The Relationship Between Synchronization Among Neuronal
... random noisy input was provided to all units in one of the two areas (area 1). In some simulations, the mean interarea delay was increased to 8 ms to mimic a greater separation between the areas. In other simulations, excitatory NMDA synaptic channels were incorporated. These NMDA channels were used ...
... random noisy input was provided to all units in one of the two areas (area 1). In some simulations, the mean interarea delay was increased to 8 ms to mimic a greater separation between the areas. In other simulations, excitatory NMDA synaptic channels were incorporated. These NMDA channels were used ...
Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity Orchestrates the Response of Pyramidal
... subpopulations, dynamically re-wiring networks over timescales of tens of milliseconds. A number of phenomenological models (Tsodyks and Markram, 1997; Abbott et al., 1997; Tsodyks et al., 1998) have been developed that can be used to classify the dynamics of synapses as being: either depressing, re ...
... subpopulations, dynamically re-wiring networks over timescales of tens of milliseconds. A number of phenomenological models (Tsodyks and Markram, 1997; Abbott et al., 1997; Tsodyks et al., 1998) have been developed that can be used to classify the dynamics of synapses as being: either depressing, re ...
aud
... (also known as the external auditory meatus), the ear drum (also known as the tympanic membrane), and the middle ear, which contains three very small bones called the auditory ossicles. The primary function of the conductive mechanism is to transmit the vibrations that are picked up at the tympanic ...
... (also known as the external auditory meatus), the ear drum (also known as the tympanic membrane), and the middle ear, which contains three very small bones called the auditory ossicles. The primary function of the conductive mechanism is to transmit the vibrations that are picked up at the tympanic ...
to receive a reprint - Institute for Learning and Brain Sciences
... high-frequency nouns than did low-capacity readers. Therefore, differences in comprehension ability may reflect differences in the adaptability of a neural network in the face of changing demands. In the current study, we explored various accounts of individual differences in neural adaptability. One ...
... high-frequency nouns than did low-capacity readers. Therefore, differences in comprehension ability may reflect differences in the adaptability of a neural network in the face of changing demands. In the current study, we explored various accounts of individual differences in neural adaptability. One ...
Medical Gross Anatomy - University of Michigan
... ANS because the cell bodies of the presynaptic sympathetic neurons are located in the lateral horns (a.k.a. intermediolateral cell columns) of the spinal cord gray matter, which are found in spinal cord segments T1 through L2. There are no sympathetic presynaptic cell bodies above spinal cord level ...
... ANS because the cell bodies of the presynaptic sympathetic neurons are located in the lateral horns (a.k.a. intermediolateral cell columns) of the spinal cord gray matter, which are found in spinal cord segments T1 through L2. There are no sympathetic presynaptic cell bodies above spinal cord level ...
Modeling goal-directed spatial navigation in the rat based on physiological
... of the fornix remove much of the amplitude of theta rhythm. This impairs the ability to learn reversal tasks, in which a previously rewarded behavior must be replaced with an opposite behavior. For example, rats have difficulty learning a right turn response after initially learning a left turn resp ...
... of the fornix remove much of the amplitude of theta rhythm. This impairs the ability to learn reversal tasks, in which a previously rewarded behavior must be replaced with an opposite behavior. For example, rats have difficulty learning a right turn response after initially learning a left turn resp ...
Auditory physiology chapter
... (also known as the external auditory meatus), the ear drum (also known as the tympanic membrane), and the middle ear, which contains three very small bones called the auditory ossicles. The primary function of the conductive mechanism is to transmit the vibrations that are picked up at the tympanic ...
... (also known as the external auditory meatus), the ear drum (also known as the tympanic membrane), and the middle ear, which contains three very small bones called the auditory ossicles. The primary function of the conductive mechanism is to transmit the vibrations that are picked up at the tympanic ...
Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]
... all gastropod molluscs (Croll, 1983) uses olfaction as the principal sensory modality for perception at a distance (Chase et al., 1978; Chase and Croll, 1981; Chase, 1982). Several recent reports have described associative conditioning to odors in gastropod molluscs (Croll and Chase, 1980; Sahley et ...
... all gastropod molluscs (Croll, 1983) uses olfaction as the principal sensory modality for perception at a distance (Chase et al., 1978; Chase and Croll, 1981; Chase, 1982). Several recent reports have described associative conditioning to odors in gastropod molluscs (Croll and Chase, 1980; Sahley et ...
doc midterm 1 chapter notes
... He defined the term reflex: An automatic, stereotyped movement that is produced as a direct result of a stimulus. He said that energy coming from an outside source would be reflected back through the nervous system to the muscles, which would contract (we of course have a different explanation for t ...
... He defined the term reflex: An automatic, stereotyped movement that is produced as a direct result of a stimulus. He said that energy coming from an outside source would be reflected back through the nervous system to the muscles, which would contract (we of course have a different explanation for t ...
Text S1.
... An 8 by 8 grid of electrodes with 333 µm inter-electrode spacing was included. The inter-electrode spacing, which was larger than the inter-electrode spacing of 200 µm in MEAs, was selected so that the distance from each peripheral electrode to the edge of the network were also the inter-electrode s ...
... An 8 by 8 grid of electrodes with 333 µm inter-electrode spacing was included. The inter-electrode spacing, which was larger than the inter-electrode spacing of 200 µm in MEAs, was selected so that the distance from each peripheral electrode to the edge of the network were also the inter-electrode s ...
MSc Thesis Template Document
... Figure 40 Synapse or Syndesis or Synapsis .................................................................................. 37 Figure 41 The Synaptic Gap at a Synapse .................................................................................... 38 Figure 42 Neurons: Synapses in the Neural Ne ...
... Figure 40 Synapse or Syndesis or Synapsis .................................................................................. 37 Figure 41 The Synaptic Gap at a Synapse .................................................................................... 38 Figure 42 Neurons: Synapses in the Neural Ne ...
Code-specific policy gradient rules for spiking neurons
... Here, Y (t) = ti δ(t − ti ) is now a sum of δ-functions. Note that the learning rule (16) was already proposed by Xie and Seung [13] and Florian [3] and, slightly modified for supervised learning, by Pfister et al. [5]. Following the same line, policy gradient rules can also be derived for the intri ...
... Here, Y (t) = ti δ(t − ti ) is now a sum of δ-functions. Note that the learning rule (16) was already proposed by Xie and Seung [13] and Florian [3] and, slightly modified for supervised learning, by Pfister et al. [5]. Following the same line, policy gradient rules can also be derived for the intri ...
midbrain Brain stem
... Figure 12.12 Inferior view of the brain, showing the three parts of the brain stem: midbrain, pons, and medulla ...
... Figure 12.12 Inferior view of the brain, showing the three parts of the brain stem: midbrain, pons, and medulla ...
Electrical Interactions via the Extracellular Potential Near Cell Bodies
... of extracellular potential, we did not explicitly model all the elements in the space surrounding the cell. Instead, the local potential is replaced by its average over a small volume, and the medium is treated as an homogeneous isotroptic dielectric. Local geometrical irregularities will cause vari ...
... of extracellular potential, we did not explicitly model all the elements in the space surrounding the cell. Instead, the local potential is replaced by its average over a small volume, and the medium is treated as an homogeneous isotroptic dielectric. Local geometrical irregularities will cause vari ...
Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks
... the ®ring behaviour of cortical neurons13,14. We focused on spike responses to transient membrane-potential excursions, implied by the physiological ®ndings1±5. As a rule, such transients are explained by convergent inputs from simultaneously spiking neurons onto a target neuron (Fig. 1a). These tra ...
... the ®ring behaviour of cortical neurons13,14. We focused on spike responses to transient membrane-potential excursions, implied by the physiological ®ndings1±5. As a rule, such transients are explained by convergent inputs from simultaneously spiking neurons onto a target neuron (Fig. 1a). These tra ...
excitation and inhibition of the reflex eye withdrawal of the crab
... withdrawal is supported by some evidence. (1) The burst is of the same size, duration and frequency as those recorded from the optic tracts of intact animals during eye withdrawal (Horridge & Sandeman, 1964). (2) Simultaneous records taken from the optic tract and eye muscles during eye withdrawal s ...
... withdrawal is supported by some evidence. (1) The burst is of the same size, duration and frequency as those recorded from the optic tracts of intact animals during eye withdrawal (Horridge & Sandeman, 1964). (2) Simultaneous records taken from the optic tract and eye muscles during eye withdrawal s ...
Preview as PDF - Pearson Higher Education
... cells (extending from inner to outer areas like the spokes of a wheel) help guide migrating neurons to form the outer layers of the brain. Other glia are involved in getting nutrients to the neurons, cleaning up the remains of neurons that have died, communicating with neurons and other glial cells, ...
... cells (extending from inner to outer areas like the spokes of a wheel) help guide migrating neurons to form the outer layers of the brain. Other glia are involved in getting nutrients to the neurons, cleaning up the remains of neurons that have died, communicating with neurons and other glial cells, ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... – Sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers innervate the same cells. • Actions counteract each other. – Heart rate. ...
... – Sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers innervate the same cells. • Actions counteract each other. – Heart rate. ...
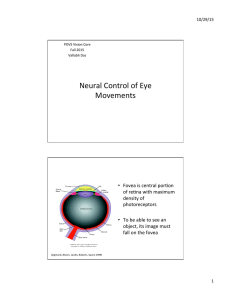
Neural Control of Eye Movements
... • A common feature of neural control systems are top-down and boeom-up influences • Boeom-up control à Gather parameters of the sensory signal to develop the motor command – Decoding of error signals; for example reDnal error posiDon for saccades; direcDon and speed for pursuit – Influence ...
... • A common feature of neural control systems are top-down and boeom-up influences • Boeom-up control à Gather parameters of the sensory signal to develop the motor command – Decoding of error signals; for example reDnal error posiDon for saccades; direcDon and speed for pursuit – Influence ...
Implications of Polychronous Neuronal Groups for the Nature of Mental Representations
... it is important to understand how they are generated and propagated. An individual neuron remains at its resting potential until it receives, or “observes”, a sufficient number of spikes in a short enough period of time, at which point this coincident input causes the neuron to generate an action po ...
... it is important to understand how they are generated and propagated. An individual neuron remains at its resting potential until it receives, or “observes”, a sufficient number of spikes in a short enough period of time, at which point this coincident input causes the neuron to generate an action po ...
Artificial Intelligence (AI). Neural Networks
... the neuron is said to fire. The impulse is sent from the cell body (soma), through the axon, which influences the dendrites of the next neuron over narrow gaps called synapses. They translate the pulse in some degree into excitatory or inhibitory impulse of the next neuron (fig.9). ...
... the neuron is said to fire. The impulse is sent from the cell body (soma), through the axon, which influences the dendrites of the next neuron over narrow gaps called synapses. They translate the pulse in some degree into excitatory or inhibitory impulse of the next neuron (fig.9). ...
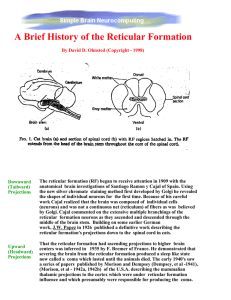
A Brief History of the Reticular Formation
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...
62 Cranial Nerve VII: The Facial Nerve And Taste
... synkinetic movements are almost always present on the involved side . 2 . Because of the contractures, the face at rest may be more deeply etched on the side of the previous palsy . This can give a false impression of weakness on the opposite side . ...
... synkinetic movements are almost always present on the involved side . 2 . Because of the contractures, the face at rest may be more deeply etched on the side of the previous palsy . This can give a false impression of weakness on the opposite side . ...






![Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017009313_1-932f7069dbfdd3fd3915bbe942d02b0f-300x300.png)