* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download review_one - MSU Solar Physics
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
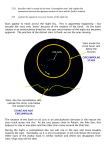
Review Sheet Physics 101 Exam One February 5 Go to the following rooms, based on team number: Teams 1-33: EPS 103 Teams 34-66: Leon Johnson 339 Teams 67-100: Roberts 101 Understand and be prepared to explain the following: Unit 1 The three components to measuring radiation The difference between light gathering power and resolving power The ways in which the atmosphere is not helpful to astronomy, and ways around it Compare and contrast reflecting and refracting telescopes Why the largest telescopes are reflecting and not refracting Unit 2 How the motion of the stars depends on the Earth’s revolution, rotation, and your location Why the directions on a star map are not the same as on a street map Explain the different apparent motion of circumpolar versus seasonal stars Explain why seasonal stars are not visible all throughout the year Unit 3 Understand the difference between apparent magnitude, absolute magnitude and luminosity How the method of trigonometric parallax works and its limitations How is the apparent motion of a star related to its distance from us? Explain the idea of a standard candle, and how it helps us measure stellar distances Unit 4 Understand the concept of the EM spectrum, similarities and differences between types of radiation What is blackbody radiation and what is its relationship to temperature? Prisms, raindrops and diffraction gratings do what to white light? Separating sunlight by wavelength tells us what about the Sun? Recognize the difference between continuous, emission and absorption spectra Know the position and shape of the following asterisms, visible at 10 pm on February 1st: Draco, Leo, Hydra, Orion, Pisces Unit 3 Understand the difference between apparent magnitude, absolute magnitude and luminosity How the method of trigonometric parallax works and its limitations How is the apparent motion of a star related to its distance from us? Explain the idea of a standard candle, and how it helps us measure stellar distances Unit 4 Understand the concept of the EM spectrum, similarities and differences between types of radiation What is blackbody radiation and what is its relationship to temperature? Prisms, raindrops and diffraction gratings do what to white light? Separating sunlight by wavelength tells us what about the Sun? Recognize the difference between continuous, emission and absorption spectra Know the position and shape of the following asterisms, visible at 10 pm on February 1st: Draco, Leo, Hydra, Orion, Pisces Review Sheet Physics 101 Exam One February 5 Go to the following rooms, based on team number: Teams 1-33: EPS 103 Teams 34-66: Leon Johnson 339 Teams 67-100: Roberts 101 Understand and be prepared to explain the following: Unit 1 The three components to measuring radiation The difference between light gathering power and resolving power The ways in which the atmosphere is not helpful to astronomy, and ways around it Compare and contrast reflecting and refracting telescopes Why the largest telescopes are reflecting and not refracting Unit 2 How the motion of the stars depends on the Earth’s revolution, rotation, and your location Why the directions on a star map are not the same as on a street map Explain the different apparent motion of circumpolar versus seasonal stars Explain why seasonal stars are not visible all throughout the year