nervous system outline PPT
... Directs the functions of all human body systems – 100 Billion Nerve cells ...
... Directs the functions of all human body systems – 100 Billion Nerve cells ...
Chapter 15 - Austin Community College
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
Exercise and the Bra..
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
The CNS - Mr. Lesiuk
... The Cerebellum – “little brain” The cerebellum receives sensory input from eyes, ears, joints and muscles and receives motor input from the cerebral cortex. It integrates this information to maintain posture, coordination and ...
... The Cerebellum – “little brain” The cerebellum receives sensory input from eyes, ears, joints and muscles and receives motor input from the cerebral cortex. It integrates this information to maintain posture, coordination and ...
The Human Brain
... below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
... below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
Name: The nervous system Reference URL: http://faculty
... Go to: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/chmodel.html#string There are several ideas for making a model neuron or brain. Choose the model you wish to make. You will need to bring the materials you need (check out the requirements for each model). Your model must be completely labelled and you ne ...
... Go to: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/chmodel.html#string There are several ideas for making a model neuron or brain. Choose the model you wish to make. You will need to bring the materials you need (check out the requirements for each model). Your model must be completely labelled and you ne ...
The Brain Game: Adopted from Rod Plotnik: Table created by Mary
... 14. Philip—Dopamine—seems to be the key transmitter of the pleasure system. 15. Grandma Mary—Broca’s Area—the part of the language system located in the frontal lobe (left hemisphere) is most important for producing speech. 16. The suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates our natural bi ...
... 14. Philip—Dopamine—seems to be the key transmitter of the pleasure system. 15. Grandma Mary—Broca’s Area—the part of the language system located in the frontal lobe (left hemisphere) is most important for producing speech. 16. The suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates our natural bi ...
Malleable vs. Fixed Intelligence
... “efficient” your brain--because brain signals have more paths to follow through your brain. Think about it this way: Looking at this map--is it easier to travel from Rio de Janeiro to London or from Rio de Janeiro to Chicago? Now imagine that the airplane=brain signal/thought, and Rio, Chicago, and ...
... “efficient” your brain--because brain signals have more paths to follow through your brain. Think about it this way: Looking at this map--is it easier to travel from Rio de Janeiro to London or from Rio de Janeiro to Chicago? Now imagine that the airplane=brain signal/thought, and Rio, Chicago, and ...
What is Psychology? - Weber State University
... How Neurons Communicate • Synapse: Site where a nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another; includes the axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and receptor sites on receiving cell. • Neurotransmitter: Chemical substance that is released by transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the act ...
... How Neurons Communicate • Synapse: Site where a nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another; includes the axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and receptor sites on receiving cell. • Neurotransmitter: Chemical substance that is released by transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the act ...
Unit 3A Notes
... you ready for action. 2. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. 6. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, we’re like robots. The brain is what makes us human ...
... you ready for action. 2. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. 6. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, we’re like robots. The brain is what makes us human ...
Part1
... Resting potential maintained by concentration differences of ions inside and outside of cell There are channels in membrane selective to different ions. Channels may be open or closed. ...
... Resting potential maintained by concentration differences of ions inside and outside of cell There are channels in membrane selective to different ions. Channels may be open or closed. ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... ‘synthetic physiology’ on these cells, controlling their state to assess how they contribute to organism or system-level functions. In summary, we have identified optogenetic proteins that act as molecular tools to make neurons controllable with pulses of colored light. We are now developing high-co ...
... ‘synthetic physiology’ on these cells, controlling their state to assess how they contribute to organism or system-level functions. In summary, we have identified optogenetic proteins that act as molecular tools to make neurons controllable with pulses of colored light. We are now developing high-co ...
The Biology of Mind take
... trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
The Biology of Mind take 2
... trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
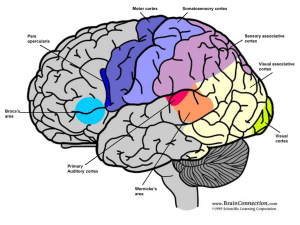
The Structures of the Brain
... • Pianists have larger than average auditory cortex (Bavelier et al 2001) • Deaf people have enhanced visual cortex (Pantev et al 1998) • Visual cortex in occipital lobe receives visual stimulus • Auditory areas in temporal lobe • Active during auditory hallucinations in schizophrenics ...
... • Pianists have larger than average auditory cortex (Bavelier et al 2001) • Deaf people have enhanced visual cortex (Pantev et al 1998) • Visual cortex in occipital lobe receives visual stimulus • Auditory areas in temporal lobe • Active during auditory hallucinations in schizophrenics ...
Unit 3B Study Guide
... 6. Define cerebral cortex. Name the four lobes that make up the cortex and state their locations. 7. Name the three functional divisions of the cortex and describe their functions. 8. Name and describe the role of the areas in the association cortex involved in understanding and producing language. ...
... 6. Define cerebral cortex. Name the four lobes that make up the cortex and state their locations. 7. Name the three functional divisions of the cortex and describe their functions. 8. Name and describe the role of the areas in the association cortex involved in understanding and producing language. ...
brain and spinal cord
... The human brain is the most complex system, natural or man made, in the world. About 3 lbs.; About the size of a grapefruit;Pinkish/gray in color; About 100 billion nerve cells; At a loss rate of 200,000 per day during our adult lives we still end up with over 98% of or brain cells. ...
... The human brain is the most complex system, natural or man made, in the world. About 3 lbs.; About the size of a grapefruit;Pinkish/gray in color; About 100 billion nerve cells; At a loss rate of 200,000 per day during our adult lives we still end up with over 98% of or brain cells. ...
The nervous system
... as a response to a sensory input. Many threads of research suggest that motor activity exists well before the maturation of the sensory systems, and senses only influence behavior without dictating it. This has brought the conception of the CNS as an autonomous system. ...
... as a response to a sensory input. Many threads of research suggest that motor activity exists well before the maturation of the sensory systems, and senses only influence behavior without dictating it. This has brought the conception of the CNS as an autonomous system. ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers
... The two hemispheres serve some different functions. How do we know about these differences? Brain damage studies revealed many functions of the left hemisphere. Brain scans and split brain studies show more about the functions of the two hemispheres, and how they coordinate with each other. ...
... The two hemispheres serve some different functions. How do we know about these differences? Brain damage studies revealed many functions of the left hemisphere. Brain scans and split brain studies show more about the functions of the two hemispheres, and how they coordinate with each other. ...
Chapter 2 - davis.k12.ut.us
... B) threshold. C) synapse. D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refrac ...
... B) threshold. C) synapse. D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refrac ...
A.1 Neural Development
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... 1. Split-Brain Studies. Split-brain (severed corpus callosum) data demonstrate that each hemisphere is superior in certain abilities. The left hemisphere controls spoken language, and the right controls recognition of faces and tasks dealing with spatial relations, such as drawing three-dimensional ...
... 1. Split-Brain Studies. Split-brain (severed corpus callosum) data demonstrate that each hemisphere is superior in certain abilities. The left hemisphere controls spoken language, and the right controls recognition of faces and tasks dealing with spatial relations, such as drawing three-dimensional ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.