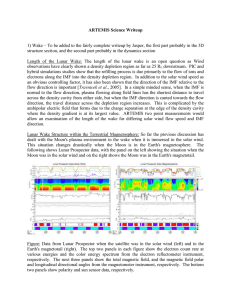
Winter wk 3 – Thus.20.Jan.05
... p.13: If a CME travels at 1 million miles per hour, how long does it take to reach Earth? p.16: The 2 May 1994 event dumped 4600 GW-hr of electricity into Earth’s upper atmosphere. How much energy is that in Joules? p.16: If the Earth’s mean magnetic field is B0=0.5 Gauss, and one Tesla=104 Gauss, b ...
... p.13: If a CME travels at 1 million miles per hour, how long does it take to reach Earth? p.16: The 2 May 1994 event dumped 4600 GW-hr of electricity into Earth’s upper atmosphere. How much energy is that in Joules? p.16: If the Earth’s mean magnetic field is B0=0.5 Gauss, and one Tesla=104 Gauss, b ...
Magnetic Forces
... Earth is a giant magnet, that is, the Earth produces a magnetic field. The North end of a magnet is attracted to the GEOGRAPHIC north pole, which is where the opposite pole must be… So, the magnetic South Pole is in GEOGRAPHIC North and the magnetic North Pole is in GEOGRAPHIC South. ...
... Earth is a giant magnet, that is, the Earth produces a magnetic field. The North end of a magnet is attracted to the GEOGRAPHIC north pole, which is where the opposite pole must be… So, the magnetic South Pole is in GEOGRAPHIC North and the magnetic North Pole is in GEOGRAPHIC South. ...
Magnetic field modelling Directional drilling Earth`s magnetic field
... Earth’s magnetic field can be mathematically ...
... Earth’s magnetic field can be mathematically ...
Magnetism_and_Electromagnetism_Review
... stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons. ...
... stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons. ...
The role of the helical kink instability in solar coronal ejections
... Email: [email protected] Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are large-scale eruptive events observed on the Sun that are powered by the Sun's magnetic field. They are formed as magnetic flux ropes, i.e. magnetic fields twisted about each other. CMEs are the most important drivers of space weat ...
... Email: [email protected] Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are large-scale eruptive events observed on the Sun that are powered by the Sun's magnetic field. They are formed as magnetic flux ropes, i.e. magnetic fields twisted about each other. CMEs are the most important drivers of space weat ...
Magnetism
... • Earth’s magnetosphere is the region of space where the Earth’s magnetic field is confined by the solar wind plasma, blowing outward from the Sun. • The magnetosphere prevents most of the particles from the Sun, carried by solar wind, from hitting the Earth. This asymmetrical region surrounds Earth ...
... • Earth’s magnetosphere is the region of space where the Earth’s magnetic field is confined by the solar wind plasma, blowing outward from the Sun. • The magnetosphere prevents most of the particles from the Sun, carried by solar wind, from hitting the Earth. This asymmetrical region surrounds Earth ...
Magnetosphere - UMass Lowell
... the magnetosphere system; the magnetospheric circulation is determined by redistributing its plasma and fields in a way that allows for dissipation of this energy. This dissipation occurs in the form of: • energizing particles which give up their • dispelling blobs of plasma out the energy to the ne ...
... the magnetosphere system; the magnetospheric circulation is determined by redistributing its plasma and fields in a way that allows for dissipation of this energy. This dissipation occurs in the form of: • energizing particles which give up their • dispelling blobs of plasma out the energy to the ne ...
EM_Jeopardy
... What is electromagnetic induction? What is alternating current? What is a generator? What is a turbine? What is hydroelectricity (or sun or tides)? What is a non-renewable resource? ...
... What is electromagnetic induction? What is alternating current? What is a generator? What is a turbine? What is hydroelectricity (or sun or tides)? What is a non-renewable resource? ...
PracticeQuiz
... 3.Although the polar regions radiate away more heat energy than they receive by insolation in the course of a year, they are prevented from becoming progressively colder each year by the: a. conduction of heat through the interior of the earth b. concentration of earth's magnetic field lines at the ...
... 3.Although the polar regions radiate away more heat energy than they receive by insolation in the course of a year, they are prevented from becoming progressively colder each year by the: a. conduction of heat through the interior of the earth b. concentration of earth's magnetic field lines at the ...
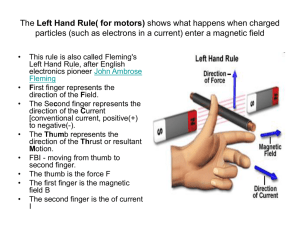
The Left Hand Rule - World of Teaching
... of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, the wheels on electric cars, locomotives and conveyor belts. ...
... of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, the wheels on electric cars, locomotives and conveyor belts. ...
Aurora

An aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere), where their energy is lost. The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emits light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration imparted to the precipitating particles. Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes. Different aspects of an aurora are elaborated in various sections below.