Review of Engineering Thermodynamics - Part A
... temperature, but pressure and volume changed. There was no heat or work transfer, so the first law for this experiment is: 1Q2 ...
... temperature, but pressure and volume changed. There was no heat or work transfer, so the first law for this experiment is: 1Q2 ...
isuintroduction
... the subject, then dividing the product by the temperature and the universal gas constant. The universal gas constant is an ideal gas law. It is an equation that provides us with the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of an ideal gas. An ideal gas is a gas with atoms tha ...
... the subject, then dividing the product by the temperature and the universal gas constant. The universal gas constant is an ideal gas law. It is an equation that provides us with the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of an ideal gas. An ideal gas is a gas with atoms tha ...
Chapter 9 Canonical ensemble
... N1 = const, N2 = const, and E1 + E2 = E = const. Both systems are in thermal equilibrium at temperature T . The wall between them allows interchange of heat but not of particles. The system A1 may be any relatively small macroscopic system such as, for instance, a bottle of water in a lake, while th ...
... N1 = const, N2 = const, and E1 + E2 = E = const. Both systems are in thermal equilibrium at temperature T . The wall between them allows interchange of heat but not of particles. The system A1 may be any relatively small macroscopic system such as, for instance, a bottle of water in a lake, while th ...
Problem Set 5 - 2004
... (4) At low temperatures, the molar specific heat of diamond varies with temperature as: ...
... (4) At low temperatures, the molar specific heat of diamond varies with temperature as: ...
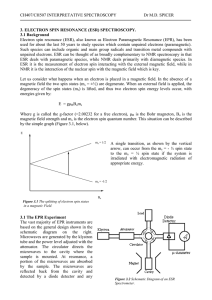
ESR Theory - Personal WWW Pages
... It should be noted that ESR is a remarkably sensitive technique. Samples with concentrations as low as 10-9 M can be detected in favourable cases. This is in contrast to NMR which ideally requires samples of at least 10-2 M. ESR is also versatile, in that a range of sample types can be studied. It i ...
... It should be noted that ESR is a remarkably sensitive technique. Samples with concentrations as low as 10-9 M can be detected in favourable cases. This is in contrast to NMR which ideally requires samples of at least 10-2 M. ESR is also versatile, in that a range of sample types can be studied. It i ...
Review E: Simple Harmonic Motion and Mechanical Energy
... g) What is mechanical energy of the spring-mass system as a function of time? Solutions: a) Choose the origin at the equilibrium position. Choose the positive x -direction to the right. Define x ( t ) to be the position of the mass with respect to the equilibrium position. ...
... g) What is mechanical energy of the spring-mass system as a function of time? Solutions: a) Choose the origin at the equilibrium position. Choose the positive x -direction to the right. Define x ( t ) to be the position of the mass with respect to the equilibrium position. ...
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
... If an ideal gas undergoes an isobaric process, which of the following statements is true? (a) The temperature of the gas doesn’t change. (b) Work is done on or by the gas. (c) No energy is transferred by heat to or from the gas. (d) The volume of the gas remains the same. (e) The pressure of the gas ...
... If an ideal gas undergoes an isobaric process, which of the following statements is true? (a) The temperature of the gas doesn’t change. (b) Work is done on or by the gas. (c) No energy is transferred by heat to or from the gas. (d) The volume of the gas remains the same. (e) The pressure of the gas ...
無投影片標題
... the instantaneous position and velocity of the particle are no longer deterministic. Thus, the electrons motion in solids must be analyzed by a probability theory. Quantum mechanics Newtonian mechanics Schrodinger’s equation: to describe the position probability of a particle. ...
... the instantaneous position and velocity of the particle are no longer deterministic. Thus, the electrons motion in solids must be analyzed by a probability theory. Quantum mechanics Newtonian mechanics Schrodinger’s equation: to describe the position probability of a particle. ...
Chapter 7 Covalent Bonding Outline Covalent Bonding Introduction
... • Na forms Na+ 1s22s22p63s1 1s22s22p6 • F forms F1s22s22p5 1s22s22p6 • Some atoms share electrons rather than ionize • Sharing results in atoms becoming isoelectronic with the nearest noble gas, as they do in forming ions ...
... • Na forms Na+ 1s22s22p63s1 1s22s22p6 • F forms F1s22s22p5 1s22s22p6 • Some atoms share electrons rather than ionize • Sharing results in atoms becoming isoelectronic with the nearest noble gas, as they do in forming ions ...
Document
... Macroscopic Properties of the System The properties of the system which arise from the bulk ...
... Macroscopic Properties of the System The properties of the system which arise from the bulk ...
Learning Goals - Issaquah Connect
... Name: _______________________________ Period: ____ Date: _____ ...
... Name: _______________________________ Period: ____ Date: _____ ...
Chapter 9
... a) Describe very briefly how you might have to generalize the work-energy theorem for a situation where you are pushing hard against a wall, the wall is not moving, yet you get tired! You’re definitely using up energy. Where did that energy come from and where did it go? Hint: Although you can give ...
... a) Describe very briefly how you might have to generalize the work-energy theorem for a situation where you are pushing hard against a wall, the wall is not moving, yet you get tired! You’re definitely using up energy. Where did that energy come from and where did it go? Hint: Although you can give ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.