worksheet
... How do Astronomers know how much matter is in a galaxy? How do they know dark matter exists? In this project, you will use some real galaxy data and make some measurements in the way that astronomers do. ...
... How do Astronomers know how much matter is in a galaxy? How do they know dark matter exists? In this project, you will use some real galaxy data and make some measurements in the way that astronomers do. ...
ph607-14-a3uni - University of Kent
... in solar masses per year. 3. Describe the colour, stellar population and gas content of E, SO and Irr galaxies. 4. Explain the difference between the monolithic and hierarchical theories for the ...
... in solar masses per year. 3. Describe the colour, stellar population and gas content of E, SO and Irr galaxies. 4. Explain the difference between the monolithic and hierarchical theories for the ...
Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy
... – This is called cosmological _______________. – Proven by observing a faint glow of __________________ that is a remnant of _________ from the Big Bang. – Early Universe = __________ and ____________ – Today’s Universe = __________ and ________ ___________ because of ...
... – This is called cosmological _______________. – Proven by observing a faint glow of __________________ that is a remnant of _________ from the Big Bang. – Early Universe = __________ and ____________ – Today’s Universe = __________ and ________ ___________ because of ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... A. The once-smaller universe is expanding in all directions. B. The Sun and Earth are located at the center of the universe. C. Everything in the universe is moving the same direction. D. Massive black holes are drawing galaxies away from Earth. 4. We know that nearly all galaxies are moving away fr ...
... A. The once-smaller universe is expanding in all directions. B. The Sun and Earth are located at the center of the universe. C. Everything in the universe is moving the same direction. D. Massive black holes are drawing galaxies away from Earth. 4. We know that nearly all galaxies are moving away fr ...
Graphing the Big Dipper Although they look close together from
... Graphing the Big Dipper Although they look close together from Earth, the stars in the Big Dipper are actually very far apart. They also vary tremendously in their distances from Earth. In this activity, you will graph the stars of the Big Dipper to make these differences clearer. Materials Graphing ...
... Graphing the Big Dipper Although they look close together from Earth, the stars in the Big Dipper are actually very far apart. They also vary tremendously in their distances from Earth. In this activity, you will graph the stars of the Big Dipper to make these differences clearer. Materials Graphing ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
galaxies
... • stars are clumped closely together, especially near the center of the cluster (densely) • surround our disk as a halo Image at http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/star%20cluster/globular /1999/26/image/a/results/50/ ...
... • stars are clumped closely together, especially near the center of the cluster (densely) • surround our disk as a halo Image at http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/star%20cluster/globular /1999/26/image/a/results/50/ ...
Russell Diagram
... How do the following properties differ with respect to the Sun for the listed main sequence types? What properties would not change for non-main sequence stars? ...
... How do the following properties differ with respect to the Sun for the listed main sequence types? What properties would not change for non-main sequence stars? ...
1-1 H. Color Index: A color index is the difference of two color
... Distance modulus is an indicator of the distance of an object expressed in terms of its absolute and apparent magnitudes. More specifically, distance modulus is defined as m-M. If the distance modulus is 0, the object is 10 parsecs distant. If m-M is less than zero or negative, this means the object ...
... Distance modulus is an indicator of the distance of an object expressed in terms of its absolute and apparent magnitudes. More specifically, distance modulus is defined as m-M. If the distance modulus is 0, the object is 10 parsecs distant. If m-M is less than zero or negative, this means the object ...
The Merger of Two Disk Galaxies
... disk form the planets, moons, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Note that this process is repeated on a smaller scale in the outer solar system, where miniature disks form around the Jovian planets. ...
... disk form the planets, moons, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Note that this process is repeated on a smaller scale in the outer solar system, where miniature disks form around the Jovian planets. ...
Homework #9 - Solutions - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... in the Pleiades star cluster The Pleiades star cluster is a young open star cluster located in the spiral arms, thus we would expect population I stars. d) in intergalactic space (beyond the halo) We would expect to see only old extreme population II stars (and possibly population III stars which ar ...
... in the Pleiades star cluster The Pleiades star cluster is a young open star cluster located in the spiral arms, thus we would expect population I stars. d) in intergalactic space (beyond the halo) We would expect to see only old extreme population II stars (and possibly population III stars which ar ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
Astronomy 401 Lecture 1 Overview of the Universe 1 Class overview
... where v is the radial velocity of the galaxy. Therefore we can get the Hubble constant from dividing velocity by distance, and it has the units km s−1 Mpc−1 (note that the actual units are inverse time). Hubble’s original estimate was H0 = 500 km s−1 Mpc−1 , but he was severely underestimating the d ...
... where v is the radial velocity of the galaxy. Therefore we can get the Hubble constant from dividing velocity by distance, and it has the units km s−1 Mpc−1 (note that the actual units are inverse time). Hubble’s original estimate was H0 = 500 km s−1 Mpc−1 , but he was severely underestimating the d ...
GO 1_ Early Theorieso Of Space And Technology
... stars and planets, they have sought ways to explain it. • First calendars were lunar, accurate for hunters, gatherers and fishermen. • Settled societies needed a more precise solar (Sun) calendar to predict planting and harvesting time • Figuring out the regular motions of the Sun and Moon with the ...
... stars and planets, they have sought ways to explain it. • First calendars were lunar, accurate for hunters, gatherers and fishermen. • Settled societies needed a more precise solar (Sun) calendar to predict planting and harvesting time • Figuring out the regular motions of the Sun and Moon with the ...
Winning Entries in this week’s Galaxy
... • Π, Θ, Z velocities but relative to Local Standard of Rest • LSR is point instantaneously centered on Sun, but moving in a perfectly circular orbit. • Solar motion = motion of sun relative to LSR ...
... • Π, Θ, Z velocities but relative to Local Standard of Rest • LSR is point instantaneously centered on Sun, but moving in a perfectly circular orbit. • Solar motion = motion of sun relative to LSR ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Some stars end their lives in cataclysmic explosions: spectacular supernovae, which briefly become the most brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astr ...
... Some stars end their lives in cataclysmic explosions: spectacular supernovae, which briefly become the most brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astr ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... – Most stars fall in the region called main sequence. – Curved line sloping from top left to lower right of HR diagram. ...
... – Most stars fall in the region called main sequence. – Curved line sloping from top left to lower right of HR diagram. ...
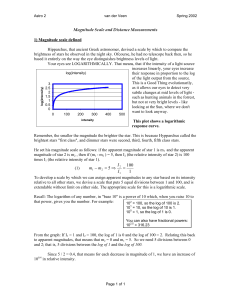
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... To develop a scale by which we can assign apparent magnitudes to any star based on its intensity relative to all other stars, we devise a scale that puts 5 equal divisions between 1 and 100, and is extendable without limit on either side. The appropriate scale for this is a logarithmic scale. Recall ...
... To develop a scale by which we can assign apparent magnitudes to any star based on its intensity relative to all other stars, we devise a scale that puts 5 equal divisions between 1 and 100, and is extendable without limit on either side. The appropriate scale for this is a logarithmic scale. Recall ...
Refer to the class notes which describe how Aristarchus figured out
... 2. Computing the uncertainty in distance to a star based on its parallax can be a tricky thing. Consider the case of Joe and the star Rigel. Joe measures a parallax half-angle of π = 0.004 arcsec to Rigel. He estimates the uncertainty in his measurement to be +/- 0.003 arcsec. In other words, the pa ...
... 2. Computing the uncertainty in distance to a star based on its parallax can be a tricky thing. Consider the case of Joe and the star Rigel. Joe measures a parallax half-angle of π = 0.004 arcsec to Rigel. He estimates the uncertainty in his measurement to be +/- 0.003 arcsec. In other words, the pa ...
Lecture 1 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Astronomical Unit = distance from the Earth to the Sun Light Year = distance light travels in 1 yr = 9.4 x 1017 cm Parsec = 3.26 light years = 3.08 x 1018 cm Factoid: the nearest star is 1.30 pc or 4.22 light years ...
... Astronomical Unit = distance from the Earth to the Sun Light Year = distance light travels in 1 yr = 9.4 x 1017 cm Parsec = 3.26 light years = 3.08 x 1018 cm Factoid: the nearest star is 1.30 pc or 4.22 light years ...
solution
... white dwarf or neutron star, the giant swells beyond its Roche lobe and the smaller, more dense companion takes on inflating matter from its bigger companion, this causes the mass of the core remnant to exceed about 3 M , thus forming a black hole; and finally 3) two neutron stars are in close orbi ...
... white dwarf or neutron star, the giant swells beyond its Roche lobe and the smaller, more dense companion takes on inflating matter from its bigger companion, this causes the mass of the core remnant to exceed about 3 M , thus forming a black hole; and finally 3) two neutron stars are in close orbi ...
Parallaxes are very small The position of Ursa Major
... arcseconds. A star near the center of our Galaxy has a parallax of about 0.0001 arcseconds. In order to measure such small angles we need an instrument like Gaia. ...
... arcseconds. A star near the center of our Galaxy has a parallax of about 0.0001 arcseconds. In order to measure such small angles we need an instrument like Gaia. ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 5
... 18. Which of the stars in the diagram above has the brightest absolute visual magnitude? ...
... 18. Which of the stars in the diagram above has the brightest absolute visual magnitude? ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.