No Slide Title
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsyst = - qsurr. Since the combustion process occurs under conditions of constant volume, q = E, the change in internal energy. Example: 1.412 g of carbon (M = 12.01 g/mol) are burned in ...
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsyst = - qsurr. Since the combustion process occurs under conditions of constant volume, q = E, the change in internal energy. Example: 1.412 g of carbon (M = 12.01 g/mol) are burned in ...
unit ii chemical thermodynamics
... • The physical or chemical changes which proceed by themselves without the intervention of any external agents are known as spontaneous process. • All natural process are spontaneous. • All spontaneous process proceed in one direction and are thermodynamically irreversible. • Examples: Heat flow f ...
... • The physical or chemical changes which proceed by themselves without the intervention of any external agents are known as spontaneous process. • All natural process are spontaneous. • All spontaneous process proceed in one direction and are thermodynamically irreversible. • Examples: Heat flow f ...
Chapter 9 Partial Differential Equations
... We begin by seeking solutions u which are subject to Dirichlet boundary conditions of the form u |x,y ∈ ∂R = g(x, y), where ∂R denotes the boundary of the region R and g(x, y) is a given function of x and y to be evaluated at points on the boundary. The general technique for obtaining the numerical ...
... We begin by seeking solutions u which are subject to Dirichlet boundary conditions of the form u |x,y ∈ ∂R = g(x, y), where ∂R denotes the boundary of the region R and g(x, y) is a given function of x and y to be evaluated at points on the boundary. The general technique for obtaining the numerical ...
chapter10-bur.320702..
... Energy is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. In principal any kind of energy can be converted into an equivalent amount of work or heat. We divide energy into two general types: kinetic energy (due to motion in a particular direction) EK = 1/2 mv2 potential energy (due to position or composit ...
... Energy is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. In principal any kind of energy can be converted into an equivalent amount of work or heat. We divide energy into two general types: kinetic energy (due to motion in a particular direction) EK = 1/2 mv2 potential energy (due to position or composit ...
File
... 2. The conditions in which ΔG is always positive is when ΔH is _________________ and ΔS is _________________. 3. When the situation is indeterminate, a low temperature favors the ( entropy / enthalpy ) factor, and a high temperature favors the ( entropy / enthalpy ) factor. Answer Problems 4-6 with ...
... 2. The conditions in which ΔG is always positive is when ΔH is _________________ and ΔS is _________________. 3. When the situation is indeterminate, a low temperature favors the ( entropy / enthalpy ) factor, and a high temperature favors the ( entropy / enthalpy ) factor. Answer Problems 4-6 with ...
IC2414251429
... to initiate the cooling mechanism. e. The sensor keeps recording the values and if the temperature values reach lower limit set (here 45.5 oc) the relay is de-powered. f. So the fan and motor are turned off, this is done in order to save power. g. The readings of temperature are still monitored and ...
... to initiate the cooling mechanism. e. The sensor keeps recording the values and if the temperature values reach lower limit set (here 45.5 oc) the relay is de-powered. f. So the fan and motor are turned off, this is done in order to save power. g. The readings of temperature are still monitored and ...
variable specific heat theory
... metre (cubic metre at NTP i.e ., 760 mm of Hg pressure and 0 K temperature) by 1 K. Thus, volumetric specific heat is expressed as kJ/NTP m3/K. When a body is heated, the energy transferred to it as heat, is used in two w ays: (i) in increasing the internal energy of the body, i.e ., to speed up the ...
... metre (cubic metre at NTP i.e ., 760 mm of Hg pressure and 0 K temperature) by 1 K. Thus, volumetric specific heat is expressed as kJ/NTP m3/K. When a body is heated, the energy transferred to it as heat, is used in two w ays: (i) in increasing the internal energy of the body, i.e ., to speed up the ...
Chapter 15 PPT
... Thermodynamics is the study of the changes in energy and transfers of energy that accompany chemical and physical processes. In this chapter we will address 3 fundamental questions. Will two (or more) substances react when they are mixed under specified conditions? If they do react, what energy chan ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of the changes in energy and transfers of energy that accompany chemical and physical processes. In this chapter we will address 3 fundamental questions. Will two (or more) substances react when they are mixed under specified conditions? If they do react, what energy chan ...
File
... (e) Flow of water from a hill to the ground. (f) Mixing of gases. In all the above cases, the system reaches a state of greater disorder. Eventhough the energy of the system increases (endothermic) during the above changes the processes are spontaneous because they are accompanied with increase in e ...
... (e) Flow of water from a hill to the ground. (f) Mixing of gases. In all the above cases, the system reaches a state of greater disorder. Eventhough the energy of the system increases (endothermic) during the above changes the processes are spontaneous because they are accompanied with increase in e ...
Thermodynamic Units and Properties
... Introduction The operator is provided with information that is displayed using various units of measurement. The operator must be able to convert between these units of measurement to ensure that the plant is operating within established limits. Instrument readings may provide information in units t ...
... Introduction The operator is provided with information that is displayed using various units of measurement. The operator must be able to convert between these units of measurement to ensure that the plant is operating within established limits. Instrument readings may provide information in units t ...
Entropy in chemical thermodynamics
... The second law can also be used to predict whether a physical process will proceed spontaneously. Spontaneous changes in isolated systems occur with an increase in entropy. Correspondence The statistical definition of entropy matches up with the thermodynamic formula for calculating entropy, because ...
... The second law can also be used to predict whether a physical process will proceed spontaneously. Spontaneous changes in isolated systems occur with an increase in entropy. Correspondence The statistical definition of entropy matches up with the thermodynamic formula for calculating entropy, because ...
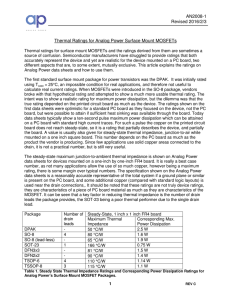
Thermal Ratings of Surface Mount Packages
... Thermal ratings for surface mount MOSFETs and the ratings derived from them are sometimes a source of confusion. Semiconductor manufacturers have struggled to provide ratings that both accurately represent the device and yet are realistic for the device mounted on a PC board, two different aspects t ...
... Thermal ratings for surface mount MOSFETs and the ratings derived from them are sometimes a source of confusion. Semiconductor manufacturers have struggled to provide ratings that both accurately represent the device and yet are realistic for the device mounted on a PC board, two different aspects t ...
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
... introduces the lever rule as a basic material balance tool. Many programs probably cover some of that material in the Materials and Energy Balances course but the topics are central to subsequent discussions so that a separate chapter is justified. Chapter 9 extends the fundamental relationships, whi ...
... introduces the lever rule as a basic material balance tool. Many programs probably cover some of that material in the Materials and Energy Balances course but the topics are central to subsequent discussions so that a separate chapter is justified. Chapter 9 extends the fundamental relationships, whi ...
Chapter 6 Thermochem 110 F11 IP
... PROBLEM: You place 50.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter at 25.00oC and carefully add 25.0 mL of 0.500 M HCl, also at 25.00oC. After stirring, the final temperature is 27.21oC. Calculate qsoln (in J) and ΔHrxn (in kJ/mol). (Assume the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes a ...
... PROBLEM: You place 50.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter at 25.00oC and carefully add 25.0 mL of 0.500 M HCl, also at 25.00oC. After stirring, the final temperature is 27.21oC. Calculate qsoln (in J) and ΔHrxn (in kJ/mol). (Assume the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes a ...
Chapter 10
... State functions are properties that are determined by the state of the system, regardless of how that condition was achieved. ...
... State functions are properties that are determined by the state of the system, regardless of how that condition was achieved. ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.