Cosmology 2 - schoolphysics
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
Measuring the Distance to Stars Using Parallax
... Notice from the pictures that astronomers measure the star’s position against background stars, first in December and again in June when the Earth is opposite from where it was 6 months ago. Now notice that the Earth in December to the star and back to the Earth in June makes an angle. It is this an ...
... Notice from the pictures that astronomers measure the star’s position against background stars, first in December and again in June when the Earth is opposite from where it was 6 months ago. Now notice that the Earth in December to the star and back to the Earth in June makes an angle. It is this an ...
relax it`s only parallax!
... much your pencil appears to shift with respect to the distant objects. This is called parallax: the apparent shift of a foreground object with respect to background objects due only to a change in the observer’s position. ...
... much your pencil appears to shift with respect to the distant objects. This is called parallax: the apparent shift of a foreground object with respect to background objects due only to a change in the observer’s position. ...
Hubble`s Law is the relation between the recession velocity of a
... formation implies that elliptical galaxies were once more efficient then spirals, not the other way around. Also, while population I stars are younger than population II stars, not all (or even most) population I stars are bright blue O stars. Most (like our sun) are plain old mid or low mass stars ...
... formation implies that elliptical galaxies were once more efficient then spirals, not the other way around. Also, while population I stars are younger than population II stars, not all (or even most) population I stars are bright blue O stars. Most (like our sun) are plain old mid or low mass stars ...
1 Name: Date: PARALLAX EXERCISE1 The goal of this
... only 0.75" (arcseconds), which is only 1/4800 of a degree. Using such small angles in the formula we used above is somewhat difficult. Thus, astronomers have created a special unit, the parsec, for working with the distances to the stars. A parsec is the distance at which a star will have a parallax ...
... only 0.75" (arcseconds), which is only 1/4800 of a degree. Using such small angles in the formula we used above is somewhat difficult. Thus, astronomers have created a special unit, the parsec, for working with the distances to the stars. A parsec is the distance at which a star will have a parallax ...
14_creationism
... • Birth: collapse of gas cloud forms protostar. • Main sequence: center of star becomes hot ...
... • Birth: collapse of gas cloud forms protostar. • Main sequence: center of star becomes hot ...
HR Diagram of a Star Cluster
... A cluster of stars which is localized in space is usually localized in time also. Surprisingly, the brightness (magnitude) of the stars in two different color bands can be interpreted to tell the cluster's age and distance from Earth. This is done by plotting a magnitude vs. color diagram (as Hertzs ...
... A cluster of stars which is localized in space is usually localized in time also. Surprisingly, the brightness (magnitude) of the stars in two different color bands can be interpreted to tell the cluster's age and distance from Earth. This is done by plotting a magnitude vs. color diagram (as Hertzs ...
PowerPoint File
... Lecture 30- The Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy Distance to the center of the globular cluster distribution: 8500 parsecs = 8.5 kiloparsecs ...
... Lecture 30- The Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy Distance to the center of the globular cluster distribution: 8500 parsecs = 8.5 kiloparsecs ...
Scientists confirm most distant galaxy ever
... and the stretching of space-time makes light waves stretch as well. This phenomenon, called "red shift," is similar to the Doppler effect of sound -- for instance, the pitch of a police-car siren sounds higher when it's getting closer to you and lower as it moves away because the car is moving. The ...
... and the stretching of space-time makes light waves stretch as well. This phenomenon, called "red shift," is similar to the Doppler effect of sound -- for instance, the pitch of a police-car siren sounds higher when it's getting closer to you and lower as it moves away because the car is moving. The ...
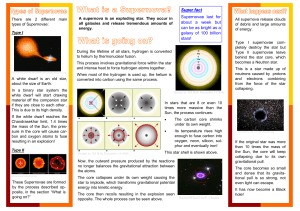
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
January 23
... A globular cluster is a roughly spherical collection of up to millions of stars bound together by the force of gravity. Astronomers can measure the velocities of the stars (rotation curves) in the cluster to get an idea of the mass distribution (as shown Monday). Assuming the stars have roughly the ...
... A globular cluster is a roughly spherical collection of up to millions of stars bound together by the force of gravity. Astronomers can measure the velocities of the stars (rotation curves) in the cluster to get an idea of the mass distribution (as shown Monday). Assuming the stars have roughly the ...
The Realm of Physics
... many times does your heart beat in your lifetime. • Ie. We live approximately 102 years, each year contains approximately 107 seconds, and our heart beats about 1 time per second. So, your heart beats about 109 times in your lifetime. ...
... many times does your heart beat in your lifetime. • Ie. We live approximately 102 years, each year contains approximately 107 seconds, and our heart beats about 1 time per second. So, your heart beats about 109 times in your lifetime. ...
Oct 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... 3. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of a star with a known luminosity relative to the Sun. 4. Briefly describe how the behavior of degenerate He differs from "normal" He when it is heated, and what role this difference plays in leading to the sudden onset of Hefusion ("helium flash") in the core ...
... 3. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of a star with a known luminosity relative to the Sun. 4. Briefly describe how the behavior of degenerate He differs from "normal" He when it is heated, and what role this difference plays in leading to the sudden onset of Hefusion ("helium flash") in the core ...
Untitled
... 100,000 light years away SMC has roughly one million stars Gravitational forces from our own Galaxy may be pulling the SMC apart. Typical sizes of small galaxies like this are ~10,000 light years ...
... 100,000 light years away SMC has roughly one million stars Gravitational forces from our own Galaxy may be pulling the SMC apart. Typical sizes of small galaxies like this are ~10,000 light years ...
E.S. 14: The Universe Universe Formation: The Big Bang Theory
... B. Spiral galaxies have spiral arms that start close to the center. i. Ex: The Milky Way ...
... B. Spiral galaxies have spiral arms that start close to the center. i. Ex: The Milky Way ...
Properties of Stars in general
... • Now, if we can find a binary system with a star of mass m in orbit around another star of unknown mass, we can deduce its mass too. • In this way, through observations of stellar binary systems we have been able to find the masses of stars of different types. • It turns out that the absolute brig ...
... • Now, if we can find a binary system with a star of mass m in orbit around another star of unknown mass, we can deduce its mass too. • In this way, through observations of stellar binary systems we have been able to find the masses of stars of different types. • It turns out that the absolute brig ...
Hubble - schoolphysics
... and therefore to the measurement of the size of the Universe. At present its value if thought to be about 70 kms-1 Mpc-1. This means that: The velocity of recession of a galaxy increases by 70 kms-1 for every 1 Mpc increase in distance. The value of H can be found by measuring the distance of anothe ...
... and therefore to the measurement of the size of the Universe. At present its value if thought to be about 70 kms-1 Mpc-1. This means that: The velocity of recession of a galaxy increases by 70 kms-1 for every 1 Mpc increase in distance. The value of H can be found by measuring the distance of anothe ...
Astro 210 Lecture 4 Sept. 4, 2013 Announcements: • PS 1 available
... hence brightness is “apparent” – depends on observer but L is intrinsic fundamental property of a star Q: how can we determine a star’s L? ...
... hence brightness is “apparent” – depends on observer but L is intrinsic fundamental property of a star Q: how can we determine a star’s L? ...
Milky Way galaxy - Uplift North Hills Prep
... Before October 6, 1923, astronomers thought the Andromeda Nebula and similar objects were bright pockets of matter inside the Milky Way. On that day astronomer Edwin Hubble noticed, looking at the photograps, a particular type of star inside the Andromeda Nebula. Hubble realized that the star (Ceph ...
... Before October 6, 1923, astronomers thought the Andromeda Nebula and similar objects were bright pockets of matter inside the Milky Way. On that day astronomer Edwin Hubble noticed, looking at the photograps, a particular type of star inside the Andromeda Nebula. Hubble realized that the star (Ceph ...
1. The distances to the most remote galaxies can be
... 26. H-R diagrams of very young clusters of stars: a) have all their stars on the main sequence. b) Have only their high mass stars on the main sequence while the low-mass protostars are still contracting (and hence are not on the main sequence yet). c) Have only their low mass stars on the main seq ...
... 26. H-R diagrams of very young clusters of stars: a) have all their stars on the main sequence. b) Have only their high mass stars on the main sequence while the low-mass protostars are still contracting (and hence are not on the main sequence yet). c) Have only their low mass stars on the main seq ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 15 1. Where in the Galaxy is the
... a. Our Galaxy is but one of many [billions] of galaxies in the universe. 5. How did Edwin Hubble prove that M31 is not a nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy? M31 is the Andromeda Galaxy, called “Andromeda Nebula” at the time. Hubble identified several stars in M31 as Cepheid variables, and measured their ...
... a. Our Galaxy is but one of many [billions] of galaxies in the universe. 5. How did Edwin Hubble prove that M31 is not a nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy? M31 is the Andromeda Galaxy, called “Andromeda Nebula” at the time. Hubble identified several stars in M31 as Cepheid variables, and measured their ...
Faintest Star Cluster Yet Found on Outskirts of Milky Way | Globular
... tiny little thing sort of southwest of Ursa Minor, but still very close. When I looked in more detail, it looked like a very tiny cluster of stars." Follow-up observations with the huge Keck II telescope, also on Mauna Kea, confirmed the find. Keck spectroscopic measurements, which separate light in ...
... tiny little thing sort of southwest of Ursa Minor, but still very close. When I looked in more detail, it looked like a very tiny cluster of stars." Follow-up observations with the huge Keck II telescope, also on Mauna Kea, confirmed the find. Keck spectroscopic measurements, which separate light in ...
review_one - MSU Solar Physics
... Understand and be prepared to explain the following: Unit 1 The three components to measuring radiation The difference between light gathering power and resolving power The ways in which the atmosphere is not helpful to astronomy, and ways around it Compare and contrast reflecting and refrac ...
... Understand and be prepared to explain the following: Unit 1 The three components to measuring radiation The difference between light gathering power and resolving power The ways in which the atmosphere is not helpful to astronomy, and ways around it Compare and contrast reflecting and refrac ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... stars and classify their power output and compare them with more distant stars The following very bright objects of known luminosity can be identified in distant galaxies • Cepheid Variable Stars ...
... stars and classify their power output and compare them with more distant stars The following very bright objects of known luminosity can be identified in distant galaxies • Cepheid Variable Stars ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.