Lecture 15: The Brain
... Now review the following structures which you should have seen previously and learn the flow of CSF through the brain. 1. The lateral ventricles (largest in the brain) are separated by the spetum pelucidum and are found in the cerebral hemispheres, just inferior to the corpus callosum. 2. The late ...
... Now review the following structures which you should have seen previously and learn the flow of CSF through the brain. 1. The lateral ventricles (largest in the brain) are separated by the spetum pelucidum and are found in the cerebral hemispheres, just inferior to the corpus callosum. 2. The late ...
Brain Development Infancy and Early Childhood Phyllis L
... Synaptogenisis Dendrites As dendrite branches multiply, they provide an increasing surface area for (synaptic terminals) from other neurons. The larger the number of neuronal connections, the higher the possibilities for neural, and therefore, cognitive activity Axons Variety of lengths, depending ...
... Synaptogenisis Dendrites As dendrite branches multiply, they provide an increasing surface area for (synaptic terminals) from other neurons. The larger the number of neuronal connections, the higher the possibilities for neural, and therefore, cognitive activity Axons Variety of lengths, depending ...
PSYCH-UNIT-2-0 -NOTES-BIO-INTRO
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
Neurons, Hormones, and the Brain
... Central Nervous System= 2 parts • Brain and spinal cord • Spinal cord- Extension of the brain • Runs from the base of the brain down the center of the back • Protected by a column of bones, spinal ...
... Central Nervous System= 2 parts • Brain and spinal cord • Spinal cord- Extension of the brain • Runs from the base of the brain down the center of the back • Protected by a column of bones, spinal ...
The Nervous System
... (CNS)/ Brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Ø Bundles of nerve fibers or axons that conduct information to and from the central nervous system Ø Includes sensory neurons and motor neurons ...
... (CNS)/ Brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Ø Bundles of nerve fibers or axons that conduct information to and from the central nervous system Ø Includes sensory neurons and motor neurons ...
document
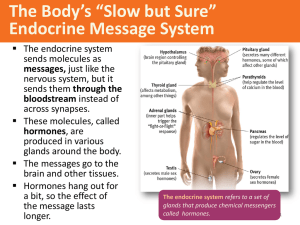
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
Brain Imaging for Fun and Profit Presentation
... ‣ Radiologists perform qualitative “lightbox” reads. ‣ Most psychiatric and neurological disorders are invisible to reading radiologists. ...
... ‣ Radiologists perform qualitative “lightbox” reads. ‣ Most psychiatric and neurological disorders are invisible to reading radiologists. ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn’t” -Emerson Pugh, The Biological Origin of Human Values (1977) ...
... understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn’t” -Emerson Pugh, The Biological Origin of Human Values (1977) ...
Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... 2. B: The transfer of a message from one neuron to another occurs by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters into the spaces called synapses between the neurons. The axon is the long threadlike fiber that transmits the message. 3. A: The “reward” system is part of the limbic system, which gets ...
... 2. B: The transfer of a message from one neuron to another occurs by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters into the spaces called synapses between the neurons. The axon is the long threadlike fiber that transmits the message. 3. A: The “reward” system is part of the limbic system, which gets ...
Brain Anatomy and Function p. 95
... because it is the basis for understanding treatment of mental disorders with psychotropic drugs. Human consciousness, behavior, learning, memory, emotion, and creativity are all the result of physiological brain functions. Neurotransmission is the communication between neurons conducted by neurotran ...
... because it is the basis for understanding treatment of mental disorders with psychotropic drugs. Human consciousness, behavior, learning, memory, emotion, and creativity are all the result of physiological brain functions. Neurotransmission is the communication between neurons conducted by neurotran ...
Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... 2. B: The transfer of a message from one neuron to another occurs by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters into the spaces called synapses between the neurons. The axon is the long threadlike fiber that transmits the message. 3. A: The “reward” system is part of the limbic system, which gets ...
... 2. B: The transfer of a message from one neuron to another occurs by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters into the spaces called synapses between the neurons. The axon is the long threadlike fiber that transmits the message. 3. A: The “reward” system is part of the limbic system, which gets ...
Emotional Wiring Different in Men and Women
... For women, the cluster communicates with brain regions that help them respond to sensors inside the body, such as the insular cortex and hypothalamus. These areas tune in to and regulate women's hormones, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion and respiration. "Throughout evolution, women have had to ...
... For women, the cluster communicates with brain regions that help them respond to sensors inside the body, such as the insular cortex and hypothalamus. These areas tune in to and regulate women's hormones, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion and respiration. "Throughout evolution, women have had to ...
Introduction to Cognitive Development 2012
... – Anthropology: to help separate characteristics of the mind from characteristics of culture – Researchers often collaborate and/or work across these disciplines 6. Note that cognitive psychology refers to theories of information processing and involve experiments with behavioral data (i.e. how peop ...
... – Anthropology: to help separate characteristics of the mind from characteristics of culture – Researchers often collaborate and/or work across these disciplines 6. Note that cognitive psychology refers to theories of information processing and involve experiments with behavioral data (i.e. how peop ...
Brain Plasticity-
... the process by which that knowledge is retained over time.” The capacity of the brain to change with learning is plasticity. So how does the brain change with learning? According to Durbach (2000), there appear to be at least two types of modifications that occur in the brain with learning: 1. A cha ...
... the process by which that knowledge is retained over time.” The capacity of the brain to change with learning is plasticity. So how does the brain change with learning? According to Durbach (2000), there appear to be at least two types of modifications that occur in the brain with learning: 1. A cha ...
Cerebrum Renatus Conference (3)
... that this idea of the ‘valvules’ would explain involuntary movement—stimuli would present themselves on the skin, which would in turn pull on the strands connecting to the valvules, which then in turn control the release of animal spirits, which would cause some muscular activity. However, for volun ...
... that this idea of the ‘valvules’ would explain involuntary movement—stimuli would present themselves on the skin, which would in turn pull on the strands connecting to the valvules, which then in turn control the release of animal spirits, which would cause some muscular activity. However, for volun ...
Neuronal Growth In The Brain May Explain Phantom Limb Syndrome
... The nerve endings in the hand, arm, face and other parts of the body are connected to the brain through the spinal cord. Sensory information from each part of the body is localized in specific areas of the brainstem, thalamus and cortex. These areas show up much more clearly in the cortex of monkey ...
... The nerve endings in the hand, arm, face and other parts of the body are connected to the brain through the spinal cord. Sensory information from each part of the body is localized in specific areas of the brainstem, thalamus and cortex. These areas show up much more clearly in the cortex of monkey ...
Chapter 3 Class Notes / Biological Foundations
... Neurons do not actually touch each other to send their messages along a neural pathway. The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the ...
... Neurons do not actually touch each other to send their messages along a neural pathway. The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the ...
Histology Laboratories Molecules to Systems
... Normal Brain Compared to Brain from Parkinson’s Patient, H&E Which section is from the normal brain and why do you conclude this? ...
... Normal Brain Compared to Brain from Parkinson’s Patient, H&E Which section is from the normal brain and why do you conclude this? ...
Notes Module #1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... Wernicke’s Area Works to help us understand language. Located in left, temporal lobe. If it’s damaged, ...
... Wernicke’s Area Works to help us understand language. Located in left, temporal lobe. If it’s damaged, ...
The Brain - Wando High School
... Central Nervous System- made up of the brain and spinal cord. --Spinal Cord: can act as a brain itself activating nerve impulses before we know it. (reflex) ...
... Central Nervous System- made up of the brain and spinal cord. --Spinal Cord: can act as a brain itself activating nerve impulses before we know it. (reflex) ...
1. Receptor cells
... partly the results of how our sensory systems are programmed and partly the result of what we are exposed to. ...
... partly the results of how our sensory systems are programmed and partly the result of what we are exposed to. ...
Read the perspective by Temel and Jahanshahi here.
... fell into disuse with the rise of drugs targeting the central nervous system. An increased understanding of the neuronal function was the determining factor for the successful application of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with Parkinson’s disease. In contrast to earlie ...
... fell into disuse with the rise of drugs targeting the central nervous system. An increased understanding of the neuronal function was the determining factor for the successful application of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with Parkinson’s disease. In contrast to earlie ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers
... • Their littermate twins are group-housed in cages with toys, which are changed frequently • Richer environments led to heavier, thicker brains, more synapses, and better learning ...
... • Their littermate twins are group-housed in cages with toys, which are changed frequently • Richer environments led to heavier, thicker brains, more synapses, and better learning ...
Chapter 3 - Victoria College
... INTRODUCTION • Brain = center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action • Center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory ...
... INTRODUCTION • Brain = center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action • Center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory ...