chapter – 21
... • The layer of cells which covers the cerebral hemisphere is called cerebral cartex and thrown in to prominent folds. • Cerebral cortex is grey in colours because of the presence of more cell bodies and dendrites. • It contains motor areas, sensory areas and association areas for complex functions. ...
... • The layer of cells which covers the cerebral hemisphere is called cerebral cartex and thrown in to prominent folds. • Cerebral cortex is grey in colours because of the presence of more cell bodies and dendrites. • It contains motor areas, sensory areas and association areas for complex functions. ...
sensory receptor
... as if the limb were still there. This is called phantom limb sensation. Possible causes: Impulses from the proximal portions of sensory neurons ...
... as if the limb were still there. This is called phantom limb sensation. Possible causes: Impulses from the proximal portions of sensory neurons ...
Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems
... as if the limb were still there. This is called phantom limb sensation. Possible causes: Impulses from the proximal portions of sensory neurons ...
... as if the limb were still there. This is called phantom limb sensation. Possible causes: Impulses from the proximal portions of sensory neurons ...
phys chapter 45 [10-24
... o Depressed conduction through Cl- or K+ channels or both; decreases diffusion of Cl- to inside of postsynaptic neuron or decreases diffusion of K+ out of neuron; effect is to make internal membrane more positive than normal, just in a slower fashion o Changes in internal metabolism of postsynaptic ...
... o Depressed conduction through Cl- or K+ channels or both; decreases diffusion of Cl- to inside of postsynaptic neuron or decreases diffusion of K+ out of neuron; effect is to make internal membrane more positive than normal, just in a slower fashion o Changes in internal metabolism of postsynaptic ...
Slide ()
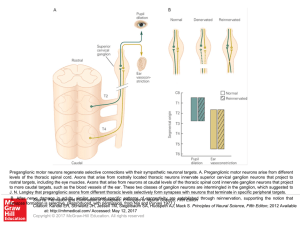
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
C8003 Psychobiology sample paper 2016-17
... GABA depolarises the postsynaptic cell as a consequence of chloride movement into that cell GABA-A receptors have a single binding site at which GABA and alcohol interact GABA is taken up into the presynaptic cell after it acts at the receptor GABA-A receptors require second messenger systems to hav ...
... GABA depolarises the postsynaptic cell as a consequence of chloride movement into that cell GABA-A receptors have a single binding site at which GABA and alcohol interact GABA is taken up into the presynaptic cell after it acts at the receptor GABA-A receptors require second messenger systems to hav ...
The Loss of Glutamate-GABA Harmony in Anxiety Disorders
... relatively good efficacy, a variety of adverse effects is also described. The most common are: ability to induce tolerance, sedation, myorelaxation, and dependence (Millan, 2003). Moreover, memory impartment and interaction with alcohol can occur. That is supposed to be connected with the activation ...
... relatively good efficacy, a variety of adverse effects is also described. The most common are: ability to induce tolerance, sedation, myorelaxation, and dependence (Millan, 2003). Moreover, memory impartment and interaction with alcohol can occur. That is supposed to be connected with the activation ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Synapses and Electroconvulsive
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
ALTERATIONS IN NEUROLOGIC FUNCTIONING
... collapse of neuron skeleton inside neurons Senile plaques of beta amyloid in interstitial fluid around neurons – byproduct of normal amyloid precursor protein (membrane protein) – Believe that plaques cause tau protein to form ...
... collapse of neuron skeleton inside neurons Senile plaques of beta amyloid in interstitial fluid around neurons – byproduct of normal amyloid precursor protein (membrane protein) – Believe that plaques cause tau protein to form ...
Glutamatergic Modulation of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and its
... Abstract: The Pedunculopontine Nucleus (PPN) is the cholinergic arm of the Reticular Activating System and is involved in cortical arousal. More specifically, the PPN is active during waking and REM sleep. The PPN receives input from many areas of the brain, including glutamatergic input from other ...
... Abstract: The Pedunculopontine Nucleus (PPN) is the cholinergic arm of the Reticular Activating System and is involved in cortical arousal. More specifically, the PPN is active during waking and REM sleep. The PPN receives input from many areas of the brain, including glutamatergic input from other ...
Electroconvulsive therapy - a shocking topic
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
Introduction to Psychology
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
The Nervous System
... – Relay information from central nervous system to organs – Involuntary: You do not consciously control these – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
... – Relay information from central nervous system to organs – Involuntary: You do not consciously control these – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
The Nervous System - Ione Community Charter School
... – Relay information from central nervous system to organs – Involuntary: You do not consciously control these – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
... – Relay information from central nervous system to organs – Involuntary: You do not consciously control these – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
The Nervous System
... – Relay information from central nervous system to organs – Involuntary: You do not consciously control these – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
... – Relay information from central nervous system to organs – Involuntary: You do not consciously control these – Sympathetic Nervous System: controls in times of stress, such as the flight or fight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System: controls body in times of rest ...
Neuroscience and Behavior Notes 2-2 (obj 7-10)
... communication system. Communication is carried out by hormones synthesized by a set of glands. ...
... communication system. Communication is carried out by hormones synthesized by a set of glands. ...
Chapter 96: Molecular And Cellular Biology Of Addiction
... drugs appear to produce both reward and reinforcement by means of at least two mechanisms: (a) activation of the VTA, which results in dopamine release in the NAc; and (b) direct binding to opiate receptors in the NAc, an action that is independent of dopamine. Activation of VTA dopamine neurons by ...
... drugs appear to produce both reward and reinforcement by means of at least two mechanisms: (a) activation of the VTA, which results in dopamine release in the NAc; and (b) direct binding to opiate receptors in the NAc, an action that is independent of dopamine. Activation of VTA dopamine neurons by ...
Biological Bases of Behavior, Barron`s Neuroanatomy, pages 78
... 10. Why are neurotransmitters important ? - enable neurons to communicate 11. What does it take for a neuron to fire? - terminal buttons on one neuron are stimulated and release transmitters into the synapse - neurotransmitters fit reception sites on the dendrites of the next neuron - next neuron ce ...
... 10. Why are neurotransmitters important ? - enable neurons to communicate 11. What does it take for a neuron to fire? - terminal buttons on one neuron are stimulated and release transmitters into the synapse - neurotransmitters fit reception sites on the dendrites of the next neuron - next neuron ce ...
Part 3
... 2. MAPK pathway activation leads to phosphorylation of MAPK (erk) and translocation of the activated erk into the nucleus. The presence of the activated MAPK – erk in the cytosol and nucleus can be visualized by staining of infected HeLa cells with monoclonal antibodies specific for the phosphorylat ...
... 2. MAPK pathway activation leads to phosphorylation of MAPK (erk) and translocation of the activated erk into the nucleus. The presence of the activated MAPK – erk in the cytosol and nucleus can be visualized by staining of infected HeLa cells with monoclonal antibodies specific for the phosphorylat ...
neurons and the nervous system
... Receive messages from other neurons and send them to the cell body Cell Body or Soma The control center of the neuron. Function: Directs impulses from the dendrites to the axon. Nucleus Control center of the Soma. Function: Tells the soma what to do. ...
... Receive messages from other neurons and send them to the cell body Cell Body or Soma The control center of the neuron. Function: Directs impulses from the dendrites to the axon. Nucleus Control center of the Soma. Function: Tells the soma what to do. ...
File
... 1) Draw a brief flow chart that shows the pathway of nerve communication when you accidentally touch something too hot (i.e. the reflex arc pathway). Make sure to include the following terms: relay neuron, spinal cord, motor nerve, sensory nerve, effector, ...
... 1) Draw a brief flow chart that shows the pathway of nerve communication when you accidentally touch something too hot (i.e. the reflex arc pathway). Make sure to include the following terms: relay neuron, spinal cord, motor nerve, sensory nerve, effector, ...
د. غسان The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): The ANS coordinates
... The preganglionic neurons that arise from the brainstem exit the CNS through the cranial nerves. The occulomotor nerve (III) innervates the eyes; the facial nerve (VII) innervates the lacrimal gland, the salivary glands and the mucus membranes of the nasal cavity; the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) inn ...
... The preganglionic neurons that arise from the brainstem exit the CNS through the cranial nerves. The occulomotor nerve (III) innervates the eyes; the facial nerve (VII) innervates the lacrimal gland, the salivary glands and the mucus membranes of the nasal cavity; the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) inn ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – PARASYMPATHETIC
... outflow:parasympathetic cranial nerve nuclei and sacral spinal segments) ...
... outflow:parasympathetic cranial nerve nuclei and sacral spinal segments) ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – PARASYMPATHETIC
... outflow:parasympathetic cranial nerve nuclei and sacral spinal segments) ...
... outflow:parasympathetic cranial nerve nuclei and sacral spinal segments) ...