Stars and the Sun
... – Luminosity: measure of the amount of energy given off. Measured as compared to the Sun (1), logarithmic 102, 104 – Apparent magnitude: as seen from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighter! – Absolute magnitude: if all stars were same distance from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighte ...
... – Luminosity: measure of the amount of energy given off. Measured as compared to the Sun (1), logarithmic 102, 104 – Apparent magnitude: as seen from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighter! – Absolute magnitude: if all stars were same distance from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighte ...
M = 5.5 - The Millstone
... Absolute Magnitude, we must have a measure of the stellar distance (by other means). Absolute magnitude, M, expresses the brightness of a star as it would be if it were placed 10 parsecs away. Since all stars would be placed at the same distance, absolute magnitudes show differences in actual lumino ...
... Absolute Magnitude, we must have a measure of the stellar distance (by other means). Absolute magnitude, M, expresses the brightness of a star as it would be if it were placed 10 parsecs away. Since all stars would be placed at the same distance, absolute magnitudes show differences in actual lumino ...
Stellar types - schoolphysics
... Red giants Red giants are very large stars with surface temperatures less than about 4700 K. They have diameters between 10 and 200 times that of the Sun. In spite of their relatively low surface temperature their enormous surface area means that they have luminosities between 100 and 10000 times th ...
... Red giants Red giants are very large stars with surface temperatures less than about 4700 K. They have diameters between 10 and 200 times that of the Sun. In spite of their relatively low surface temperature their enormous surface area means that they have luminosities between 100 and 10000 times th ...
Monday, April 28
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
Astronomy and Humanism by Ray Thompson A. EARLY
... This brings us to Edwin Hubble of Mount Wilson Observatory who concentrated on determining the distances to numerous galaxies using Henrietta's discovery. However, he made one further discovery in 1924. Using spectroscopy (introduced, you remember, by Newton) he noticed that the spectra of very dist ...
... This brings us to Edwin Hubble of Mount Wilson Observatory who concentrated on determining the distances to numerous galaxies using Henrietta's discovery. However, he made one further discovery in 1924. Using spectroscopy (introduced, you remember, by Newton) he noticed that the spectra of very dist ...
Characteristics of Stars Stars Analyzing Starlight Star Characteristics
... motion visible to the unaided eye caused by Earth's rotation appear to move counter-clockwise around Polaris (the North Star) different stars appear in different seasons circumpolar stars - always visible in the night sky ...
... motion visible to the unaided eye caused by Earth's rotation appear to move counter-clockwise around Polaris (the North Star) different stars appear in different seasons circumpolar stars - always visible in the night sky ...
How the univ works
... 21. ____________ always produce the same amount of light and are used to measure distance to galaxies. ...
... 21. ____________ always produce the same amount of light and are used to measure distance to galaxies. ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
1 - TeacherWeb
... 38. What is learned from studying the spectra lines of star light? 39. Most stars are in the “main sequence” of their life cycle and burn for billions of years. Why don’t stars in the main sequence either explode right away or become crushed by their own gravity? ...
... 38. What is learned from studying the spectra lines of star light? 39. Most stars are in the “main sequence” of their life cycle and burn for billions of years. Why don’t stars in the main sequence either explode right away or become crushed by their own gravity? ...
Watching Galaxies Form Near the Beginning of Time
... Evidence for global winds escaping systems Exist in groupings with bright galaxies/AGN Are these the early units predicted by hierarchical schemes (and fitting dark-matter ...
... Evidence for global winds escaping systems Exist in groupings with bright galaxies/AGN Are these the early units predicted by hierarchical schemes (and fitting dark-matter ...
1 - UCSC Physics - University of California, Santa Cruz
... A binary pulsar system provides an excellent laboratory for testing some of the most bizarre predictions of general relativity. The two pulsars in the J0737-3039 system are actually very far apart compared to their sizes. In a true scale model, if the pulsars were the sizes of marbles, they would be ...
... A binary pulsar system provides an excellent laboratory for testing some of the most bizarre predictions of general relativity. The two pulsars in the J0737-3039 system are actually very far apart compared to their sizes. In a true scale model, if the pulsars were the sizes of marbles, they would be ...
Galaxies and the Universe - Grandview Independent School
... extreme cases, billion solar masses. Our own galaxy, the Milky Way is no exception. ...
... extreme cases, billion solar masses. Our own galaxy, the Milky Way is no exception. ...
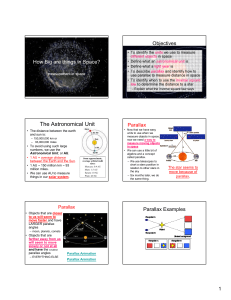
The Astronomical Unit
... • To identify when to use the inverse square law to determine the distance to a star – Explain what the inverse square law says ...
... • To identify when to use the inverse square law to determine the distance to a star – Explain what the inverse square law says ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... from or toward our solar system. 26. the apparent shift in the wavelength of light emitted by a light source moving toward or away from an observer 27. that those galaxies are moving away from Earth 28. A 29. D 30. A 31. B 32. Parallax is the apparent shift in a star’s position when viewed from diff ...
... from or toward our solar system. 26. the apparent shift in the wavelength of light emitted by a light source moving toward or away from an observer 27. that those galaxies are moving away from Earth 28. A 29. D 30. A 31. B 32. Parallax is the apparent shift in a star’s position when viewed from diff ...
name - New York Science Teacher
... TASK# 1: MAGNITUDE & BRIGHTNESS You will begin by learning how to identify stars by their magnitude (brightness), color, and temperature, and spectral class. PART 1: Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on ...
... TASK# 1: MAGNITUDE & BRIGHTNESS You will begin by learning how to identify stars by their magnitude (brightness), color, and temperature, and spectral class. PART 1: Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on ...
What Is a Light-year?
... next closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. Proxima Centauri is 40 trillion (40,000,000,000,000) kilometers from Earth. (4) a (5) number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For (6) reason, • astronomers use a different (7) of (8) when they talk about distances between stars. In o ...
... next closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. Proxima Centauri is 40 trillion (40,000,000,000,000) kilometers from Earth. (4) a (5) number is difficult to understand and use in calculations. For (6) reason, • astronomers use a different (7) of (8) when they talk about distances between stars. In o ...
Quiz 1
... d) exploding stars near the center of our galaxy. 23. For the most distant objects shown in #22,23, the light we received left: a) before the Earth was formed. b) about thirty thousand years ago c) more than 20 billion years ago d) a few seconds before the image was taken. 24. Why do astronomers int ...
... d) exploding stars near the center of our galaxy. 23. For the most distant objects shown in #22,23, the light we received left: a) before the Earth was formed. b) about thirty thousand years ago c) more than 20 billion years ago d) a few seconds before the image was taken. 24. Why do astronomers int ...
form b - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... (b) Cepheid variables change their brightness too quickly to detect at great distances. (c) Most galaxies in the universe are elliptical and don’t have Cepheid variables. (d) The luminosity of SN Type Ia explosions is much greater than Cepheid variables. (e) Cepheid variables are not found in the mo ...
... (b) Cepheid variables change their brightness too quickly to detect at great distances. (c) Most galaxies in the universe are elliptical and don’t have Cepheid variables. (d) The luminosity of SN Type Ia explosions is much greater than Cepheid variables. (e) Cepheid variables are not found in the mo ...
The Cosmic Dawn : Physics of the First Luminous Objects
... One of the paramount problems in modern cosmology is to elucidate how the first generation of luminous objects, stars, accreting black holes (BHs) and galaxies, shaped the early universe at the end of the cosmic dark ages. According to the modern theory of cosmological structure formation, the hiera ...
... One of the paramount problems in modern cosmology is to elucidate how the first generation of luminous objects, stars, accreting black holes (BHs) and galaxies, shaped the early universe at the end of the cosmic dark ages. According to the modern theory of cosmological structure formation, the hiera ...
OUSNMAR05 - The Open University
... Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standard candles” in measuring distances to nearby galaxies. Maximum brightness occurs on 6th, 11th, 16th, 22nd and 27th. Mu ( ...
... Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standard candles” in measuring distances to nearby galaxies. Maximum brightness occurs on 6th, 11th, 16th, 22nd and 27th. Mu ( ...
Homework # 2, due 17 Feb
... think the observable stars able in regions B and C would be more or less metal rich than what is actually in your model sky? 5. Consider hydrogen gas in the galactic plane. Assume the Sun is at a distance of R0 = 8 kpc from the Galactic center with the average Galactic rotational velocity at that di ...
... think the observable stars able in regions B and C would be more or less metal rich than what is actually in your model sky? 5. Consider hydrogen gas in the galactic plane. Assume the Sun is at a distance of R0 = 8 kpc from the Galactic center with the average Galactic rotational velocity at that di ...
Study Guide for Stars and Galaxies Quiz ANSWER KEY
... c. chemical composition d. size e. brightness 2. Which 2 things does the brightness of a star depend on? a. size b. temperature 3. What is a lightyear? The distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. 4. Define and describe parallax. Why is it useful for o ...
... c. chemical composition d. size e. brightness 2. Which 2 things does the brightness of a star depend on? a. size b. temperature 3. What is a lightyear? The distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. 4. Define and describe parallax. Why is it useful for o ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.