Our Universe
... • Most are located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter • do not have a specific orbit, they cluster in the belt and are continuously knocked out or pulled in my Jupiter. ...
... • Most are located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter • do not have a specific orbit, they cluster in the belt and are continuously knocked out or pulled in my Jupiter. ...
Document
... a greater or lesser extent) common to all stars. – If the laws of science we know apply to the entire universe (which we assume), then, given sufficient time, life must have originated elsewhere in the cosmos. • The opposing view maintains that intelligent life on Earth is the product of a series of ...
... a greater or lesser extent) common to all stars. – If the laws of science we know apply to the entire universe (which we assume), then, given sufficient time, life must have originated elsewhere in the cosmos. • The opposing view maintains that intelligent life on Earth is the product of a series of ...
Stellar Masses
... • In essence there is only one way of measuring masses and that is through the gravitational interaction with other bodies. • If we were able to observe the Solar system from a distance, say several hundred AU, then we could measure the periods of the planetary orbits and deduce the solar mass from ...
... • In essence there is only one way of measuring masses and that is through the gravitational interaction with other bodies. • If we were able to observe the Solar system from a distance, say several hundred AU, then we could measure the periods of the planetary orbits and deduce the solar mass from ...
Aust Curriculum Connections 2012
... Seasonal stars and constellations. Constellations, planets and tonight’s sky. The other planets: orbits and time for a “year”. What are the planets made of? Could I land on Jupiter? How many “years” old would I be if I lived on other planets? How long would it take to travel there? Why are some bodi ...
... Seasonal stars and constellations. Constellations, planets and tonight’s sky. The other planets: orbits and time for a “year”. What are the planets made of? Could I land on Jupiter? How many “years” old would I be if I lived on other planets? How long would it take to travel there? Why are some bodi ...
ASTR 2020 Space Astronomy Homework #3 Due Tuesday, 4
... Due Tuesday, 4 October, in class 1] Dwarf planets vs. terrestrial planets or gas giants. Give three reasons why it was appropriate to re-classify Pluto as a “dwarf planet” in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union. ...
... Due Tuesday, 4 October, in class 1] Dwarf planets vs. terrestrial planets or gas giants. Give three reasons why it was appropriate to re-classify Pluto as a “dwarf planet” in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union. ...
As two continental plates move toward each other, what landforms
... 7. The moon and the sun appear to move across the sky each day because of A. the Sun’s movement in the sky B. the Earth’s revolution around the sun C. the Earth’s rotation on its axis D. the Moon’s shadow on the Earth ...
... 7. The moon and the sun appear to move across the sky each day because of A. the Sun’s movement in the sky B. the Earth’s revolution around the sun C. the Earth’s rotation on its axis D. the Moon’s shadow on the Earth ...
planets
... For about 500 million years after its initial formation, the Earth remained at a rather stable 2000 degrees Fahrenheit (874.68 degrees Celsius). Comprised predominantly of iron and silicates, the Earth also contained small amounts of radioactive elements, mostly uranium, thorium, and potassium. As t ...
... For about 500 million years after its initial formation, the Earth remained at a rather stable 2000 degrees Fahrenheit (874.68 degrees Celsius). Comprised predominantly of iron and silicates, the Earth also contained small amounts of radioactive elements, mostly uranium, thorium, and potassium. As t ...
reasons for seasons
... period of time a __________. There are _________ days in a ________. It takes one year for Earth to ______________ once around the ________. If I am _________ years old (enter your own age), then I have made _________ trips around the Sun during my life. Earth’s orbit around the Sun traces out an al ...
... period of time a __________. There are _________ days in a ________. It takes one year for Earth to ______________ once around the ________. If I am _________ years old (enter your own age), then I have made _________ trips around the Sun during my life. Earth’s orbit around the Sun traces out an al ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... 38. Regions of space in which there are numerous galaxies grouped together are called Galactic Clusters. ...
... 38. Regions of space in which there are numerous galaxies grouped together are called Galactic Clusters. ...
SPA 302: THE EVOLUTION OF STARS LECTURE 1: BASICS OF
... 1.3.2 Brightness and Luminosity of Stars The luminosity of a star, denoted by L, is one of the most important characteristics of stars. It is measured in Watts (W) or as a multiple of the Sun's luminosity Lʘ and it is the amount of energy emitted per unit are of a star surface per second. However, i ...
... 1.3.2 Brightness and Luminosity of Stars The luminosity of a star, denoted by L, is one of the most important characteristics of stars. It is measured in Watts (W) or as a multiple of the Sun's luminosity Lʘ and it is the amount of energy emitted per unit are of a star surface per second. However, i ...
Quiz 1 Review
... Type II: high mass star cant fuse iron and outer layers collide with core 23. What do stars between 5-10 solar masses become? Neutron star 24. Explain how a neutron star is formed. After the supernova 20% of the star still remains and this mass still has a huge gravitational force. This gravitationa ...
... Type II: high mass star cant fuse iron and outer layers collide with core 23. What do stars between 5-10 solar masses become? Neutron star 24. Explain how a neutron star is formed. After the supernova 20% of the star still remains and this mass still has a huge gravitational force. This gravitationa ...
Stars Jeopardy
... In average sized stars, elements are fused down to ____ on the periodic table. ...
... In average sized stars, elements are fused down to ____ on the periodic table. ...
AST 301—Review for Exam 3 Consult “Guide to Reading and Study
... The final section on the discovery of extrasolar planets is one of the most exciting and evolving areas in astronomy at this time, so I want to make sure you study that well. Make sure you understand that there are several techniques that could be used to detect extrasolar planets, but that basicall ...
... The final section on the discovery of extrasolar planets is one of the most exciting and evolving areas in astronomy at this time, so I want to make sure you study that well. Make sure you understand that there are several techniques that could be used to detect extrasolar planets, but that basicall ...
Celestial Objects
... dependent upon: (1) the star’s luminosity, which is the total energy it actually emits per second in all directions and (2) the star’s distance from the Earth (the inverse square law of light propagation, B = 1/d2). ...
... dependent upon: (1) the star’s luminosity, which is the total energy it actually emits per second in all directions and (2) the star’s distance from the Earth (the inverse square law of light propagation, B = 1/d2). ...
Astronomy Unit Period
... __________ 31. High-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ...
... __________ 31. High-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ...
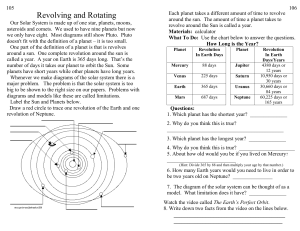
Revolving and Rotating
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
the interstellar medium - Howard University Physics and Astronomy
... such as carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S). • Water (H2O), currently mostly liquid in Earth’s oceans, has about 300 times the mass of Earth’s current atmosphere. If temperatures on the early Earth were sufficiently high, H2O would have been the primary cons ...
... such as carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S). • Water (H2O), currently mostly liquid in Earth’s oceans, has about 300 times the mass of Earth’s current atmosphere. If temperatures on the early Earth were sufficiently high, H2O would have been the primary cons ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.