How to Anesthetize Donkeys for Surgical Procedures in the Field
... 0.02– 0.05 mg/kg) IV or IM. Adding butorphanolf to an ␣-2 agonist produces superior sedation and analgesia at a dose of 0.03 mg/kg (range, 0.02– 0.05 mg/ kg) IV or IM. Buprenorphineg can be administered at 0.006 mg/kg IV, IM, or sublingual. This drug does not produce sedation when given alone and ca ...
... 0.02– 0.05 mg/kg) IV or IM. Adding butorphanolf to an ␣-2 agonist produces superior sedation and analgesia at a dose of 0.03 mg/kg (range, 0.02– 0.05 mg/ kg) IV or IM. Buprenorphineg can be administered at 0.006 mg/kg IV, IM, or sublingual. This drug does not produce sedation when given alone and ca ...
Subutex - A Prisoners Guide. Lifeline Publications
... Dogs, drug testing and getting caught Subutex has become very popular recently - in a number of jails it has become the number one drug of choice. The prison service are aware of this and are about to step up their response. At present sniffer dogs are being trained so they can detect buprenorphine ...
... Dogs, drug testing and getting caught Subutex has become very popular recently - in a number of jails it has become the number one drug of choice. The prison service are aware of this and are about to step up their response. At present sniffer dogs are being trained so they can detect buprenorphine ...
1 Name: Thyroglobulin (Proloid) Class: Thyroid Hormone Mech.: T3
... w/vit. D). Hypercalciuria. Enhances action of digitalis. ∴ IV infusion may ppt arrhythmias. High level of irritation (esp. IM). Drug interactions—↓ bioavailability and/or oral absorption of some drugs (e.g., etidronate, tetracyclines, iron salts, atenolol, norfloxacin). Thiazide diuretic-induced hyp ...
... w/vit. D). Hypercalciuria. Enhances action of digitalis. ∴ IV infusion may ppt arrhythmias. High level of irritation (esp. IM). Drug interactions—↓ bioavailability and/or oral absorption of some drugs (e.g., etidronate, tetracyclines, iron salts, atenolol, norfloxacin). Thiazide diuretic-induced hyp ...
1 Diosynth Biotechnology – Riding the Biomanufacturing Wave
... is a certified cGMP manufacturer. However, besides benefiting from general industry growth, Diosynth also enjoys some advantages by virtue of its function as a CMO. While large biotechnology or pharmaceutical firms are able to provide add-on services, they lack the agility of smaller firms, given th ...
... is a certified cGMP manufacturer. However, besides benefiting from general industry growth, Diosynth also enjoys some advantages by virtue of its function as a CMO. While large biotechnology or pharmaceutical firms are able to provide add-on services, they lack the agility of smaller firms, given th ...
Oncobiguanides: Paracelsus’ law and nonconventional routes
... use [7]. Perhaps it is time to consider that, as with any drug, there is a metformin dose range that is without any effect, one corresponding to “diabetobiguanides” with a pharmacological effect (e.g., insulin sensitization in type 2 diabetes, prevention of insulin-dependent carcinogenesis, indirect ...
... use [7]. Perhaps it is time to consider that, as with any drug, there is a metformin dose range that is without any effect, one corresponding to “diabetobiguanides” with a pharmacological effect (e.g., insulin sensitization in type 2 diabetes, prevention of insulin-dependent carcinogenesis, indirect ...
Valium (diazepam)
... Valium (diazepam) is a benzodiazepine indicated for treatment of anxiety disorders or short-term relief of symptoms of anxiety, seizure disorder, and skeletal muscle spasms as a muscle relaxant. The use of a drug for its approved indications is called its labeled use. In clinical practice, however, ...
... Valium (diazepam) is a benzodiazepine indicated for treatment of anxiety disorders or short-term relief of symptoms of anxiety, seizure disorder, and skeletal muscle spasms as a muscle relaxant. The use of a drug for its approved indications is called its labeled use. In clinical practice, however, ...
Adverse Reactions
... Pulmonary toxicity is both dose and age related, being more common in patients over 70 years of age and in those receiving over 400 units total dose. This toxicity, however, is unpredictable and has been seen in young patients receiving low doses ...
... Pulmonary toxicity is both dose and age related, being more common in patients over 70 years of age and in those receiving over 400 units total dose. This toxicity, however, is unpredictable and has been seen in young patients receiving low doses ...
Document
... and the initial findings from observational studies suggested an increased risk of cardiovascular events in concomitant users of clopidogrel and PPIs. Recently published data from a randomized clinical trial suggest that this risk is likely clinically insignificant. Nevertheless, because of potentia ...
... and the initial findings from observational studies suggested an increased risk of cardiovascular events in concomitant users of clopidogrel and PPIs. Recently published data from a randomized clinical trial suggest that this risk is likely clinically insignificant. Nevertheless, because of potentia ...
of poor ORIGINAL ARTICLES
... EMs and PMs,3 the definition of a metabolic "ratio" is not possible. The age or sex of the subjects had no apparent influence on their phenotype (Table I). Results of microsomal incubations with R- and Smephenytoin are summarized in Table II. In liver microsomes of mephenytoin EMs phenotyped in vivo ...
... EMs and PMs,3 the definition of a metabolic "ratio" is not possible. The age or sex of the subjects had no apparent influence on their phenotype (Table I). Results of microsomal incubations with R- and Smephenytoin are summarized in Table II. In liver microsomes of mephenytoin EMs phenotyped in vivo ...
... While exposure of wt sGC-overexpressing cells to HMR1766 led to higher cGMP levels, BAY 58-2667 was a more potent sGC activator. Mutating His to Phe at β1 105 abolished sGC responsiveness to sodium nitroprusside (SNP), due to heme loss. In contrast, BAY 58-2667 and HMR-1766 activated heme-free H105F ...
Usual Adult Dose for Pain
... Opiates are a class of medications used for management of moderate to severe pain. They act on what are called “opiate receptors” in the nervous system and the brain, and diminish the experience of pain by the person. Medications in this class that are commonly used by experts in pain management are ...
... Opiates are a class of medications used for management of moderate to severe pain. They act on what are called “opiate receptors” in the nervous system and the brain, and diminish the experience of pain by the person. Medications in this class that are commonly used by experts in pain management are ...
LOCAL ANESTHETICS - Professor Dr Ghaleb
... • Amide local anesthetics • They are transported into the liver before their biotransformation. The two ...
... • Amide local anesthetics • They are transported into the liver before their biotransformation. The two ...
Chapter 35: Medication Administration
... • Distribution depends on: – Circulation: limited blood flow can inhibit distribution – Membrane permeability • Blood brain barrier and Placenta ...
... • Distribution depends on: – Circulation: limited blood flow can inhibit distribution – Membrane permeability • Blood brain barrier and Placenta ...
Iodine and Tyrosine
... If pregnant or lactating, consult your physician before taking this product. Too much iodine can actually be contraindicated for healthy thyroid function. Iodine supplementation should be closely monitored by a health professional. In sensitive individuals, iodine has been reported to cause an acne- ...
... If pregnant or lactating, consult your physician before taking this product. Too much iodine can actually be contraindicated for healthy thyroid function. Iodine supplementation should be closely monitored by a health professional. In sensitive individuals, iodine has been reported to cause an acne- ...
Prescribing Review
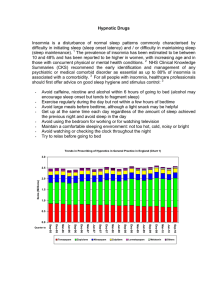
... for chronic insomnia in adults (benzodiazepines – 52 RCTs, Z-drugs – 48 RCTs and antidepressants – 8 RCTs). Sleep onset latency was significantly decreased, but only a small average improvement was achieved. When measured by polysomnography the weighted mean difference was: Benzodiazepines: - 10.0 m ...
... for chronic insomnia in adults (benzodiazepines – 52 RCTs, Z-drugs – 48 RCTs and antidepressants – 8 RCTs). Sleep onset latency was significantly decreased, but only a small average improvement was achieved. When measured by polysomnography the weighted mean difference was: Benzodiazepines: - 10.0 m ...
Chemistry for Changing Times 11th Edition Hill and Kolb
... Newer NSAIDs only block the COX-2 enzyme and do not experience the side effects of the older NSAIDs. Unfortunately, some have side effects of increased risks of heart attack and stroke as well as allergic reactions and internal bleeding. ...
... Newer NSAIDs only block the COX-2 enzyme and do not experience the side effects of the older NSAIDs. Unfortunately, some have side effects of increased risks of heart attack and stroke as well as allergic reactions and internal bleeding. ...
Pharmacological Characterization of Noroxymorphone as a New
... morphine (1 and 5 g/10 L). Pretreatment with subcutaneous naloxone (1 mg/kg) 15 min before intrathecal drug administration significantly decreased the antinociceptive effect of both noroxymorphone and morphine, indicating an opioid receptormediated antinociceptive effect. In the hotplate, paw pres ...
... morphine (1 and 5 g/10 L). Pretreatment with subcutaneous naloxone (1 mg/kg) 15 min before intrathecal drug administration significantly decreased the antinociceptive effect of both noroxymorphone and morphine, indicating an opioid receptormediated antinociceptive effect. In the hotplate, paw pres ...
QA135_4chondroitin_DI
... receiving warfarin who self-medicated with glucosamine-chondroitin supplements (6,7). In one, a 69year-old man with chronic atrial fibrillation was receiving oral warfarin 47.5mg/week when he started to take glucosamine hydrochloride 3000mg and chondroitin sulphate 2400mg daily. Other medications th ...
... receiving warfarin who self-medicated with glucosamine-chondroitin supplements (6,7). In one, a 69year-old man with chronic atrial fibrillation was receiving oral warfarin 47.5mg/week when he started to take glucosamine hydrochloride 3000mg and chondroitin sulphate 2400mg daily. Other medications th ...
Essentials of ADHD Medications: From Mechanisms of Action to
... insoluble capsule is divided into three compartments: the first one contains the lowest concentration of the drug; the second one contains the highest concentration of the drug; and the third compartment contains molecules that expand with water, resulting in the third compartment pushing out the dr ...
... insoluble capsule is divided into three compartments: the first one contains the lowest concentration of the drug; the second one contains the highest concentration of the drug; and the third compartment contains molecules that expand with water, resulting in the third compartment pushing out the dr ...
IFU - Beckman Coulter
... 1. The test is designed for use with human urine only. 2. Do not dilute the urine samples since this is a qualitative assay. Dilution of samples may produce erroneous results. 3. Interference has been demonstrated from mefenamic acid, a nonopioid analgesic.10 4. Adulteration of the urine sample may ...
... 1. The test is designed for use with human urine only. 2. Do not dilute the urine samples since this is a qualitative assay. Dilution of samples may produce erroneous results. 3. Interference has been demonstrated from mefenamic acid, a nonopioid analgesic.10 4. Adulteration of the urine sample may ...
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHODS FOR ESTIMATION OF FORMOTEROL BULK DRUG AND ITS PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORMS
... presence of Ferric chloride in method A , Potassium Ferericynide in presence of FeCl3 in method B. and Gibb’s reagent in presence Borax in method C .The above methods are simple, sensitive, accurate and precise and can be used for the routine quality control of this drug in bulk as well as in ...
... presence of Ferric chloride in method A , Potassium Ferericynide in presence of FeCl3 in method B. and Gibb’s reagent in presence Borax in method C .The above methods are simple, sensitive, accurate and precise and can be used for the routine quality control of this drug in bulk as well as in ...
CHLOROMYCETIN CAPSULES
... concentrations are found in liver and kidney, and lowest concentrations are found in brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Chloramphenicol enters CSF even in the absence of meningeal inflammation, appearing in concentrations about half of those found in the blood. INDICATIONS AND USAGE (3) Chloramphe ...
... concentrations are found in liver and kidney, and lowest concentrations are found in brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Chloramphenicol enters CSF even in the absence of meningeal inflammation, appearing in concentrations about half of those found in the blood. INDICATIONS AND USAGE (3) Chloramphe ...
Drug interaction

A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance (usually another drug) affects the activity of a drug when both are administered together. This action can be synergistic (when the drug's effect is increased) or antagonistic (when the drug's effect is decreased) or a new effect can be produced that neither produces on its own. Typically, interactions between drugs come to mind (drug-drug interaction). However, interactions may also exist between drugs and foods (drug-food interactions), as well as drugs and medicinal plants or herbs (drug-plant interactions). People taking antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take food containing tyramine as hypertensive crisis may occur (an example of a drug-food interaction). These interactions may occur out of accidental misuse or due to lack of knowledge about the active ingredients involved in the relevant substances.It is therefore easy to see the importance of these pharmacological interactions in the practice of medicine. If a patient is taking two drugs and one of them increases the effect of the other it is possible that an overdose may occur. The interaction of the two drugs may also increase the risk that side effects will occur. On the other hand, if the action of a drug is reduced it may cease to have any therapeutic use because of under dosage. Notwithstanding the above, on occasion these interactions may be sought in order to obtain an improved therapeutic effect. Examples of this include the use of codeine with paracetamol to increase its analgesic effect. Or the combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin in order to overcome bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. It should also be remembered that there are interactions that, from a theoretical standpoint, may occur but in clinical practice have no important repercussions.The pharmaceutical interactions that are of special interest to the practice of medicine are primarily those that have negative effects for an organism. The risk that a pharmacological interaction will appear increases as a function of the number of drugs administered to a patient at the same time.It is possible that an interaction will occur between a drug and another substance present in the organism (i.e. foods or alcohol). Or in certain specific situations a drug may even react with itself, such as occurs with dehydration. In other situations, the interaction does not involve any effect on the drug. In certain cases, the presence of a drug in an individual's blood may affect certain types of laboratory analysis (analytical interference).It is also possible for interactions to occur outside an organism before administration of the drugs has taken place. This can occur when two drugs are mixed, for example, in a saline solution prior to intravenous injection. Some classic examples of this type of interaction include that Thiopentone and Suxamethonium should not be placed in the same syringe and same is true for Benzylpenicillin and Heparin. These situations will all be discussed under the same heading due to their conceptual similarity.Drug interactions may be the result of various processes. These processes may include alterations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug, such as alterations in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug. Alternatively, drug interactions may be the result of the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug, e.g. the co-administration of a receptor antagonist and an agonist for the same receptor.