lecture 02
... CT technique developed – when highly focused x-rays are passed through the body, the beam is affected in predictable ways by the relative density of the tissue – by passing a beam through the body at many different angles it becomes possible (using sophisticated math techniques) to re-construct an i ...
... CT technique developed – when highly focused x-rays are passed through the body, the beam is affected in predictable ways by the relative density of the tissue – by passing a beam through the body at many different angles it becomes possible (using sophisticated math techniques) to re-construct an i ...
2007 ANZSNP program and abstracts
... years, mean duration=41years) and age-matched controls (n=23) was assessed on a voxel level from SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) and magnetic resonance images respectively. Statistical analysis was performed using ‘SPM2’ software on a ‘Matlab version 7’ platform. Regional volume ...
... years, mean duration=41years) and age-matched controls (n=23) was assessed on a voxel level from SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) and magnetic resonance images respectively. Statistical analysis was performed using ‘SPM2’ software on a ‘Matlab version 7’ platform. Regional volume ...
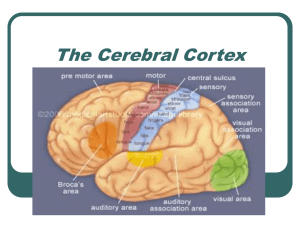
The Cerebral Cortex
... ¾ of the cerebral cortex is uncommitted to sensory or muscular activity Neurons in these association areas integrate information & therefore cannot be neatly mapped Found in all four lobes & increase in more intelligent animals. ...
... ¾ of the cerebral cortex is uncommitted to sensory or muscular activity Neurons in these association areas integrate information & therefore cannot be neatly mapped Found in all four lobes & increase in more intelligent animals. ...
The effect of neural synchronization on information transmission
... tuned to 16 orientations and projected nonspecifically to 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transiently synchronized responses. Because similarly tuned LNP ...
... tuned to 16 orientations and projected nonspecifically to 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transiently synchronized responses. Because similarly tuned LNP ...
T C N B
... Brain abnormalities in subjects with MR are very common. Postmortem studies have found brain abnormalities in 34 –98% of deceased, severely retarded patients [Curry et al., 1997]. Computerized tomography and structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies have reported abnormalities affecting a ...
... Brain abnormalities in subjects with MR are very common. Postmortem studies have found brain abnormalities in 34 –98% of deceased, severely retarded patients [Curry et al., 1997]. Computerized tomography and structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies have reported abnormalities affecting a ...
AGING PRESENTATION
... technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the structural changes in neurons as they lose their dendritic trees and spines with age. ...
... technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the structural changes in neurons as they lose their dendritic trees and spines with age. ...
The neuronal representation of information in the human brain
... related to the activations found in human imaging studies, which of course reflect the average activity of hundreds of thousands of neurons, so provide little evidence about how the information is encoded by the neurons. What are unique to humans are the findings on neuronal responses related to human ...
... related to the activations found in human imaging studies, which of course reflect the average activity of hundreds of thousands of neurons, so provide little evidence about how the information is encoded by the neurons. What are unique to humans are the findings on neuronal responses related to human ...
ch.6
... the brain’s central core, responsible for sensory and motor control and the processing of thinking and language ...
... the brain’s central core, responsible for sensory and motor control and the processing of thinking and language ...
Document
... 3.0 From ‘where’ to ‘what’: the functional roles of brain regions The major lobes: visible and hidden How to locate the prefrontal cortex: The frontal lobe lies anterior to the central sulcus. The two purple gyri (hills) immediately in front of the central sulcus are call the motor and premotor cort ...
... 3.0 From ‘where’ to ‘what’: the functional roles of brain regions The major lobes: visible and hidden How to locate the prefrontal cortex: The frontal lobe lies anterior to the central sulcus. The two purple gyri (hills) immediately in front of the central sulcus are call the motor and premotor cort ...
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems - Biology at Mott
... the limbic system and other parts of the brain including the sensory areas The limbic system is a ring of structures around the brainstem that includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe and helps store an emotional experience as an emot ...
... the limbic system and other parts of the brain including the sensory areas The limbic system is a ring of structures around the brainstem that includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe and helps store an emotional experience as an emot ...
100 Fascinating Facts You Never Knew About the
... responsible for your ability to read someone else’s face for clues to how they are feeling. 43. Ringing in the ears. For years, medical professionals believed that tinnitus was due to a function within the mechanics of the ear, but newer evidence shows that it is actually a function of the brain. 44 ...
... responsible for your ability to read someone else’s face for clues to how they are feeling. 43. Ringing in the ears. For years, medical professionals believed that tinnitus was due to a function within the mechanics of the ear, but newer evidence shows that it is actually a function of the brain. 44 ...
What is EEG? Elana Zion
... is, essentially, the sum of the electric field (in the direction perpendicular to the scalp) that is produced by a large population of neurons. The spatial resolution of a single electrode is in the order of one centimeter of the cortex, which contains hundreds of thousands of neurons. Particularly ...
... is, essentially, the sum of the electric field (in the direction perpendicular to the scalp) that is produced by a large population of neurons. The spatial resolution of a single electrode is in the order of one centimeter of the cortex, which contains hundreds of thousands of neurons. Particularly ...
Biological Neurons and Neural Networks, Artificial Neurons
... The human nervous system can be broken down into three stages that may be represented in block diagram form as: ...
... The human nervous system can be broken down into three stages that may be represented in block diagram form as: ...
Coherence a measure of the brain networks: past and present
... no information on directionality. Coherence is the most common measure used to determine if different areas of the brain are generating signals that are significantly correlated (coherent) or not significantly correlated (not coherent). Strictly speaking coherence is a statistic that is used to dete ...
... no information on directionality. Coherence is the most common measure used to determine if different areas of the brain are generating signals that are significantly correlated (coherent) or not significantly correlated (not coherent). Strictly speaking coherence is a statistic that is used to dete ...
What are brain and spinal cord cancers?
... It is possible to have a genetic predisposition to developing a tumour. This means that you may have a fault in your genes, passed down from your parents, that increases your risk. For example, some people have a genetic condition called neurofibromatosis which causes nerve tissue to grow tumours. ...
... It is possible to have a genetic predisposition to developing a tumour. This means that you may have a fault in your genes, passed down from your parents, that increases your risk. For example, some people have a genetic condition called neurofibromatosis which causes nerve tissue to grow tumours. ...
Component process model of memory
... CT technique developed – when highly focused x-rays are passed through the body, the beam is affected in predictable ways by the relative density of the tissue – by passing a beam through the body at many different angles it becomes possible (using sophisticated math techniques) to re-construct an i ...
... CT technique developed – when highly focused x-rays are passed through the body, the beam is affected in predictable ways by the relative density of the tissue – by passing a beam through the body at many different angles it becomes possible (using sophisticated math techniques) to re-construct an i ...
BRAINS OF NORWAY
... been describing in mathematics for millennia.” The appealing simplicity gives hope, he says, that the entire brain uses computational principles that scientists may eventually understand. That understanding could take a long time to reach. It seems unlikely that the neural codes that the brain uses ...
... been describing in mathematics for millennia.” The appealing simplicity gives hope, he says, that the entire brain uses computational principles that scientists may eventually understand. That understanding could take a long time to reach. It seems unlikely that the neural codes that the brain uses ...
ANATOMICAL TERMS
... diameter of the fibre and the presence or absence of myelin o Travel fast in the presence of myelin ...
... diameter of the fibre and the presence or absence of myelin o Travel fast in the presence of myelin ...
The Nervous System - Plain Local Schools
... • The most important functional part of the cerebrum is the cerebral cortex, which is an outer fringe of gray matter (contains nearly 75% of all the neuron cell bodies in the nervous system) • The cerebral cortex is divided into functional zones known as lobes ...
... • The most important functional part of the cerebrum is the cerebral cortex, which is an outer fringe of gray matter (contains nearly 75% of all the neuron cell bodies in the nervous system) • The cerebral cortex is divided into functional zones known as lobes ...
The outer layer of the cerebral cortex is divided into different areas
... modulation of auditory cortical activity by visual signals from moving lips (8) or from facial expressions (4) during speech perception. It is unlikely that multisensory neurons by themselves could account for all cross-modal effects without some feedback from the visual (or in some cases the audito ...
... modulation of auditory cortical activity by visual signals from moving lips (8) or from facial expressions (4) during speech perception. It is unlikely that multisensory neurons by themselves could account for all cross-modal effects without some feedback from the visual (or in some cases the audito ...
Hybrots - Computing Science and Mathematics
... animals, most of humans' and wild animals' inputs are the consequences of their recent actions. The same is true for the Neurally-controlled Animats. Imaging neural structure and function Using re-embodied cultured networks has some unique advantages when compared to in vivo research. It is a living ...
... animals, most of humans' and wild animals' inputs are the consequences of their recent actions. The same is true for the Neurally-controlled Animats. Imaging neural structure and function Using re-embodied cultured networks has some unique advantages when compared to in vivo research. It is a living ...
acetylcholine
... Although dopamine is synthesized by only several hundred thousand cells, it fulfils an exceedingly important role in the higher parts of the CNS. These dopaminergic neurons can be divided into three subgroups with different functions. The first group regulates movements: a deficit of dopamine in thi ...
... Although dopamine is synthesized by only several hundred thousand cells, it fulfils an exceedingly important role in the higher parts of the CNS. These dopaminergic neurons can be divided into three subgroups with different functions. The first group regulates movements: a deficit of dopamine in thi ...
Characterization of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)All of the ___________________ outside of the central nervous system. ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)All of the ___________________ outside of the central nervous system. ...
LESSON 1.2 WORKBOOK How does brain structure impact its function?
... _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ ____________________________ ...
... _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ ____________________________ ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.