Absorption - INAYA Medical College
... most biologic membranes due to their solubility in the membrane bi-layers • Water-soluble drugs penetrate the cell membrane through aqueous channels or pores ...
... most biologic membranes due to their solubility in the membrane bi-layers • Water-soluble drugs penetrate the cell membrane through aqueous channels or pores ...
PHARMACEUTICAL PROCESS ENGINEERING CHAPTER 1
... • It is the process of transformation of a drug within the body to make it more hydrophilic so that it can be excreted out from the body by the kidneys. This needs to be done since drugs and chemicals are foreign substances in our body. • Metabolism is one of the most important mechanisms that the b ...
... • It is the process of transformation of a drug within the body to make it more hydrophilic so that it can be excreted out from the body by the kidneys. This needs to be done since drugs and chemicals are foreign substances in our body. • Metabolism is one of the most important mechanisms that the b ...
Drugs - University of Florida ROTC
... – The average THC level in marijuana has increased from 1.5% in 1970 to over 7.6% today. – The purity level of heroine has increased approx. 10% and now averages 35%. ...
... – The average THC level in marijuana has increased from 1.5% in 1970 to over 7.6% today. – The purity level of heroine has increased approx. 10% and now averages 35%. ...
Legislative Nomination Form
... 39. The _______________ is the only organ of the body that breaks down (metabolizes) alcohol into carbon dioxide, water, ...
... 39. The _______________ is the only organ of the body that breaks down (metabolizes) alcohol into carbon dioxide, water, ...
RL 4 Chiral drugs
... images. They contain at least two asymmetric carbon atoms. Unlike enantiomers, the physical and ...
... images. They contain at least two asymmetric carbon atoms. Unlike enantiomers, the physical and ...
Dr. Keith Baker - Designer (Dirty) Drugs
... ALD-52, N-acetyllysergic acid diethylamide, famously believed to have been the active ingredient in the "Orange Sunshine" acid of the 1960s ETH-LAD, which has been sold by some research chemical suppliers. AL-LAD, which has been sold by some research chemical suppliers. PRO-LAD, which has been sold ...
... ALD-52, N-acetyllysergic acid diethylamide, famously believed to have been the active ingredient in the "Orange Sunshine" acid of the 1960s ETH-LAD, which has been sold by some research chemical suppliers. AL-LAD, which has been sold by some research chemical suppliers. PRO-LAD, which has been sold ...
Law20060112 - Dr Ted Williams
... Authorized by Durham-Humphrey Manufacturer or FDA can initiate Insurance company can initiate (e.g. Prilosec) OTC Drug Review Process primary mechanism by which drugs are switched • There is a committee at FDA which advises on Rx to OTC switches • Rx examples switched to OTC: Benadryl, ...
... Authorized by Durham-Humphrey Manufacturer or FDA can initiate Insurance company can initiate (e.g. Prilosec) OTC Drug Review Process primary mechanism by which drugs are switched • There is a committee at FDA which advises on Rx to OTC switches • Rx examples switched to OTC: Benadryl, ...
chapt12_lecture
... • Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test • E-test diffusion test • Dilution tests – minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) - smallest concentration of drug that visibly inhibits growth • Provide profile of drug sensitivity – antibiogram which guides the choice of a suitable drug ...
... • Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test • E-test diffusion test • Dilution tests – minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) - smallest concentration of drug that visibly inhibits growth • Provide profile of drug sensitivity – antibiogram which guides the choice of a suitable drug ...
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
... A potent enzyme inhibitor is likely to inhibit the metabolism of ANY drug that is metabolized by that enzyme Some substrates for a particular enzyme are also inhibitors or inducers of that same enzyme Some inhibitors affect more than one enzyme Magnitude of inhibition may depend upon the dos ...
... A potent enzyme inhibitor is likely to inhibit the metabolism of ANY drug that is metabolized by that enzyme Some substrates for a particular enzyme are also inhibitors or inducers of that same enzyme Some inhibitors affect more than one enzyme Magnitude of inhibition may depend upon the dos ...
Clinical Trials
... 2. Rational drug design of a new drug based on an understanding of biologic mechanisms, drug receptor structure, and drug structure 3. Chemical modification of a known molecule ...
... 2. Rational drug design of a new drug based on an understanding of biologic mechanisms, drug receptor structure, and drug structure 3. Chemical modification of a known molecule ...
Extended Drug Burden Score (eDBS)
... values (0-3) were divided by 3 to result in a Drug Burden (DB) score of 0-1 (0, 0.33, 0.66 and 1) Each drug was assessed for sedative properties (based on publically available adverse effect information) and those with sedation as a side effect were allocated an Drug Burden (DB) score of 1.0 Commonl ...
... values (0-3) were divided by 3 to result in a Drug Burden (DB) score of 0-1 (0, 0.33, 0.66 and 1) Each drug was assessed for sedative properties (based on publically available adverse effect information) and those with sedation as a side effect were allocated an Drug Burden (DB) score of 1.0 Commonl ...
lab#1 pharmacology
... • According to different tissue to be used, there is a different physiological solution prepared. • But all or most of them contain the following ingredients at different concentrations: 1- Nacl → to adjust the isotonicity. ...
... • According to different tissue to be used, there is a different physiological solution prepared. • But all or most of them contain the following ingredients at different concentrations: 1- Nacl → to adjust the isotonicity. ...
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
... A potent enzyme inhibitor is likely to inhibit the metabolism of ANY drug that is metabolized by that enzyme Some substrates for a particular enzyme are also inhibitors or inducers of that same enzyme Some inhibitors affect more than one enzyme Magnitude of inhibition may depend upon the dos ...
... A potent enzyme inhibitor is likely to inhibit the metabolism of ANY drug that is metabolized by that enzyme Some substrates for a particular enzyme are also inhibitors or inducers of that same enzyme Some inhibitors affect more than one enzyme Magnitude of inhibition may depend upon the dos ...
Glicron CR Capsule
... Care should be exercised in patients with hepatic and/or renal impairment and a small starting dose should be used with careful patient monitoring. As with our other sulfonylureas, hypoglycemia will occur if the patients’ dietary intake is reduced or if they are receiving a larger dose of gliclazide ...
... Care should be exercised in patients with hepatic and/or renal impairment and a small starting dose should be used with careful patient monitoring. As with our other sulfonylureas, hypoglycemia will occur if the patients’ dietary intake is reduced or if they are receiving a larger dose of gliclazide ...
Document
... or types of patients that warrant closer observation for specific side effects when given drug Hx of bronchial asthma, HTN ...
... or types of patients that warrant closer observation for specific side effects when given drug Hx of bronchial asthma, HTN ...
General Toxicology
... Entero-hepatic circulation: • Drugs & chemicals excreted into the bile enter the intestine and are either reabsorbed into the blood or eliminated in the feces • Some drugs are excreted as water-soluble glcuronide conjugates that are hydrolyzed by intestinal bacteria resulting in reforming of the par ...
... Entero-hepatic circulation: • Drugs & chemicals excreted into the bile enter the intestine and are either reabsorbed into the blood or eliminated in the feces • Some drugs are excreted as water-soluble glcuronide conjugates that are hydrolyzed by intestinal bacteria resulting in reforming of the par ...
Prodrugs and active metabolites among antidepressive
... interest it is worth to mention that individual genetic differences in drug metabolism may significantly modify drug response (Sárosi et al., 2008). Active metabolite(s) of drugs may significantly modify clinical effect as these metabolites may have different pharmacokinetics than the parent compoun ...
... interest it is worth to mention that individual genetic differences in drug metabolism may significantly modify drug response (Sárosi et al., 2008). Active metabolite(s) of drugs may significantly modify clinical effect as these metabolites may have different pharmacokinetics than the parent compoun ...
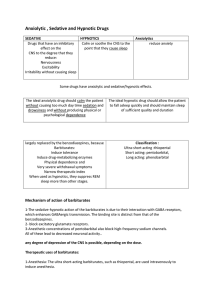
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs
... largely replaced by the benzodiazepines, because Barbiturates: Induce tolerance Induce drug-metabolizing enzymes Physical dependence and Very severe withdrawal symptoms Narrow therapeutic index When used as hypnotics, they suppress REM sleep more than other stages. ...
... largely replaced by the benzodiazepines, because Barbiturates: Induce tolerance Induce drug-metabolizing enzymes Physical dependence and Very severe withdrawal symptoms Narrow therapeutic index When used as hypnotics, they suppress REM sleep more than other stages. ...
ELIMINATION OF DRUGS
... • Facilitated diffusion – with the help of proteins-transporters: glucose, aminoacids, vitamins (specific gastromucoprotein synthesized in stomach is necessary for absorption of vitamin В12 in small intestine) • Filtration – through pores in membrane, the size of which is around 0,35-0,8 nm. Substan ...
... • Facilitated diffusion – with the help of proteins-transporters: glucose, aminoacids, vitamins (specific gastromucoprotein synthesized in stomach is necessary for absorption of vitamin В12 in small intestine) • Filtration – through pores in membrane, the size of which is around 0,35-0,8 nm. Substan ...
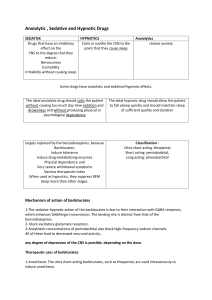
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs SEDATIVE HYPNOTICS
... largely replaced by the benzodiazepines, because Barbiturates: Induce tolerance Induce drug-metabolizing enzymes Physical dependence and Very severe withdrawal symptoms Narrow therapeutic index When used as hypnotics, they suppress REM sleep more than other stages. ...
... largely replaced by the benzodiazepines, because Barbiturates: Induce tolerance Induce drug-metabolizing enzymes Physical dependence and Very severe withdrawal symptoms Narrow therapeutic index When used as hypnotics, they suppress REM sleep more than other stages. ...
Quiz 1 Key - chem.uwec.edu
... 1. On a single graph, draw a typical dose/response curve for the new natural product drug, hartseloic acid. Also draw dose/response curve for the drug in the presence of (A) , a competitive antagonist and (B) a non-competitive antagonist. In addition, include a curve for a newly discovered similar d ...
... 1. On a single graph, draw a typical dose/response curve for the new natural product drug, hartseloic acid. Also draw dose/response curve for the drug in the presence of (A) , a competitive antagonist and (B) a non-competitive antagonist. In addition, include a curve for a newly discovered similar d ...
Lesson Plan I: March 17, March 19
... bodies, and part of its function is to break down the chemicals in the food and drugs we digest. 2. How does a drug change when it enters the body? When a drug enters the liver, special proteins called enzymes bind to the drug and break it down. Enzymes break down a drug to either dispose of it or ...
... bodies, and part of its function is to break down the chemicals in the food and drugs we digest. 2. How does a drug change when it enters the body? When a drug enters the liver, special proteins called enzymes bind to the drug and break it down. Enzymes break down a drug to either dispose of it or ...
Rating Definition
... O the study of substances that interact with living systems through a chemical process, by binding to regulatory molecules which activate or inhibit a normal body process O The short definition O the study of the drug’s actions on the body ...
... O the study of substances that interact with living systems through a chemical process, by binding to regulatory molecules which activate or inhibit a normal body process O The short definition O the study of the drug’s actions on the body ...
Drug interaction

A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance (usually another drug) affects the activity of a drug when both are administered together. This action can be synergistic (when the drug's effect is increased) or antagonistic (when the drug's effect is decreased) or a new effect can be produced that neither produces on its own. Typically, interactions between drugs come to mind (drug-drug interaction). However, interactions may also exist between drugs and foods (drug-food interactions), as well as drugs and medicinal plants or herbs (drug-plant interactions). People taking antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take food containing tyramine as hypertensive crisis may occur (an example of a drug-food interaction). These interactions may occur out of accidental misuse or due to lack of knowledge about the active ingredients involved in the relevant substances.It is therefore easy to see the importance of these pharmacological interactions in the practice of medicine. If a patient is taking two drugs and one of them increases the effect of the other it is possible that an overdose may occur. The interaction of the two drugs may also increase the risk that side effects will occur. On the other hand, if the action of a drug is reduced it may cease to have any therapeutic use because of under dosage. Notwithstanding the above, on occasion these interactions may be sought in order to obtain an improved therapeutic effect. Examples of this include the use of codeine with paracetamol to increase its analgesic effect. Or the combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin in order to overcome bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. It should also be remembered that there are interactions that, from a theoretical standpoint, may occur but in clinical practice have no important repercussions.The pharmaceutical interactions that are of special interest to the practice of medicine are primarily those that have negative effects for an organism. The risk that a pharmacological interaction will appear increases as a function of the number of drugs administered to a patient at the same time.It is possible that an interaction will occur between a drug and another substance present in the organism (i.e. foods or alcohol). Or in certain specific situations a drug may even react with itself, such as occurs with dehydration. In other situations, the interaction does not involve any effect on the drug. In certain cases, the presence of a drug in an individual's blood may affect certain types of laboratory analysis (analytical interference).It is also possible for interactions to occur outside an organism before administration of the drugs has taken place. This can occur when two drugs are mixed, for example, in a saline solution prior to intravenous injection. Some classic examples of this type of interaction include that Thiopentone and Suxamethonium should not be placed in the same syringe and same is true for Benzylpenicillin and Heparin. These situations will all be discussed under the same heading due to their conceptual similarity.Drug interactions may be the result of various processes. These processes may include alterations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug, such as alterations in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug. Alternatively, drug interactions may be the result of the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug, e.g. the co-administration of a receptor antagonist and an agonist for the same receptor.