Inorganic Analysis Methods - Armstrong State University
... • Neutron activation analysis measures the gamma-ray frequencies of specimens that have been bombarded with neutrons. • This method is highly sensitive and nondestructive analysis for simultaneously identifying and quantitating 20 to 30 trace elements. • Forensic analysis has employed neutron activa ...
... • Neutron activation analysis measures the gamma-ray frequencies of specimens that have been bombarded with neutrons. • This method is highly sensitive and nondestructive analysis for simultaneously identifying and quantitating 20 to 30 trace elements. • Forensic analysis has employed neutron activa ...
Document
... interplanar spacing, a0, can be approximated as being sinusoidal and we can write σ=σth sin (2πx/λ) ...
... interplanar spacing, a0, can be approximated as being sinusoidal and we can write σ=σth sin (2πx/λ) ...
dx cx dx and x - Cameron University
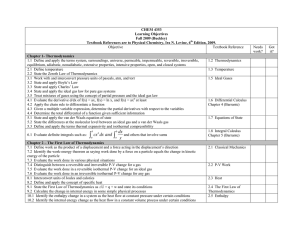
... 3.1 Work with and interconvert pressure units of pascals, atm, and torr 3.2 State and apply Boyle’s Law 3.3 State and apply Charles’ Law 3.4 State and apply the ideal gas law for pure gas systems 3.5 Treat mixtures of gases using the concept of partial pressure and the ideal gas law 4.1 Evaluate the ...
... 3.1 Work with and interconvert pressure units of pascals, atm, and torr 3.2 State and apply Boyle’s Law 3.3 State and apply Charles’ Law 3.4 State and apply the ideal gas law for pure gas systems 3.5 Treat mixtures of gases using the concept of partial pressure and the ideal gas law 4.1 Evaluate the ...
Electronic Structure - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Much information about Electronic Structure comes from spectroscopic evidence. ...
... Much information about Electronic Structure comes from spectroscopic evidence. ...
Lecture 2: Energy Balance - San Jose State University
... •What does temperature mean physically? Answer: statistical averaged speed of air molecules ...
... •What does temperature mean physically? Answer: statistical averaged speed of air molecules ...
Learning Outcomes
... Under certain circumstances electromagnetic radiation may be regarded as a stream of particles, rather than waves. These particles are known as photons. The energy (E) of radiation, and the energy associated with photons, is related to frequency by Planck’s constant (h) in the expressions: E = h ...
... Under certain circumstances electromagnetic radiation may be regarded as a stream of particles, rather than waves. These particles are known as photons. The energy (E) of radiation, and the energy associated with photons, is related to frequency by Planck’s constant (h) in the expressions: E = h ...
Document
... An amount of heat equal to 2500 J is added to a system, and 1800 J of work is done on the system. What is the change in internal energy of the system? A. ...
... An amount of heat equal to 2500 J is added to a system, and 1800 J of work is done on the system. What is the change in internal energy of the system? A. ...
Hartree-Fock Theory
... under the Born-Oppenheimer approximation: adiabatic surfaces. These are surfaces that can be achieved step by step from calculations developed. They may be significant changes in the characters of orbital obtained. According to an internuclear distance ionic or covalent change significantly. In the ...
... under the Born-Oppenheimer approximation: adiabatic surfaces. These are surfaces that can be achieved step by step from calculations developed. They may be significant changes in the characters of orbital obtained. According to an internuclear distance ionic or covalent change significantly. In the ...
Simple Harmonic Motion Forces in a Spring Energy Stored in a Spring
... Question: A block with a mass of 1.0 kg is released from rest on a frictionless incline. At the bottom of the incline, which is 1.8 m vertically below where the block started, the block slides across a horizontal frictionless surface before encountering a spring that has a spring constant of 100 N/m ...
... Question: A block with a mass of 1.0 kg is released from rest on a frictionless incline. At the bottom of the incline, which is 1.8 m vertically below where the block started, the block slides across a horizontal frictionless surface before encountering a spring that has a spring constant of 100 N/m ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... Another interpretation of the repulsive interactions can be as a direct consequence of the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that any two particles are excluded from having the same set of quantum numbers. Thus the rule forbids the electrons from occupying the same quantum state and electrons ...
... Another interpretation of the repulsive interactions can be as a direct consequence of the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that any two particles are excluded from having the same set of quantum numbers. Thus the rule forbids the electrons from occupying the same quantum state and electrons ...
Higher Revision Cards
... V = volume of gas, in metres cubed (m3) T = temperature of gas, in Kelvin (K) The mass is kept constant. K = °C + 273.15 At 0 K, or absolute zero, all particle motion stops. Particles have no energy, and this is the lowest possible temperature. The kinetic theory of gas states that pressure is cause ...
... V = volume of gas, in metres cubed (m3) T = temperature of gas, in Kelvin (K) The mass is kept constant. K = °C + 273.15 At 0 K, or absolute zero, all particle motion stops. Particles have no energy, and this is the lowest possible temperature. The kinetic theory of gas states that pressure is cause ...
Higher Revision Cards A4
... V = volume of gas, in metres cubed (m3) T = temperature of gas, in Kelvin (K) The mass is kept constant. K = °C + 273.15 At 0 K, or absolute zero, all particle motion stops. Particles have no energy, and this is the lowest possible temperature. The kinetic theory of gas states that pressure is cause ...
... V = volume of gas, in metres cubed (m3) T = temperature of gas, in Kelvin (K) The mass is kept constant. K = °C + 273.15 At 0 K, or absolute zero, all particle motion stops. Particles have no energy, and this is the lowest possible temperature. The kinetic theory of gas states that pressure is cause ...
The elastic potential energy
... Since there is no friction, the reaction between the ring and the wire is at any instant perpendicular to the wire, and therefore to the direction of motion of the ring. Hence this force does no work as the ring slides on the wire. Therefore, we may use the energy equation with the potential energy ...
... Since there is no friction, the reaction between the ring and the wire is at any instant perpendicular to the wire, and therefore to the direction of motion of the ring. Hence this force does no work as the ring slides on the wire. Therefore, we may use the energy equation with the potential energy ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.