Observing Information for Waddesdon, 4th October 2014
... This is an asterism of three bright stars, Deneb, Vega and Altair. It is easily visible with the unaided eye and is useful for locating other objects at this time of year. Deneb is the bright star that’s very high to the SE. It’s the brightest star in the constellation Cygnus. It is 1400 light years ...
... This is an asterism of three bright stars, Deneb, Vega and Altair. It is easily visible with the unaided eye and is useful for locating other objects at this time of year. Deneb is the bright star that’s very high to the SE. It’s the brightest star in the constellation Cygnus. It is 1400 light years ...
Unit 1
... • Low-mass stars create carbon and oxygen in their cores at the end of their lifespan, thanks to the higher temperatures and pressures present in a red giant star • High-mass stars produce heavier elements like silicon, magnesium, etc., by nuclear fusion in their cores – Temperatures are much higher ...
... • Low-mass stars create carbon and oxygen in their cores at the end of their lifespan, thanks to the higher temperatures and pressures present in a red giant star • High-mass stars produce heavier elements like silicon, magnesium, etc., by nuclear fusion in their cores – Temperatures are much higher ...
ASTRONOMY 1102 1
... Core collapse SN: the death of a massive star; Carbon{detonation SN or Type Ia SN: the collapse of a WD pushed over the brink (maximum mass is Chandrasekhar Mass = 1.4 M ). This can happen because of accretion or a merger of two WD. The ejected envelope is seen for 104 years as a SN remnant. The f ...
... Core collapse SN: the death of a massive star; Carbon{detonation SN or Type Ia SN: the collapse of a WD pushed over the brink (maximum mass is Chandrasekhar Mass = 1.4 M ). This can happen because of accretion or a merger of two WD. The ejected envelope is seen for 104 years as a SN remnant. The f ...
Unit Two Worksheet – Astronomy
... Continuous spectrum of light emitted by a solid, liquid, or gas under high pressure Continuous spectrum produced when white light is passed through a cool gas under low pressure A series of bright lights of certain wavelengths that are produced by a hot gas under low pressure ...
... Continuous spectrum of light emitted by a solid, liquid, or gas under high pressure Continuous spectrum produced when white light is passed through a cool gas under low pressure A series of bright lights of certain wavelengths that are produced by a hot gas under low pressure ...
Stars_and_Galaxies
... Starlight, Starbright • The stars that are closer to us appear to be brighter • Stars shine because of fusion in its core. Two hydrogen atoms fuse into one helium atom. • This is why a star shines for billions of years! ...
... Starlight, Starbright • The stars that are closer to us appear to be brighter • Stars shine because of fusion in its core. Two hydrogen atoms fuse into one helium atom. • This is why a star shines for billions of years! ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... telescope have been observed every few hundred years by humans and were recorded as long ago as 1054 by Chinese astronomers. Many more supernovae are observed, in our own and other galaxies, with telescopes. (There are two types of supernovae. This is a description of type II supernovae. Type I supe ...
... telescope have been observed every few hundred years by humans and were recorded as long ago as 1054 by Chinese astronomers. Many more supernovae are observed, in our own and other galaxies, with telescopes. (There are two types of supernovae. This is a description of type II supernovae. Type I supe ...
Stars and Galaxies PP 2013
... High mass supergiants may undergo a supernova, where the core suddenly collapses and explodes. A neutron star is what remains after the supernova. It is composed mainly of neutrons and is very dense. If it spins and releases radiation it is called a pulsar. ...
... High mass supergiants may undergo a supernova, where the core suddenly collapses and explodes. A neutron star is what remains after the supernova. It is composed mainly of neutrons and is very dense. If it spins and releases radiation it is called a pulsar. ...
The Marathon
... magnitude 4.0 star Delta Ceti. If you have trouble tracking down Delta Ceti then use 2.53 magnitude Mekar (Alpha Ceti), which is 4° away from M74. The famous Triangulum Galaxy (M33) is next. It's directly between the stars Hamal (in Aries) and Mirach (in Andromeda). This is a large face-on galaxy, m ...
... magnitude 4.0 star Delta Ceti. If you have trouble tracking down Delta Ceti then use 2.53 magnitude Mekar (Alpha Ceti), which is 4° away from M74. The famous Triangulum Galaxy (M33) is next. It's directly between the stars Hamal (in Aries) and Mirach (in Andromeda). This is a large face-on galaxy, m ...
WIRO: Spectral Analysis P1
... catalog of stellar spectra, and whose work assisted Ejnar Hertzsprung in his verification of a distinction between dwarf stars and giant stars.. ...
... catalog of stellar spectra, and whose work assisted Ejnar Hertzsprung in his verification of a distinction between dwarf stars and giant stars.. ...
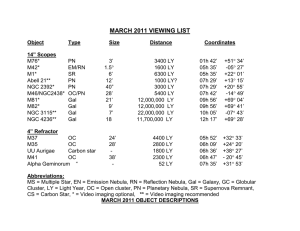
March
... standard planetary nebula with a 16th magnitude central star. The unusual appearance is due to the angle of the nebular ring that is expanding outward from the white dwarf at about 42 K/sec. Most of the visible light is emitted in the OIII doubly ionized Oxygen band so the use of a nebula or OIII fi ...
... standard planetary nebula with a 16th magnitude central star. The unusual appearance is due to the angle of the nebular ring that is expanding outward from the white dwarf at about 42 K/sec. Most of the visible light is emitted in the OIII doubly ionized Oxygen band so the use of a nebula or OIII fi ...
The Change in Gravitational Potential Energy of Objects
... objects near stars in stellar metamorphosis changes as the stars evolve. Explanation is provided. In stellar metamorphosis, exoplanets are evolved/evolving and dead stars. They have lost the majority of their mass, and their gravitational fields and radii have diminished considerably, as well as the ...
... objects near stars in stellar metamorphosis changes as the stars evolve. Explanation is provided. In stellar metamorphosis, exoplanets are evolved/evolving and dead stars. They have lost the majority of their mass, and their gravitational fields and radii have diminished considerably, as well as the ...
After Dark M S
... What are cosmic rays and how were they discovered? How can particles of light with trillions of times the energy of the light particles from the sun be used to do astronomy and learn about the sources of cosmic rays? HAWC, a cosmic ray observatory currently under construction, will detect and measur ...
... What are cosmic rays and how were they discovered? How can particles of light with trillions of times the energy of the light particles from the sun be used to do astronomy and learn about the sources of cosmic rays? HAWC, a cosmic ray observatory currently under construction, will detect and measur ...
Galaxies and Stars Questions KEY
... Generally, stars with more mass have shorter life spans because they burn their fuel more quickly than smaller stars do. The mass also determines which direction the lifespan goes and ultimately, determines what the star becomes when it dies. 7. What is the outcome of a star that runs out of hydroge ...
... Generally, stars with more mass have shorter life spans because they burn their fuel more quickly than smaller stars do. The mass also determines which direction the lifespan goes and ultimately, determines what the star becomes when it dies. 7. What is the outcome of a star that runs out of hydroge ...
1.1 Fundamental Observers
... by careful measures of by the Hubble diagram (luminosity vs. distance) of Type Ia supernovae. Its nature is still totally unclear. One of the aims of observational cosmology is to determine the relative contributions of these different components to the total mass-energy density of the Universe. In ...
... by careful measures of by the Hubble diagram (luminosity vs. distance) of Type Ia supernovae. Its nature is still totally unclear. One of the aims of observational cosmology is to determine the relative contributions of these different components to the total mass-energy density of the Universe. In ...
c - Fsusd
... 7) A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a ______. a) quasar b) binary system c) black hole d) pulsar ...
... 7) A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a ______. a) quasar b) binary system c) black hole d) pulsar ...
Powerpoint for today
... Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius ( ...
... Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius ( ...
O star
... spectral type and the luminosity class of a star from its spectrum. This is extraordinarily valuable, as it means that, just from the spectrum of a star, one can plot it in on the H-R diagram. BUT: if you can plot a star on the H-R diagram, you know its absolute magnitude! And if you know its absolu ...
... spectral type and the luminosity class of a star from its spectrum. This is extraordinarily valuable, as it means that, just from the spectrum of a star, one can plot it in on the H-R diagram. BUT: if you can plot a star on the H-R diagram, you know its absolute magnitude! And if you know its absolu ...
NAME_______________________________________
... 5. In the modern classification of apparent magnitude, a difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightness. _________________________ ...
... 5. In the modern classification of apparent magnitude, a difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightness. _________________________ ...
abstract english
... neutron star are believed to also emit a light signal as the two stars collide in the final stages of their dance around each other. We can measure the motion of the system relative to Earth by determining the wavelength composition of the light. By measuring hundreds of these orbiting neutron stars ...
... neutron star are believed to also emit a light signal as the two stars collide in the final stages of their dance around each other. We can measure the motion of the system relative to Earth by determining the wavelength composition of the light. By measuring hundreds of these orbiting neutron stars ...
6. 1 Star Distances 6. 2 Apparent Brightness, Intrinsic Brightness
... Few binary star systems are easy to analyze; most are spectroscopic binaries in which the component stars are known only by the alternating Doppler shifts of their spectral lines. ...
... Few binary star systems are easy to analyze; most are spectroscopic binaries in which the component stars are known only by the alternating Doppler shifts of their spectral lines. ...
to View - Great Balls of Fire exhibit
... Why do the Sun and the Moon appear to be the same size in the sky? The diameter of the Sun is 400 times greater than that of the Moon, but the Sun is 400 times farther from the Earth than the Moon. That is why you can see a total eclipse of the Sun, during which the Moon blocks the light from the Su ...
... Why do the Sun and the Moon appear to be the same size in the sky? The diameter of the Sun is 400 times greater than that of the Moon, but the Sun is 400 times farther from the Earth than the Moon. That is why you can see a total eclipse of the Sun, during which the Moon blocks the light from the Su ...
here.
... - A group of gravitationally bound stars formed out of the same cloud, at the same time, and at the same distance from us. - They are ideal laboratories to study stellar evolution, and to probe the Galactic formation and evolutionary history ...
... - A group of gravitationally bound stars formed out of the same cloud, at the same time, and at the same distance from us. - They are ideal laboratories to study stellar evolution, and to probe the Galactic formation and evolutionary history ...
Lab: Inverse Square Law
... As light travels from a source it spreads out equally in all directions. The brightness of the light is the power (energy per second) per area. We all know that a light, such as a candle or a streetlight, looks dimmer the farther away from it we get. But how does the brightness change with distance? ...
... As light travels from a source it spreads out equally in all directions. The brightness of the light is the power (energy per second) per area. We all know that a light, such as a candle or a streetlight, looks dimmer the farther away from it we get. But how does the brightness change with distance? ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.