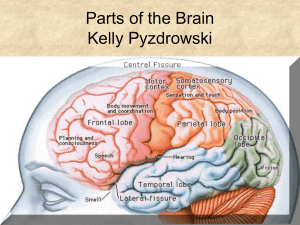
CNS
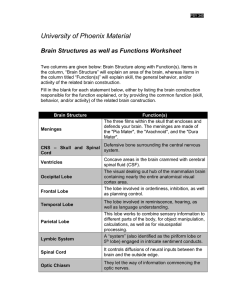
... to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocrine glands. • the midbrain is a short segment of the brainstem involved in hearing and visual reflexes. • the cerebellum is part of the hindbrain that controls muscle coordination, it contains 50% of ...
... to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocrine glands. • the midbrain is a short segment of the brainstem involved in hearing and visual reflexes. • the cerebellum is part of the hindbrain that controls muscle coordination, it contains 50% of ...
AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology
... 4. Brain Imaging Techniques a. Computed tomography (CT): takes X-ray photos to show brain damage. b. Positron emission tomography (PET): shows which part of the brain is active by showing the consumption of sugar glucose. c. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): gives a detailed picture of the brain’s s ...
... 4. Brain Imaging Techniques a. Computed tomography (CT): takes X-ray photos to show brain damage. b. Positron emission tomography (PET): shows which part of the brain is active by showing the consumption of sugar glucose. c. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): gives a detailed picture of the brain’s s ...
48.5, .6, .7
... produces cerebrospinal fluid from blood – Thalamus: main input center for sensory information going to the cerebrum and the main output center for motor information leaing the cerebrum; information from all senses is sorted in the thalamus – Hypothalamus: source of posterior pituitary and releasing ...
... produces cerebrospinal fluid from blood – Thalamus: main input center for sensory information going to the cerebrum and the main output center for motor information leaing the cerebrum; information from all senses is sorted in the thalamus – Hypothalamus: source of posterior pituitary and releasing ...
File
... environment (attack, escape, mate, or eat) These parts of the brain work together to ensure that we remember for a long time those events that are important and emotional!!! ...
... environment (attack, escape, mate, or eat) These parts of the brain work together to ensure that we remember for a long time those events that are important and emotional!!! ...
Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
... _______ 21. the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands. _______ 22. neurotransmitter that helps control alertness and arousal. _______ 23. neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning and memory. _____ ...
... _______ 21. the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands. _______ 22. neurotransmitter that helps control alertness and arousal. _______ 23. neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning and memory. _____ ...
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter. White matter consists of glial cells and myelinated axons. It does not contain the cell bodies of neurons and acts as a signal pathway for the gray matter regions of the central nervous system. Gray matter consists of glial cells and un ...
... 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter. White matter consists of glial cells and myelinated axons. It does not contain the cell bodies of neurons and acts as a signal pathway for the gray matter regions of the central nervous system. Gray matter consists of glial cells and un ...
6th Study Guide D1w:ans
... 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that is sensitive to color. 7. The type of nerve cells that allows you to see, hear, and smell are sensory receptors. 8. The layer of light receptors at the back of the eye is called the retina. 9. Th ...
... 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that is sensitive to color. 7. The type of nerve cells that allows you to see, hear, and smell are sensory receptors. 8. The layer of light receptors at the back of the eye is called the retina. 9. Th ...
Evolution2
... Modern Homo Sapiens emerged 35,000 years ago Evolution of Hominid Brains Humans only surviving hominid Cortical asymmetry: Brain specializations evolved to support the ability for language such as Wernickes and Brocas area Why is Brain Size Important? All organs and systems of the body confr ...
... Modern Homo Sapiens emerged 35,000 years ago Evolution of Hominid Brains Humans only surviving hominid Cortical asymmetry: Brain specializations evolved to support the ability for language such as Wernickes and Brocas area Why is Brain Size Important? All organs and systems of the body confr ...
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
... • Nerve cell which transmits electrical and chemical information (via neurotransmitters) throughout the body. Each nerve cell is separate from another and is called a Neuron – a string of these is a nerve cell. • Learning takes place by new dendrites actually sprouting to make connection with other ...
... • Nerve cell which transmits electrical and chemical information (via neurotransmitters) throughout the body. Each nerve cell is separate from another and is called a Neuron – a string of these is a nerve cell. • Learning takes place by new dendrites actually sprouting to make connection with other ...
Biopsychology - WordPress.com
... • All behaviour has a biological basis (a physical cause) • Our biology is a result of the interaction between the genes we inherited and the environment we grew up in • Our genes have evolved over thousands of years to make us adaptive to our changing environment ...
... • All behaviour has a biological basis (a physical cause) • Our biology is a result of the interaction between the genes we inherited and the environment we grew up in • Our genes have evolved over thousands of years to make us adaptive to our changing environment ...
HP Authorized Customer
... sensory signs between the brain and body. Involved in damaged by Alzheimer’s disease, spatial memory, short term memory, and learning. ...
... sensory signs between the brain and body. Involved in damaged by Alzheimer’s disease, spatial memory, short term memory, and learning. ...
Temprana Reflex Therapy Info
... The Brain Stem regulates many functions, many of which fall under a large category referred to as autonomic function. The brain stem also contains groups of cells called the cranial nerves which are responsible for vision, eye movement, hearing, balance, taste, facial movement and sensation, etc. Th ...
... The Brain Stem regulates many functions, many of which fall under a large category referred to as autonomic function. The brain stem also contains groups of cells called the cranial nerves which are responsible for vision, eye movement, hearing, balance, taste, facial movement and sensation, etc. Th ...
Reading the neural code in behaving animals, ~1000 neurons at a ,me
... The microscope also allows 3me-‐lapse imaging, for watching how individual cells' coding proper3es evolve over weeks. By using the integrated microscope to perform calcium-‐imaging in behaving mice as they rep ...
... The microscope also allows 3me-‐lapse imaging, for watching how individual cells' coding proper3es evolve over weeks. By using the integrated microscope to perform calcium-‐imaging in behaving mice as they rep ...
File
... This structure controls reflexes and carries sensory and motor messages to and from the brain. ...
... This structure controls reflexes and carries sensory and motor messages to and from the brain. ...
myers Chapter 02 review game
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
Brain PowerPoints - Raleigh Charter High School
... Remember – SAME (sensory = afferent, motor = efferent) ...
... Remember – SAME (sensory = afferent, motor = efferent) ...
Unit 3A–Neural Processing and the Endocrine System
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon (2 Words) a major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory; an oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures (which is why some people avoid MSG, monosodium glutamate) neurotransmitter that affects ...
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon (2 Words) a major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory; an oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures (which is why some people avoid MSG, monosodium glutamate) neurotransmitter that affects ...
Nervous System
... Lies below and behind the cerebral hemispheres Its surface is highly folded It helps coordinate muscle action It receives sensory impulses from muscles, tendons, joints, eyes and ears, as well as input from other brain centers • It processes information about body position • Controls posture by keep ...
... Lies below and behind the cerebral hemispheres Its surface is highly folded It helps coordinate muscle action It receives sensory impulses from muscles, tendons, joints, eyes and ears, as well as input from other brain centers • It processes information about body position • Controls posture by keep ...
Nervous system 1 - INAYA Medical College
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
Study Chart to Aid Learning About Brain Structure Cerebral Cortex
... Visual Cortex Visual areas V1V5 ...
... Visual Cortex Visual areas V1V5 ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint notes
... = a neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward. ...
... = a neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward. ...
Puzzle 2A: The Neuron and Nervous System
... Color that indicates high level of brain activity in PET scans Weight of the human brain, in pounds Received Nobel Prize for split-brain research ...
... Color that indicates high level of brain activity in PET scans Weight of the human brain, in pounds Received Nobel Prize for split-brain research ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.
![AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008569681_1-9cf3b4caa50d34e12653d8840c008c05-300x300.png)