Document
... Pour a liter of water at 40 degrees C into a liter of water at 20 degrees C and the final temperature of the two becomes A) less than 30 degrees C. B) at or about 30 degrees C. C) more than 30 degrees C. ...
... Pour a liter of water at 40 degrees C into a liter of water at 20 degrees C and the final temperature of the two becomes A) less than 30 degrees C. B) at or about 30 degrees C. C) more than 30 degrees C. ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics (Part II) Examples Sheet 1
... 13. Consider an ideal classical gas of volume V and temperature T , consisting of N indistinguishable particles in the extreme relativistic limit where the energy ϵ and momentum p of a particle are related by ϵ = cp, where c is the speed of light. ...
... 13. Consider an ideal classical gas of volume V and temperature T , consisting of N indistinguishable particles in the extreme relativistic limit where the energy ϵ and momentum p of a particle are related by ϵ = cp, where c is the speed of light. ...
Topics covered in PH112 - Rose
... Newton’s second law in angular form Work and rotational kinetic energy Rolling bodies, KE in terms of center of mass Angular momentum of a system of particles, and of a rigid body Conservation of angular momentum Simple harmonic motion: frequency, period, amplitude, angular frequency, wave number, p ...
... Newton’s second law in angular form Work and rotational kinetic energy Rolling bodies, KE in terms of center of mass Angular momentum of a system of particles, and of a rigid body Conservation of angular momentum Simple harmonic motion: frequency, period, amplitude, angular frequency, wave number, p ...
Themodynamic notes section 6.1
... • The entropy of a system not in thermal equilibrium will increase. • The entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the system approaches absolute zero. ...
... • The entropy of a system not in thermal equilibrium will increase. • The entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the system approaches absolute zero. ...
Exam 3 Answer Key
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
Section 1: Temperature and Heat Temperature A measure of the
... Transfer of energy between objects that are different temps. Always flows from higher temp lower temp SI unit: joules (J) Factors Affecting Heat How much heat an object absorbs or loses Mass of object Temperature change of object final temp- initial temp If there is not change, no heat flow ...
... Transfer of energy between objects that are different temps. Always flows from higher temp lower temp SI unit: joules (J) Factors Affecting Heat How much heat an object absorbs or loses Mass of object Temperature change of object final temp- initial temp If there is not change, no heat flow ...
Test Specs - Blue Valley Schools
... frequency. 4. Analyze the trends of the periodic table based on electronegativity, electron configurations, ionization energy, and atomic radius. 5. Predict the electron configuration for an element based on the number of electrons. 6. Predict the electron configuration for an element based on the l ...
... frequency. 4. Analyze the trends of the periodic table based on electronegativity, electron configurations, ionization energy, and atomic radius. 5. Predict the electron configuration for an element based on the number of electrons. 6. Predict the electron configuration for an element based on the l ...
Chapter 7
... Particles (the electron) has wave like behavior (example: the emission spectrum) Our goals in the first part of this chapter is To describe light and particles in terms of energy and wavelength, apply DeBroglie’s relationship and the photoelectric effect To describe likely positions of where the ele ...
... Particles (the electron) has wave like behavior (example: the emission spectrum) Our goals in the first part of this chapter is To describe light and particles in terms of energy and wavelength, apply DeBroglie’s relationship and the photoelectric effect To describe likely positions of where the ele ...
Slide 1
... • To determine H value when p1 is 0 or 1, one need L’Hopital’s rule lim[u(x)/v(x)] as x approaches 0 equals lim[u’(x)/v’(x)] • Therefore, as p1 approaches 0, lim[p1ln(p1)] = lim[(1/x)/(-1/x2)] = 0 • The uncertainty is therefore 0 when either p1 or p2 is zero! • Under what value of p1 while H reaches ...
... • To determine H value when p1 is 0 or 1, one need L’Hopital’s rule lim[u(x)/v(x)] as x approaches 0 equals lim[u’(x)/v’(x)] • Therefore, as p1 approaches 0, lim[p1ln(p1)] = lim[(1/x)/(-1/x2)] = 0 • The uncertainty is therefore 0 when either p1 or p2 is zero! • Under what value of p1 while H reaches ...
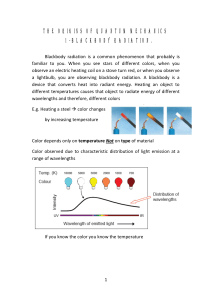
the origins of quantum mechanics 1
... 3. according to the principle of equipartition of energy an oscillator in thermal equilibrium with its environment should have an average energy equal to kT 4. We already found out that ( ...
... 3. according to the principle of equipartition of energy an oscillator in thermal equilibrium with its environment should have an average energy equal to kT 4. We already found out that ( ...
ap chemistry review – multiple choice
... (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. Explains the experimental phenomenon of e ...
... (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. Explains the experimental phenomenon of e ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.