Milky Way Galaxy
... star before the supernova will then be either a neutron star or a black hole. Which object it becomes depends on the size of the original star. A star that is 1.5 to 4 times larger than our Sun will become a neutron star. Stars that are even bigger than that will become black holes. ...
... star before the supernova will then be either a neutron star or a black hole. Which object it becomes depends on the size of the original star. A star that is 1.5 to 4 times larger than our Sun will become a neutron star. Stars that are even bigger than that will become black holes. ...
Document
... o Observed rates of period change are consistent with Classic Cepheids during their first crossing of the instability gap, whereas models have the rate of change for Polaris at four times what is observed. ...
... o Observed rates of period change are consistent with Classic Cepheids during their first crossing of the instability gap, whereas models have the rate of change for Polaris at four times what is observed. ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... • Scientists think the centre of the galaxy contains a super massive black hole. • The Milky Way is full of dust, gas and stars. • The Milky Way, along with everything else, is moving through space. ...
... • Scientists think the centre of the galaxy contains a super massive black hole. • The Milky Way is full of dust, gas and stars. • The Milky Way, along with everything else, is moving through space. ...
The hierarchical structure of the Universe (go from little to large)
... - Everything you see is part of the Galaxy • The glow of the Milky Way • Stars • Star clusters (open clusters and globular clusters) • Planetary nebulae (dying stars) • Supernova remnants (stars that blew up) • Diffuse nebulae (glowing interstellar gas) ...
... - Everything you see is part of the Galaxy • The glow of the Milky Way • Stars • Star clusters (open clusters and globular clusters) • Planetary nebulae (dying stars) • Supernova remnants (stars that blew up) • Diffuse nebulae (glowing interstellar gas) ...
fact sheet about the Andromeda galaxy
... THE SCALE OF ANDROMEDA The Andromeda galaxy itself is quite ...
... THE SCALE OF ANDROMEDA The Andromeda galaxy itself is quite ...
Absolute magnitude
... Some useful definitions: ▪ Brightness of a star is measured by logarithmic magnitude. => Brighter objects have a smaller magnitude. ▪ Apparent magnitude: how bright the star appears to us in the sky. m ▪ Absolute magnitude: how bright the star would be at a distance of 10 parsecs from us. M ...
... Some useful definitions: ▪ Brightness of a star is measured by logarithmic magnitude. => Brighter objects have a smaller magnitude. ▪ Apparent magnitude: how bright the star appears to us in the sky. m ▪ Absolute magnitude: how bright the star would be at a distance of 10 parsecs from us. M ...
The night sky - Mr. Champion
... • Chances are, at some point you have looked up during a clear night and noticed patterns and changes. • Humans have for many years speculated at what was above us. • This is the study of astronomy – what is beyond Earth. • The first would likely be the most numerous object we see – stars. ...
... • Chances are, at some point you have looked up during a clear night and noticed patterns and changes. • Humans have for many years speculated at what was above us. • This is the study of astronomy – what is beyond Earth. • The first would likely be the most numerous object we see – stars. ...
Apparent Magnitude - RanelaghALevelPhysics
... • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
... • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Implosion of a white dwarf after it accretes a certain amount of matter, reaching about 1.4 solar masses • Very predictable; used as a standard candle – Estimate distances to galaxies where they occur ...
... • Implosion of a white dwarf after it accretes a certain amount of matter, reaching about 1.4 solar masses • Very predictable; used as a standard candle – Estimate distances to galaxies where they occur ...
Chapter10 (with interactive links)
... To measure mass, astronomers look for the effects of gravity. Many stars are binary stars orbiting a common center of mass. A less massive star moves faster on a larger orbit. ...
... To measure mass, astronomers look for the effects of gravity. Many stars are binary stars orbiting a common center of mass. A less massive star moves faster on a larger orbit. ...
Lecture 4 January 31 - Center for Astrophysics and Space
... Sun shrank steadily, with T rising until, about 10 million years after it started to form, it reached its current size There is a VERY fast increase in nuclear energy production above 1,000,000K. At 15,000,000K in the core nuclear power generated finally balanced the luminosity from the surface. Tha ...
... Sun shrank steadily, with T rising until, about 10 million years after it started to form, it reached its current size There is a VERY fast increase in nuclear energy production above 1,000,000K. At 15,000,000K in the core nuclear power generated finally balanced the luminosity from the surface. Tha ...
Unit 1
... energy uncertainty D. Stopping of time in the vicinity of the black hole as the black hole travels through space-time ...
... energy uncertainty D. Stopping of time in the vicinity of the black hole as the black hole travels through space-time ...
Slides - Physics at SMU
... Empty Space is a normally perceived as being a vacuum void of energy but as special relativity tells us a vaccum is actually the lowest energy state possible. (a very different definition from "empty".) Even at this low energy state you still have some (even if its very small) energy that accumulat ...
... Empty Space is a normally perceived as being a vacuum void of energy but as special relativity tells us a vaccum is actually the lowest energy state possible. (a very different definition from "empty".) Even at this low energy state you still have some (even if its very small) energy that accumulat ...
Chapter 16 - "The Universe"
... stars with different surface temperatures. Note that the peak radiation of a cooler star is more toward the red part of the spectrum, and the peak radiation of a hotter star is more toward the blue part of the spectrum. ...
... stars with different surface temperatures. Note that the peak radiation of a cooler star is more toward the red part of the spectrum, and the peak radiation of a hotter star is more toward the blue part of the spectrum. ...
Constants and Equations
... please calculate the absolute magnitude of a Type Ia Supernova during its peak brightness. (5 pt.) 21) Assume a Type Ia Supernova is 163 Mly away from Earth, please calculate the brightest apparent magnitude of this supernova. 22) Please calculate the wavelength of Hα spectral line in nm. ...
... please calculate the absolute magnitude of a Type Ia Supernova during its peak brightness. (5 pt.) 21) Assume a Type Ia Supernova is 163 Mly away from Earth, please calculate the brightest apparent magnitude of this supernova. 22) Please calculate the wavelength of Hα spectral line in nm. ...
20 – N10/4/PHYSI/SP3/ENG/TZ0/XX Option E
... (iii) calculate the radius of Capella in terms of that of the Sun. ...
... (iii) calculate the radius of Capella in terms of that of the Sun. ...
File
... The light produced by stars reveals a vast amount of information about them and their place in the universe. 1. What is Light? Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. This means that it: a) Travels in waves (at the speed of light: 300,000 km/s) b) Does not need a medium for travel = can ...
... The light produced by stars reveals a vast amount of information about them and their place in the universe. 1. What is Light? Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. This means that it: a) Travels in waves (at the speed of light: 300,000 km/s) b) Does not need a medium for travel = can ...
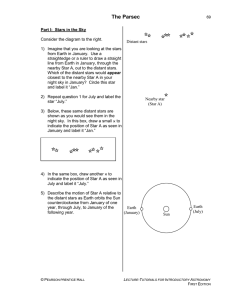
The Parsec
... 8) There is now a narrow triangle with the Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle allows us to calculate the distance to the s ...
... 8) There is now a narrow triangle with the Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle allows us to calculate the distance to the s ...
Background Information - Eu-Hou
... is B-V, which is simply an object’s magnitude as measured through the B filter, minus its magnitude as measured through the V filter. The luminosity of a star can be determined from its magnitude and distance. However, if you don’t know the distance to the star then you can’t find the luminosity. To ...
... is B-V, which is simply an object’s magnitude as measured through the B filter, minus its magnitude as measured through the V filter. The luminosity of a star can be determined from its magnitude and distance. However, if you don’t know the distance to the star then you can’t find the luminosity. To ...
User`s Guide to the Sky Notes
... Flux – The measure of the light energy from a star that hits one square meter in one second. Flux is converted back to the mv scale for consistency with charts dating back to the time of Hipparchus The apparent visual magnitude scale has limitations, so there has been a need to supplement it by: 1. ...
... Flux – The measure of the light energy from a star that hits one square meter in one second. Flux is converted back to the mv scale for consistency with charts dating back to the time of Hipparchus The apparent visual magnitude scale has limitations, so there has been a need to supplement it by: 1. ...
Exploring the Stars in Orion – Light Year Madness!
... Next to the Big Dipper (Ursa Major) and Scorpius, the Orion is the most widely recognized of all the 89 constellations in the sky. It is also one of the oldest known to humans. The Ancient Egyptians called it Osiris as long ago as 2000 BC! The brilliant stars that make up this rectangular star patte ...
... Next to the Big Dipper (Ursa Major) and Scorpius, the Orion is the most widely recognized of all the 89 constellations in the sky. It is also one of the oldest known to humans. The Ancient Egyptians called it Osiris as long ago as 2000 BC! The brilliant stars that make up this rectangular star patte ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 19. (1 pt.) If a star the size of the sun collapses to form a white dwarf the size of Earth, by what factor will its density increase? (The volume of a sphere is 43 r 3 . See Appendix A for the radii of the sun and Earth.) ...
... 19. (1 pt.) If a star the size of the sun collapses to form a white dwarf the size of Earth, by what factor will its density increase? (The volume of a sphere is 43 r 3 . See Appendix A for the radii of the sun and Earth.) ...
HR Diagram
... tell not only the temperature of a star by its spectra, but also whether it was an average star (called mainsequence), a giant, or a white dwarf. Several classifications of stars were identified from the H-R diagram, called luminosity classes. They were given a designation as follows: Ia Ib II III I ...
... tell not only the temperature of a star by its spectra, but also whether it was an average star (called mainsequence), a giant, or a white dwarf. Several classifications of stars were identified from the H-R diagram, called luminosity classes. They were given a designation as follows: Ia Ib II III I ...
2 Inch Universe Analogies
... QUESTION: If Milky Way is 2-inches big, what is the distance between these two galaxies? ...
... QUESTION: If Milky Way is 2-inches big, what is the distance between these two galaxies? ...
Stars and Galaxies Review
... they are deeper in the photosphere. they are cooler than the surrounding part of the photosphere. they are dead parts of the Sun. they are warmer than the surrounding part of the photosphere. ...
... they are deeper in the photosphere. they are cooler than the surrounding part of the photosphere. they are dead parts of the Sun. they are warmer than the surrounding part of the photosphere. ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.