Outline for CNS, PNS, and ANS
... M. precentral gyrus – convolution anterior to central sulcus N. postcentral gyrus – convolution posterior to central sulcus O. corpus callosum – largest commissure (connection) between the hemispheres. Allows them to communicate. P. primary motor area – controls voluntary muscle movements - located ...
... M. precentral gyrus – convolution anterior to central sulcus N. postcentral gyrus – convolution posterior to central sulcus O. corpus callosum – largest commissure (connection) between the hemispheres. Allows them to communicate. P. primary motor area – controls voluntary muscle movements - located ...
RFC_Cp_C_Wyart_def_EUK-v
... spinal cord to modulate movement. In the zebrafish, the researchers have shown that activation of these neurons triggers locomotion when the animal is at rest, and inhibits it when the animal is moving. These results offer hope that it will one day be possible to specifically stimulate these circuit ...
... spinal cord to modulate movement. In the zebrafish, the researchers have shown that activation of these neurons triggers locomotion when the animal is at rest, and inhibits it when the animal is moving. These results offer hope that it will one day be possible to specifically stimulate these circuit ...
MODULE 4: MOTOR AND SOMATOSENSORY PATHWAYS
... include upper versus lower motor neuron lesions, terms used to describe weakness, weakness patterns and localization, unsteady gait, multiple sclerosis, and motor neuron disease. The somatosensory systems’ anatomy in this module will include the main somatosensory pathways, posterior columns-medial ...
... include upper versus lower motor neuron lesions, terms used to describe weakness, weakness patterns and localization, unsteady gait, multiple sclerosis, and motor neuron disease. The somatosensory systems’ anatomy in this module will include the main somatosensory pathways, posterior columns-medial ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... The number of fibers in a motor unit varies according to function. Muscles that contribute to fine movements, like those acting on the eye or the fingers, usually have a small number of muscle fibers per motor unit. Example: a motor unit in the ocular muscles (of the eye) may have a membership of 3 ...
... The number of fibers in a motor unit varies according to function. Muscles that contribute to fine movements, like those acting on the eye or the fingers, usually have a small number of muscle fibers per motor unit. Example: a motor unit in the ocular muscles (of the eye) may have a membership of 3 ...
Ch6 - Unit3Biology
... • stimulate another neuron or effector • last for a very short time only (enzymes produced by muscles tissue inactive the substances for example) Example: acetycholine ...
... • stimulate another neuron or effector • last for a very short time only (enzymes produced by muscles tissue inactive the substances for example) Example: acetycholine ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... Kalaska found that activity in area 2 mostly reflected sensory feedback from the moving limb, rather than a planning-related signal, a view that is consistent with its receipt of muscle-spindle signals from area 3a. Therefore, these results suggest that area PPC is involved in planning the kinematic ...
... Kalaska found that activity in area 2 mostly reflected sensory feedback from the moving limb, rather than a planning-related signal, a view that is consistent with its receipt of muscle-spindle signals from area 3a. Therefore, these results suggest that area PPC is involved in planning the kinematic ...
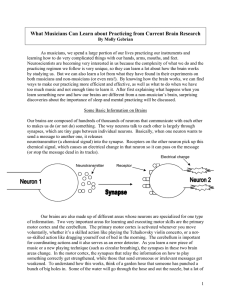
What Musicians can Learn about Practicing from Current Brain
... learning it wrong in the first place. The more times you do something wrong, whether or nor you know it’s not right, the stronger you make those messages and the weaker the correct message becomes. These changes are just the beginning, and since they occur on such a microscopic level, they are relat ...
... learning it wrong in the first place. The more times you do something wrong, whether or nor you know it’s not right, the stronger you make those messages and the weaker the correct message becomes. These changes are just the beginning, and since they occur on such a microscopic level, they are relat ...
Spinal Cord
... • Receives information from major motor pathways • Sends information to muscles • Does not contain clusters – are arranged in columns that run the length of the spinal cord ...
... • Receives information from major motor pathways • Sends information to muscles • Does not contain clusters – are arranged in columns that run the length of the spinal cord ...
CHAPTER 46 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
... 2. It is the last center receiving sensory input and carrying out integration to command motor responses. 3. The cerebrum carries out higher thought processes for learning and memory, language and speech. E. The Cerebral Hemispheres 1. The right and left cerebral hemispheres are connected by a bridg ...
... 2. It is the last center receiving sensory input and carrying out integration to command motor responses. 3. The cerebrum carries out higher thought processes for learning and memory, language and speech. E. The Cerebral Hemispheres 1. The right and left cerebral hemispheres are connected by a bridg ...
For Motor Outputs, as for Sensory Inputs, Spike Timing Carries More
... neuroscience is understanding the relationship between neural activity and the behavior it produces. In the study of neurons that control motor systems, that output has typically been quantified in terms of firing rate, measured as the number of spikes per unit time. By contrast, for sensory systems ...
... neuroscience is understanding the relationship between neural activity and the behavior it produces. In the study of neurons that control motor systems, that output has typically been quantified in terms of firing rate, measured as the number of spikes per unit time. By contrast, for sensory systems ...
Biopsychology and the Foundations of
... These two systems do not just work in cooperation during stressful situations like a car accident, but also in happier situations, such as when you earn an unexpected “A,” or “fall in love.” ...
... These two systems do not just work in cooperation during stressful situations like a car accident, but also in happier situations, such as when you earn an unexpected “A,” or “fall in love.” ...
Presentation
... These two systems do not just work in cooperation during stressful situations like a car accident, but also in happier situations, such as when you earn an unexpected “A,” or “fall in love.” ...
... These two systems do not just work in cooperation during stressful situations like a car accident, but also in happier situations, such as when you earn an unexpected “A,” or “fall in love.” ...
muscle strength testing gradation chart
... 3. Herniations at lumbar disk levels do not usually affect the nerve exiting directly at that level because of the angle and position of exit of these nerves as they exit directly beneath the pedicle they essentially escape injury by the HNP. The nerve level that is usually affected is one level low ...
... 3. Herniations at lumbar disk levels do not usually affect the nerve exiting directly at that level because of the angle and position of exit of these nerves as they exit directly beneath the pedicle they essentially escape injury by the HNP. The nerve level that is usually affected is one level low ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... motor control, memory, reasoning, and judgment. i. The left frontal lobe has Broca’s area for our ability to speak. 2) Parietal lobe—located behind the frontal lobe and involved with sensory reception and integration, and taste. 3) Temporal lobe—located laterally and receives information from our ea ...
... motor control, memory, reasoning, and judgment. i. The left frontal lobe has Broca’s area for our ability to speak. 2) Parietal lobe—located behind the frontal lobe and involved with sensory reception and integration, and taste. 3) Temporal lobe—located laterally and receives information from our ea ...
Human action recognition oriented to humanoid - CEUR
... technologies. Recently, robots has been used in more and more areas such as service robotics, field robotics, or human augmentation. By the dawn of the new millennium, the “human” factor pushes robots to rapidly assume anthropomorphic appearance and the more robots interact with people safer, smarte ...
... technologies. Recently, robots has been used in more and more areas such as service robotics, field robotics, or human augmentation. By the dawn of the new millennium, the “human” factor pushes robots to rapidly assume anthropomorphic appearance and the more robots interact with people safer, smarte ...
Brain Organizing Principles and Functions
... Disorders of Planning and Social Cognition • Caused by damage to prefrontal area – Disrupts executive control– processes that allow us to direct our own cognitive activities • e.g., setting priorities, planning, strategizing, ignoring distractors ...
... Disorders of Planning and Social Cognition • Caused by damage to prefrontal area – Disrupts executive control– processes that allow us to direct our own cognitive activities • e.g., setting priorities, planning, strategizing, ignoring distractors ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions Sympathetic and Parasympathetic have separate pathways Effectors may have dual innervation, that is they have input from both types of pathways Parasympathetic – “rest-and-repair” Sympathetic – “fight-or-flight” ...
... Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions Sympathetic and Parasympathetic have separate pathways Effectors may have dual innervation, that is they have input from both types of pathways Parasympathetic – “rest-and-repair” Sympathetic – “fight-or-flight” ...
Chapter 5
... Sleep Infants display a wide variety of behavioral states: regular and irregular sleep, drowsiness, alert inactivity, and crying. But it is sleep that is usually of greatest concern to parents. Part of the process of physical development includes changes in sleep patterns that bring the cycles of in ...
... Sleep Infants display a wide variety of behavioral states: regular and irregular sleep, drowsiness, alert inactivity, and crying. But it is sleep that is usually of greatest concern to parents. Part of the process of physical development includes changes in sleep patterns that bring the cycles of in ...
Skeletal System
... columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those consi ...
... columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those consi ...
Chapter 3
... gustatory and vision (but not smell) each have dedicated nuclei in thalamus. Not just relaying information: thalamic nuclei have reciprocal connections with cortex. Regulates level of awareness - damaged can lead to coma. ...
... gustatory and vision (but not smell) each have dedicated nuclei in thalamus. Not just relaying information: thalamic nuclei have reciprocal connections with cortex. Regulates level of awareness - damaged can lead to coma. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those consi ...
... columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those consi ...
Neural Correlates of Anticipation in Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia, and
... by piecing together several indirect lines of evidence. The most common forms of evidence to look at are: 1. Anatomy: It is fairly clear where sensory and motor information arrives at or departs from the central nervous system. Neurons that are only a few synapses away from a sensory or a motor neur ...
... by piecing together several indirect lines of evidence. The most common forms of evidence to look at are: 1. Anatomy: It is fairly clear where sensory and motor information arrives at or departs from the central nervous system. Neurons that are only a few synapses away from a sensory or a motor neur ...
Motor Areas of the Medial Wall: A Review of Their Location and
... anatomical divisions. Luppino et al. (1991) described two areas of the cingulate sulcus where intracortical microstimulation evoked body movements. Relatively low-intensity intracortical stimulation in the CMAd and CMAv (area 24d of Luppino et al., 1991) evoked movement of the fore- and hindlimbs in ...
... anatomical divisions. Luppino et al. (1991) described two areas of the cingulate sulcus where intracortical microstimulation evoked body movements. Relatively low-intensity intracortical stimulation in the CMAd and CMAv (area 24d of Luppino et al., 1991) evoked movement of the fore- and hindlimbs in ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... • basal nuclei • other deep nuclei • associated with sense of smell (less significant) Functions • controls emotions • produces feelings • interprets sensory impulses • facilitates memory storage and retrieval (learning!) ...
... • basal nuclei • other deep nuclei • associated with sense of smell (less significant) Functions • controls emotions • produces feelings • interprets sensory impulses • facilitates memory storage and retrieval (learning!) ...