The Autonomic Nervous System
... ANS structures in the PNS – ganglionic neurons, the adrenal medulla, and all autonomic ganglia – derive from the neural crest ...
... ANS structures in the PNS – ganglionic neurons, the adrenal medulla, and all autonomic ganglia – derive from the neural crest ...
DEFINITIONS - bums.ac.ir
... Immunoglobulins:Structure and Function • Definition: Glycoprotein molecules that are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which function as antibodies ...
... Immunoglobulins:Structure and Function • Definition: Glycoprotein molecules that are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which function as antibodies ...
Reading Part 5: The Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft & binds to receptors on postsynaptic neuron. Often the receptors are ligand-gated ion channels which open to let ions in. If the channels are for Na+, a depolarization of the membrane will occur. If the channels are for K+ or Cl-, ...
... Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft & binds to receptors on postsynaptic neuron. Often the receptors are ligand-gated ion channels which open to let ions in. If the channels are for Na+, a depolarization of the membrane will occur. If the channels are for K+ or Cl-, ...
Evolution of the Nervous System
... Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
... Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
Limitations in anti-obesity drug development: the critical role of
... behaviour by acting on neurons in the hypothalamus and the brainstem. During periods of satiety, the body works towards storage of the acquired nutrients. Satiety is associated with increased sympathetic activity, which promotes both insulin release by the pancreas (and thus stimulates glucose stora ...
... behaviour by acting on neurons in the hypothalamus and the brainstem. During periods of satiety, the body works towards storage of the acquired nutrients. Satiety is associated with increased sympathetic activity, which promotes both insulin release by the pancreas (and thus stimulates glucose stora ...
Evolution of the Nervous System
... Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
... Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
the autonomic nervous system
... Sympathetic stimulation often activates many different kinds of effector organs at the same time as a result of CNS stimulation or epinephrine and norepinephrine release from the adrenal medulla. ...
... Sympathetic stimulation often activates many different kinds of effector organs at the same time as a result of CNS stimulation or epinephrine and norepinephrine release from the adrenal medulla. ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... The Central Nervous System The Spinal Cord Serves as a sort of neural cable, connecting the brain with parts of the peripheral nervous system extending into the trunk and limbs. Does not connect the brain to internal organs. Responsible for simple reflexes. ...
... The Central Nervous System The Spinal Cord Serves as a sort of neural cable, connecting the brain with parts of the peripheral nervous system extending into the trunk and limbs. Does not connect the brain to internal organs. Responsible for simple reflexes. ...
HYPOTHALAMUS
... Plate 29 shows the relationship of troph-hormone producing cells to fenestrated capillaries in the anterior pituitary. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but ...
... Plate 29 shows the relationship of troph-hormone producing cells to fenestrated capillaries in the anterior pituitary. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but ...
Neuromuscular Transmission - Dr. Logothetis
... induce rapid changes, within a few milliseconds, in the permeability and potential of the postsynaptic membrane. In contrast, the postsynaptic responses triggered by activation of G protein-coupled receptors occur much more slowly, over seconds or minutes, because these receptors regulate opening an ...
... induce rapid changes, within a few milliseconds, in the permeability and potential of the postsynaptic membrane. In contrast, the postsynaptic responses triggered by activation of G protein-coupled receptors occur much more slowly, over seconds or minutes, because these receptors regulate opening an ...
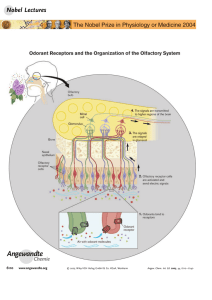
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically master ...
... own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically master ...
Tese final so frentes - Repositório da Universidade de Lisboa
... that motor neuron degeneration is caused by a complex interaction between multiple pathogenic processes. The mechanisms of motor neuron degeneration are best understood in the subtype of disease caused by mutations in the enzyme superoxide dismutase 1. This enzyme is enrolled in the degradation of f ...
... that motor neuron degeneration is caused by a complex interaction between multiple pathogenic processes. The mechanisms of motor neuron degeneration are best understood in the subtype of disease caused by mutations in the enzyme superoxide dismutase 1. This enzyme is enrolled in the degradation of f ...
The Area Postrema - Queen`s University
... of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (DMH) (van der Kooy and Koda 1983; Shapiro and Miselis 1985; see Fig. 3). Intriguingly information from the AP reaches the PVN through both monosynaptic and polysynaptic connections suggesting an integrative capacity wi ...
... of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (DMH) (van der Kooy and Koda 1983; Shapiro and Miselis 1985; see Fig. 3). Intriguingly information from the AP reaches the PVN through both monosynaptic and polysynaptic connections suggesting an integrative capacity wi ...
EFFECTS OF INTERLEUKM 1p ON JSOLATED RAT
... known as exogenous pymgens and they can trigger the synthesis of proinflammatory mediators, known as endogenous pyrogens (EPs), by cells of the immune system, especially monocytes. macrophages and neutrophils. ...
... known as exogenous pymgens and they can trigger the synthesis of proinflammatory mediators, known as endogenous pyrogens (EPs), by cells of the immune system, especially monocytes. macrophages and neutrophils. ...
Pyrokinin peptides` effect on the stomatogastric nervous system in
... lobster, central pattern generators control the behavior of muscles in its foregut, which allows the digestion of a variety of food types. The stomatogastric ganglion (STG) is a bundle of about thirty neurons in the foregut of American lobsters. It has been studied extensively since each one of the ...
... lobster, central pattern generators control the behavior of muscles in its foregut, which allows the digestion of a variety of food types. The stomatogastric ganglion (STG) is a bundle of about thirty neurons in the foregut of American lobsters. It has been studied extensively since each one of the ...
chapt07_lecture
... a) An active process needed to move organelles and proteins from the cell body to axon terminals b) Fast component moves membranous vesicles c) Slow components move microfilaments, microtubules, and proteins d) Anterograde transport – from cell body to dendrites and axon; uses kinesin molecular moto ...
... a) An active process needed to move organelles and proteins from the cell body to axon terminals b) Fast component moves membranous vesicles c) Slow components move microfilaments, microtubules, and proteins d) Anterograde transport – from cell body to dendrites and axon; uses kinesin molecular moto ...
Steroid Chemistry and Steroid Hormone Action - Rose
... being transmitted is not contained within the actual hormone molecule; instead, the hormone acts as a signal to activate (or deactivate) cellular processes. The precise nature of these processes depend on the cell type. Different types of hormones use different mechanisms to affect cellular function ...
... being transmitted is not contained within the actual hormone molecule; instead, the hormone acts as a signal to activate (or deactivate) cellular processes. The precise nature of these processes depend on the cell type. Different types of hormones use different mechanisms to affect cellular function ...
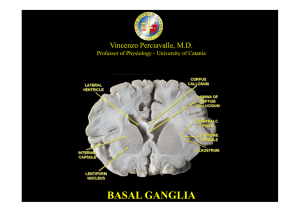
basal ganglia
... separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like those of the globus pallidus, the neurons in pars reticulata are mainly GABAergic. The SNpc is formed by dopaminergic neuron. In humans, these cells are coloured black by the pigment neuromelanin; they degree receive striatal information an ...
... separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like those of the globus pallidus, the neurons in pars reticulata are mainly GABAergic. The SNpc is formed by dopaminergic neuron. In humans, these cells are coloured black by the pigment neuromelanin; they degree receive striatal information an ...
Neurophysiological Aspects of Song Pattern Recognition and Sound
... of this species can lateralize sound with less than 1 dB difference between the two ears. Behavioral experiments suggested that separate pathways exist for song recognition and sound localization. As for the neurophysiological basis, auditory receptors respond tonically and necessarily carry all inf ...
... of this species can lateralize sound with less than 1 dB difference between the two ears. Behavioral experiments suggested that separate pathways exist for song recognition and sound localization. As for the neurophysiological basis, auditory receptors respond tonically and necessarily carry all inf ...
6th ANNUAL NEUROSCIENCE, BEHAVIOR AND HEALTH RESEARCH FORUM The University of Vermont
... Microsecond MD simulations to reveal the dynamics and mechanisms of a Class B GPCR Chenyi Liao and Jianing Li Department of Chemistry, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405 We have studied a class B G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), pituitary adenylate cyclaseactivating polypeptide receptor ( ...
... Microsecond MD simulations to reveal the dynamics and mechanisms of a Class B GPCR Chenyi Liao and Jianing Li Department of Chemistry, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405 We have studied a class B G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), pituitary adenylate cyclaseactivating polypeptide receptor ( ...
Theme 6. Vision
... Can you describe how myelination occurs in the peripheral nervous system and by which mechanism this can have an impact on speed of transmission. (6p) ...
... Can you describe how myelination occurs in the peripheral nervous system and by which mechanism this can have an impact on speed of transmission. (6p) ...
Nervous Lecture Test Questions – Set 1
... b. support neurons, by attaching to them and to capillaries c. are phagocytic d. form the myelin of CNS axons e. form the myelin of PNS axons ...
... b. support neurons, by attaching to them and to capillaries c. are phagocytic d. form the myelin of CNS axons e. form the myelin of PNS axons ...
Session 377 Visual cycle and phototransduction
... uptake. The carotenoid uptake efficiency by these receptors, however, was dependent on the concentration of carotenoids. For example – SCARB1 overexpressed cells showed significant increase in the uptake of lutein at concentrations between 1 and 10 μM, whereas SCARB2 overexpressed cells took up more ...
... uptake. The carotenoid uptake efficiency by these receptors, however, was dependent on the concentration of carotenoids. For example – SCARB1 overexpressed cells showed significant increase in the uptake of lutein at concentrations between 1 and 10 μM, whereas SCARB2 overexpressed cells took up more ...
How Does the Brain Sense Osmolality?
... These results stand in marked contrast to animals with lesions that destroy the OVLT and surrounding hypothalamus, in which osmotically stimulated AVP secretion and thirst are virtually abolished, leading to chronically elevated plasma osmolality. This raises the likelihood that different ion channe ...
... These results stand in marked contrast to animals with lesions that destroy the OVLT and surrounding hypothalamus, in which osmotically stimulated AVP secretion and thirst are virtually abolished, leading to chronically elevated plasma osmolality. This raises the likelihood that different ion channe ...