Chapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Units, and Definitions
... In order to gain an intuitive appreciation for the relative magnitudes of the different forms of energy we consider the (tongue-in-cheek) example of an attempt to cook a turkey by potential energy. The turkey is brought to the top of a 100 m building (about 30 stories) and then dropped from the ledg ...
... In order to gain an intuitive appreciation for the relative magnitudes of the different forms of energy we consider the (tongue-in-cheek) example of an attempt to cook a turkey by potential energy. The turkey is brought to the top of a 100 m building (about 30 stories) and then dropped from the ledg ...
Chapter 4 - The First Law of Thermodynamics and Energy Transport
... thinks of is called bilateral symmetry, when two halves of a whole are each other’s mirror images (bilateral symmetry is also called mirror symmetry). For example, a butterfly has bilateral symmetry. Emmy Noether was talking about symmetry with respect to a mathematical operation. We say that someth ...
... thinks of is called bilateral symmetry, when two halves of a whole are each other’s mirror images (bilateral symmetry is also called mirror symmetry). For example, a butterfly has bilateral symmetry. Emmy Noether was talking about symmetry with respect to a mathematical operation. We say that someth ...
Crystal Defect, Non-stoichiometry, and Solid Solution
... Driving force of defect: Increase of entropy of the material. ...
... Driving force of defect: Increase of entropy of the material. ...
chemistry — released items - North Carolina Public Schools
... Infer the type of bond and chemical formula formed between atoms. ...
... Infer the type of bond and chemical formula formed between atoms. ...
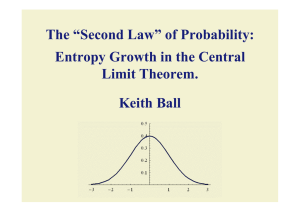
The “Second Law” of Probability: Entropy Growth in the Central Limit
... Is it true that Ent(Sn) increases with n? Shannon-Stam shows that it increases as n goes from 1 to 2 (hence 2 to 4 and so on). Carlen and Soffer found uniform estimates for entropy jump from 1 to 2. It wasn’t known that entropy increases from 2 to 3. The difficulty is that you can't express the sum ...
... Is it true that Ent(Sn) increases with n? Shannon-Stam shows that it increases as n goes from 1 to 2 (hence 2 to 4 and so on). Carlen and Soffer found uniform estimates for entropy jump from 1 to 2. It wasn’t known that entropy increases from 2 to 3. The difficulty is that you can't express the sum ...
ENERGY MANAGEMENT
... Energy consumption for the production of one tonne of steel is about 20 to 25 GJ/t of steel. Energy consumption has decreased due to the introduction of oxygen converters, continuous casting and economic pressure associated with the rise in global energy prices. In 1965, energy consumption was about ...
... Energy consumption for the production of one tonne of steel is about 20 to 25 GJ/t of steel. Energy consumption has decreased due to the introduction of oxygen converters, continuous casting and economic pressure associated with the rise in global energy prices. In 1965, energy consumption was about ...
Table 8.5. Calculation of initial energy
... plane and the yield decreases (Fig.8.5. б, point 1). The measurements corresponding to the plane channeling are marked (in angular coordinates) on a reaper square. Then, at a constant angle (), the scanning with a step is made, and the back scattering minimal yields being marked (Points 2 and 3) ...
... plane and the yield decreases (Fig.8.5. б, point 1). The measurements corresponding to the plane channeling are marked (in angular coordinates) on a reaper square. Then, at a constant angle (), the scanning with a step is made, and the back scattering minimal yields being marked (Points 2 and 3) ...
Energy dependence of the effective mass in the envelope
... concerning the well and barrier effective masses can be gathered at the energy of the transmission maximum. By varying the central well width and considering several transmission maxima, this study can be accomplished across a wide energy range, which is the procedure used in this paper. One of the ...
... concerning the well and barrier effective masses can be gathered at the energy of the transmission maximum. By varying the central well width and considering several transmission maxima, this study can be accomplished across a wide energy range, which is the procedure used in this paper. One of the ...
A Review on Semiconductors Including Applications and
... In 1839, A. E. Becquerel reported observation of a voltage between a solid and a liquid electrolyte when struck by light, the photovoltaic effect. In 1873 Willoughby Smith observed that selenium resistors exhibit decreasing resistance when light falls on them. In 1874 Karl Ferdinand Braun observed ...
... In 1839, A. E. Becquerel reported observation of a voltage between a solid and a liquid electrolyte when struck by light, the photovoltaic effect. In 1873 Willoughby Smith observed that selenium resistors exhibit decreasing resistance when light falls on them. In 1874 Karl Ferdinand Braun observed ...
Chapter 8: Magnetic and Electrical Properties 1
... is too small to sustain the multidomain structure. Thus the particle behaves as one large paramagnetic ion. ...
... is too small to sustain the multidomain structure. Thus the particle behaves as one large paramagnetic ion. ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.