Welcome Back Scientists!
... And magnetic fields can interact to create motion (motors!) But what about the opposite? What is the effect of magnetic force on electrons? http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/legacy/faraday https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yA8gZM3fghc So magnetic fields can cause electrons to move in a ...
... And magnetic fields can interact to create motion (motors!) But what about the opposite? What is the effect of magnetic force on electrons? http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/legacy/faraday https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yA8gZM3fghc So magnetic fields can cause electrons to move in a ...
Magnetic Storm Video Questions
... 8. What written record has provided scientists with valuable information regarding the magnetic field of the planet Earth? ...
... 8. What written record has provided scientists with valuable information regarding the magnetic field of the planet Earth? ...
JRoo (sercle)`s Epic Test Regarding the Field of Magnetism The test
... (Electromagnetic Principles) 4. Faraday’s Law states that a(n) ______ field can induce a(n) ______ field. a. magnetic, magnetic ...
... (Electromagnetic Principles) 4. Faraday’s Law states that a(n) ______ field can induce a(n) ______ field. a. magnetic, magnetic ...
Number 1 - HomeworkNOW.com
... A roll of duct tape or reinforced packing tape About a cup of rice (UNCOOKED) in a “zip-lock” bag ...
... A roll of duct tape or reinforced packing tape About a cup of rice (UNCOOKED) in a “zip-lock” bag ...
Magnetism
... If an atom can be a magnet then what causes magnetism? The answer is electrons in motion. Electrons in an atom are in constant motion, which creates a tiny electrical current (negative charges flowing in one direction). These tiny electrical currents can produce tiny magnetic fields. (Magnetic field ...
... If an atom can be a magnet then what causes magnetism? The answer is electrons in motion. Electrons in an atom are in constant motion, which creates a tiny electrical current (negative charges flowing in one direction). These tiny electrical currents can produce tiny magnetic fields. (Magnetic field ...
The Magnetic Field of Mars: Past, Present and Future
... volatiles. Ion pick-up becomes a significant atmospheric loss mechanism operating for billions of years, enhanced by the low gravity environment and corresponding large scale height that allow the solar wind to interact with exospheric neutrals over an extended volume of space. The MGS magnetic fiel ...
... volatiles. Ion pick-up becomes a significant atmospheric loss mechanism operating for billions of years, enhanced by the low gravity environment and corresponding large scale height that allow the solar wind to interact with exospheric neutrals over an extended volume of space. The MGS magnetic fiel ...
The History of Magnets and Electromagents
... The properties of Magnetism were known to the Greeks as early as 700 B.C. It was found that a certain type of ore had the power to attract pieces of iron which were in it's vicinity. The discovery was made in a province called Magnesia, and the ore was given the name Magnetite after its place of dis ...
... The properties of Magnetism were known to the Greeks as early as 700 B.C. It was found that a certain type of ore had the power to attract pieces of iron which were in it's vicinity. The discovery was made in a province called Magnesia, and the ore was given the name Magnetite after its place of dis ...
UNIT 2 THE BODY
... 3. What happens when the same poles of two magnets are placed together? 4. How are magnets used? 5. Describe the magnetic field generated by a magnet: ...
... 3. What happens when the same poles of two magnets are placed together? 4. How are magnets used? 5. Describe the magnetic field generated by a magnet: ...
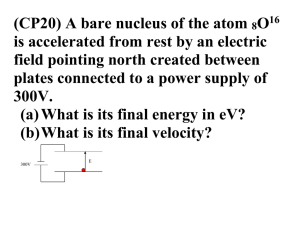
untitled text
... Department of Medicinal & Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 80708, Taiwan ...
... Department of Medicinal & Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 80708, Taiwan ...
Physics Behind the Burglar Alarm
... Like poles repel each other and unlike pole attract each other ...
... Like poles repel each other and unlike pole attract each other ...
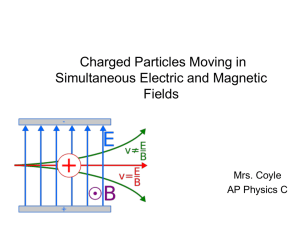
3 Simultaneous Magnetic and Electric Fields
... • Net force is the sum of the electric and magnetic force F = qE + qv x B ...
... • Net force is the sum of the electric and magnetic force F = qE + qv x B ...
Slide ()
... Basic operations of the MRI scanner. A. The static magnetic field (Bo). The protons align parallel or antiparallel to the static magnetic field, creating a small net magnetization vector. While aligned to the magnetic field, the protons precess at the Larmor frequency. B. Transmission of radiofreque ...
... Basic operations of the MRI scanner. A. The static magnetic field (Bo). The protons align parallel or antiparallel to the static magnetic field, creating a small net magnetization vector. While aligned to the magnetic field, the protons precess at the Larmor frequency. B. Transmission of radiofreque ...
Magnetism - Little Miami Schools
... A solenoid with a ferromagnetic core is called an ___________________________ o Magnetic field of an electromagnet is ____________________________ than the magnetic field of a solenoid. o There are four ways to make an electromagnet stronger ...
... A solenoid with a ferromagnetic core is called an ___________________________ o Magnetic field of an electromagnet is ____________________________ than the magnetic field of a solenoid. o There are four ways to make an electromagnet stronger ...
magnetic
... magnetic field. •Electromagnetism: Is the interaction between electricity and magnetism. (See VC) • A solenoid: is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current. (VC or p433: Fig 2) ...
... magnetic field. •Electromagnetism: Is the interaction between electricity and magnetism. (See VC) • A solenoid: is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current. (VC or p433: Fig 2) ...
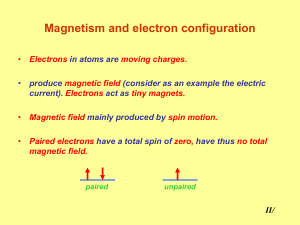
Magnetism and electron configuration
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
SA1 REVISION WORKSHEET 2
... 7. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current carrying solenoid with the help of bar magnet? 8. List the properties of magnetic lines of force. A current through a horizontal power line flows in east to west direction. What is the direction of ...
... 7. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current carrying solenoid with the help of bar magnet? 8. List the properties of magnetic lines of force. A current through a horizontal power line flows in east to west direction. What is the direction of ...
Science Demos for Carden Elementary
... Actually the Leo Stick is just a simple generator. Anytime the amount of magnetic field changes through the area of a coil, that causes an electrical current to flow in the coil. What if we arrange the Magnets and coils around in a circle then we can turn a crank, and make electricity over and over ...
... Actually the Leo Stick is just a simple generator. Anytime the amount of magnetic field changes through the area of a coil, that causes an electrical current to flow in the coil. What if we arrange the Magnets and coils around in a circle then we can turn a crank, and make electricity over and over ...
here - Physics Teacher
... 1. Complete the following sentences, using the words or groups of words in the box below. You may not need some words, and you may use others more than once. ...
... 1. Complete the following sentences, using the words or groups of words in the box below. You may not need some words, and you may use others more than once. ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.