Chapter 2
... Depolarization: sodium gates open; let sodium (+) in Repolarization: sodium gates close, potassium gates open and let potassium (+) out; potassium gates close when charge is leveled (back to -) Refractory period: time period in which the neuron ...
... Depolarization: sodium gates open; let sodium (+) in Repolarization: sodium gates close, potassium gates open and let potassium (+) out; potassium gates close when charge is leveled (back to -) Refractory period: time period in which the neuron ...
CHAPTER 3 3.1 The nervous system is the interacting network of
... theory examines the adaptive significance of human and animal behavior. Known for his conceptualization of evolutionary theory, Charles Darwin proposed natural selection as the mechanism through which changes in organisms’ appearance and behavior change over time. As evolutionary theory has taken ro ...
... theory examines the adaptive significance of human and animal behavior. Known for his conceptualization of evolutionary theory, Charles Darwin proposed natural selection as the mechanism through which changes in organisms’ appearance and behavior change over time. As evolutionary theory has taken ro ...
t1review
... 2. The relationship between the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and sensory neurons. 3. The relationship between the Central Nervous System (CNS) and interneurons. 4. The functions of Dendrites and Axons. 5. How the information is carried from the CNS to the body's tissues. 6. What is an under suppl ...
... 2. The relationship between the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and sensory neurons. 3. The relationship between the Central Nervous System (CNS) and interneurons. 4. The functions of Dendrites and Axons. 5. How the information is carried from the CNS to the body's tissues. 6. What is an under suppl ...
Psychology 300 Instructor: Sylvia S. Spencer Ph.D. TEST 1 REVIEW
... 2. The relationship between the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and sensory neurons. 3. The relationship between the Central Nervous System (CNS) and interneurons. 4. The functions of Dendrites and Axons. 5. How the information is carried from the CNS to the body's tissues. 6. What is an under suppl ...
... 2. The relationship between the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and sensory neurons. 3. The relationship between the Central Nervous System (CNS) and interneurons. 4. The functions of Dendrites and Axons. 5. How the information is carried from the CNS to the body's tissues. 6. What is an under suppl ...
057 Learning by Observation
... Answer the following questions in YOUR OWN WORDS. You only have to do TWO of the questions marked with asterisks *** ...
... Answer the following questions in YOUR OWN WORDS. You only have to do TWO of the questions marked with asterisks *** ...
Self-fulfilling Prophecy
... and almost anyone can be induced to cross it when pressured by situational forces.” ...
... and almost anyone can be induced to cross it when pressured by situational forces.” ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
brain drain answers
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
The Great Brain Drain Review - Reeths
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
The Great Brain Drain Review - Reeths
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
... VI. The more official name for a brain cell is a neuron The part that receives the message is called the dendrites and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Contains nuclei involved in a variety of behaviors The four f’s. Feeding, fleeing, fighting, and…mating. ◦ sexual behavior ◦ hunger, thirst ◦ sleep ◦ water and salt balance ◦ body temperature regulation ◦ circadian rhythms ◦ role in hormone secretion ...
... Contains nuclei involved in a variety of behaviors The four f’s. Feeding, fleeing, fighting, and…mating. ◦ sexual behavior ◦ hunger, thirst ◦ sleep ◦ water and salt balance ◦ body temperature regulation ◦ circadian rhythms ◦ role in hormone secretion ...
the brain - WordPress.com
... brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. Limbic System: The limbic ...
... brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. Limbic System: The limbic ...
comstock_daniel auditory_oddball_task
... Lobe during the experiment using a 64 sensor electrode net. ...
... Lobe during the experiment using a 64 sensor electrode net. ...
Introduction to the Brain
... Largest part of brain Controls higher mental functions Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres Surface layer of gray matter (neural cortex) ...
... Largest part of brain Controls higher mental functions Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres Surface layer of gray matter (neural cortex) ...
Document
... • visual info – Auditory cortex • auditory info – Somatosensory cortex • info from skin Association cortex – involved in complex cognitive tasks associating words with images • Broca’s area (aphasia) • Wernicke’s area (aphasia) ...
... • visual info – Auditory cortex • auditory info – Somatosensory cortex • info from skin Association cortex – involved in complex cognitive tasks associating words with images • Broca’s area (aphasia) • Wernicke’s area (aphasia) ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... In 1800, Franz Gall suggested that bumps of the skull represented mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
... In 1800, Franz Gall suggested that bumps of the skull represented mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
Brain Structure - Updated 14
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
Module 4 Notes
... areas can impair language functioning. The association areas are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. Rather, they interpret, integrate, and act on information processed by the sensory areas. They are involved in higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and sp ...
... areas can impair language functioning. The association areas are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. Rather, they interpret, integrate, and act on information processed by the sensory areas. They are involved in higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and sp ...
Neurons and the Brain
... Causes the feeling of being “revved up” or on edge Activates a “fight or flight” reaction in the autonomic nervous system ...
... Causes the feeling of being “revved up” or on edge Activates a “fight or flight” reaction in the autonomic nervous system ...
Theory of Reasoned Action and Theory of Planned Behavior
... What ISN’T in the Model Other factors such as the modifying factors in the HBM (demographics, etc.) are not directly addressed. They can have an indirect effect on the other components, but are not specifically incorporated into the model. ...
... What ISN’T in the Model Other factors such as the modifying factors in the HBM (demographics, etc.) are not directly addressed. They can have an indirect effect on the other components, but are not specifically incorporated into the model. ...
Slide ()
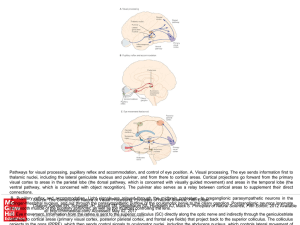
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...