Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Often one is interested in how quantities change when an object or a system is enlarged or shortened • Different quantities will change by different factors! • Typical example: how does the circumference, surface, volume of a sphere change when its radius changes? ...
... • Often one is interested in how quantities change when an object or a system is enlarged or shortened • Different quantities will change by different factors! • Typical example: how does the circumference, surface, volume of a sphere change when its radius changes? ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... The place between Mars and Jupiter is a particular region which keeps changing as the planets move; the asteroid belt is scattered over a very large area in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. ...
... The place between Mars and Jupiter is a particular region which keeps changing as the planets move; the asteroid belt is scattered over a very large area in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E2
... A star high on the main sequence has high luminosity. The rate at which energy is produced per unit mass is higher and so it will consume its mass in less time, spending less time on the main sequence. (See also the mass–luminosity relation in AHL.) ...
... A star high on the main sequence has high luminosity. The rate at which energy is produced per unit mass is higher and so it will consume its mass in less time, spending less time on the main sequence. (See also the mass–luminosity relation in AHL.) ...
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit-
... forms a Planetary Nebula around a hot, smaller and less luminous star called a White Dwarf. White Dwarfs are about the size of our Earth but still have a mass near the original Main Sequence star. Eventually the White Dwarf will dim and become a Black Dwarf. After the Variable stage of a Large Mass ...
... forms a Planetary Nebula around a hot, smaller and less luminous star called a White Dwarf. White Dwarfs are about the size of our Earth but still have a mass near the original Main Sequence star. Eventually the White Dwarf will dim and become a Black Dwarf. After the Variable stage of a Large Mass ...
The Sun and Other Stars - Tuslaw Local School District
... * 5 x’s the mass of the sun, 30 km in diameter * the gravity is so strong nothing can escape including light! ...
... * 5 x’s the mass of the sun, 30 km in diameter * the gravity is so strong nothing can escape including light! ...
Seasonal Motion
... How do we “see” that the earth is moving around the sun or v.v.? • Small discrepancy between sun’s motion and motion of stars • Sidereal vs solar day • At noon, say, the sun is not exactly in front of the same stars on the next day. – It is exactly in the south – The stars are faster, so a little w ...
... How do we “see” that the earth is moving around the sun or v.v.? • Small discrepancy between sun’s motion and motion of stars • Sidereal vs solar day • At noon, say, the sun is not exactly in front of the same stars on the next day. – It is exactly in the south – The stars are faster, so a little w ...
REVIEW FOR TEST ON THURSDAY!!!! 1. Scientist can use for
... REVIEW FOR TEST ON THURSDAY!!!! 1. Scientist can use ______________________ for satellites, solar panels, telescopes, and many other instruments, to study space, or make our lives easier. A. gravity ...
... REVIEW FOR TEST ON THURSDAY!!!! 1. Scientist can use ______________________ for satellites, solar panels, telescopes, and many other instruments, to study space, or make our lives easier. A. gravity ...
Constellations
... A. The number of months in a year B. The number of days in a month C. The number of weeks in a year D. The number of years in a decade 3. Astronomers recognize the Orion Nebula as a large celestial body. What can you infer about the Orion Nebula from its name? A. It is a star in the constellation Or ...
... A. The number of months in a year B. The number of days in a month C. The number of weeks in a year D. The number of years in a decade 3. Astronomers recognize the Orion Nebula as a large celestial body. What can you infer about the Orion Nebula from its name? A. It is a star in the constellation Or ...
Johnathan - WordPress.com
... Auriga is most prominent in the northern Hemisphere winter sky, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Auriga is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest st ...
... Auriga is most prominent in the northern Hemisphere winter sky, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Auriga is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest st ...
!
... Cygnus X-1 is believed to be a black hole. Give two examples of how astronomers can (sometimes) determine whether an X-ray-emitting object is a neutron star or black hole. (2 points)! ...
... Cygnus X-1 is believed to be a black hole. Give two examples of how astronomers can (sometimes) determine whether an X-ray-emitting object is a neutron star or black hole. (2 points)! ...
Interstellar clouds
... Luminosity of a Star • Luminosity is determined by the amount of fuel that it is burning. • Our sun fuses 4 billion kilograms of hydrogen per second. • In some 5 billion years from now the sun’s life will come to an end. • The more massive a star the shorter its life time, since increasing the mass ...
... Luminosity of a Star • Luminosity is determined by the amount of fuel that it is burning. • Our sun fuses 4 billion kilograms of hydrogen per second. • In some 5 billion years from now the sun’s life will come to an end. • The more massive a star the shorter its life time, since increasing the mass ...
Final Exam Prep
... FINAL EXAM PREPARATION: EARTH SCIENCE Final exams will be held this year starting June 19th . Finals count for 10% of your overall grade. Therefore, they can make a difference between an A and a B, a B and C etc; so please try to pass!! Our final covers just the second semester topics of Astronomy a ...
... FINAL EXAM PREPARATION: EARTH SCIENCE Final exams will be held this year starting June 19th . Finals count for 10% of your overall grade. Therefore, they can make a difference between an A and a B, a B and C etc; so please try to pass!! Our final covers just the second semester topics of Astronomy a ...
16.6 NOTES How do astronomers measure distance? Objective
... distance light travels in one year (about 10 trillion km). Light from the Sun reaches Earth in a little more than 8 minutes. Light from the North Star (Polaris), reaches earth in about 700 years. Astronomers can use parallax to find out distances to the closer stars. Parallax is the apparent change ...
... distance light travels in one year (about 10 trillion km). Light from the Sun reaches Earth in a little more than 8 minutes. Light from the North Star (Polaris), reaches earth in about 700 years. Astronomers can use parallax to find out distances to the closer stars. Parallax is the apparent change ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... hemisphere: days are longer than nights and Southern hemisphere days are shorter than nights ...
... hemisphere: days are longer than nights and Southern hemisphere days are shorter than nights ...
Jun - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... in 1753 and again in 1756, he recorded the total eclipse of the Moon in 1755, and in 1757 he recorded the start of the eclipse of Jupiter’s second satellite by the giant planet. Messier was given the job of searching for the predicted return of the comet now known as Halley’s Comet and it was whilst ...
... in 1753 and again in 1756, he recorded the total eclipse of the Moon in 1755, and in 1757 he recorded the start of the eclipse of Jupiter’s second satellite by the giant planet. Messier was given the job of searching for the predicted return of the comet now known as Halley’s Comet and it was whilst ...
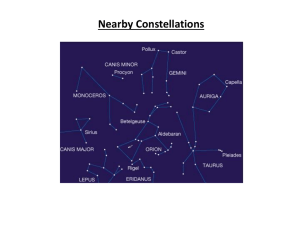
Nearby Constellations
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.