: _____
... Using the distance modulus equation, d= 10 x 10(m-M)/5 , in the Introduction to calculate the distance to the cluster in parsecs. Then convert your answer to light years. Show all work in the ...
... Using the distance modulus equation, d= 10 x 10(m-M)/5 , in the Introduction to calculate the distance to the cluster in parsecs. Then convert your answer to light years. Show all work in the ...
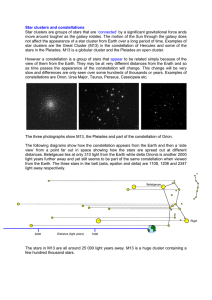
Star clusters and constellations
... Star clusters are groups of stars that are ‘connected’ by a significant gravitational force ands move around tougher as the galaxy rotates. The motion of the Sun through the galaxy does not affect the appearance of a star cluster from Earth over a long period of time. Examples of star clusters are t ...
... Star clusters are groups of stars that are ‘connected’ by a significant gravitational force ands move around tougher as the galaxy rotates. The motion of the Sun through the galaxy does not affect the appearance of a star cluster from Earth over a long period of time. Examples of star clusters are t ...
Centre of Mass
... • For life to exist on a palnet, it must also be in the habitable zone. This is the region in the solar system which is neither too hot nor too cold, but just right. Astronomers believe that in other solar systems, too, such habitable zones exist and life is more probable in those planets which fall ...
... • For life to exist on a palnet, it must also be in the habitable zone. This is the region in the solar system which is neither too hot nor too cold, but just right. Astronomers believe that in other solar systems, too, such habitable zones exist and life is more probable in those planets which fall ...
Out of this World
... travels in a very long orbit around the Sun. – Hayley’s comet orbits every 76 years ...
... travels in a very long orbit around the Sun. – Hayley’s comet orbits every 76 years ...
Early Astronomy
... Egyptian’s Observation of the Sun and Moon Motions. • Monitoring seasonal variation for agriculture Nile Flooded when sun rose near the star Sirius (the “Dog star”, in the Canis Major constellation; brightest star in the sky). • Link lunar and solar ‘birth’ and ‘death’ to religious festivals and an ...
... Egyptian’s Observation of the Sun and Moon Motions. • Monitoring seasonal variation for agriculture Nile Flooded when sun rose near the star Sirius (the “Dog star”, in the Canis Major constellation; brightest star in the sky). • Link lunar and solar ‘birth’ and ‘death’ to religious festivals and an ...
d 2
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.