1.All iron materials are not magnetized because the tiny magnetic
... field may have been as effective in changing life forms as X-rays have been in the famous heredity studies of fruit flies. 25. Magnetic levitation will reduce surface friction to near zero. Then only air friction will remain. It can be made relatively small by aerodynamic design, but there is no way ...
... field may have been as effective in changing life forms as X-rays have been in the famous heredity studies of fruit flies. 25. Magnetic levitation will reduce surface friction to near zero. Then only air friction will remain. It can be made relatively small by aerodynamic design, but there is no way ...
The Power of Magnets
... strengthened even more by wrapping the wire around a core. The atoms of certain materials, such as iron, nickel and cobalt, each behave like tiny magnets. Normally, the atoms in something like a lump of iron point in random directions and the individual magnetic fields tend to cancel each other out. ...
... strengthened even more by wrapping the wire around a core. The atoms of certain materials, such as iron, nickel and cobalt, each behave like tiny magnets. Normally, the atoms in something like a lump of iron point in random directions and the individual magnetic fields tend to cancel each other out. ...
Magnetic Fields
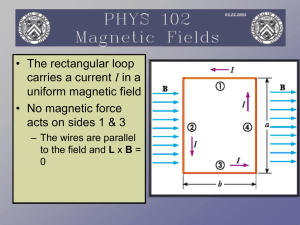
... carries a current I in a uniform magnetic field • No magnetic force acts on sides 1 & 3 – The wires are parallel to the field and L x B = ...
... carries a current I in a uniform magnetic field • No magnetic force acts on sides 1 & 3 – The wires are parallel to the field and L x B = ...
3 - Induction and Motors Notes Handout
... Electricity and Magnetism – were initially two different studies. An observation by ___________ found they were connected. Electric Current - the rate of flow of electrical charge where: I = current (amps, A) Orsted discovered that a ______________ in a wire produced a ...
... Electricity and Magnetism – were initially two different studies. An observation by ___________ found they were connected. Electric Current - the rate of flow of electrical charge where: I = current (amps, A) Orsted discovered that a ______________ in a wire produced a ...
Magnetic Globe - Arbor Scientific
... “The earth acts like there is a large bar magnet placed near its center. However, the earth is not a magnetized chunk of iron like a bar magnet. It is too hot for individual atoms to remain aligned. Currents in the molten part of the earth beneath the crust provide a better explanation for the earth ...
... “The earth acts like there is a large bar magnet placed near its center. However, the earth is not a magnetized chunk of iron like a bar magnet. It is too hot for individual atoms to remain aligned. Currents in the molten part of the earth beneath the crust provide a better explanation for the earth ...
Activity Lesson Plan
... • explain that like poles repel each other while opposite poles attract each other • describe magnetism as a force with force lines extending from an object into space • recognize that most magnetic objects contain iron (some other less common elements are also magnetic) • demonstrate that iron-cont ...
... • explain that like poles repel each other while opposite poles attract each other • describe magnetism as a force with force lines extending from an object into space • recognize that most magnetic objects contain iron (some other less common elements are also magnetic) • demonstrate that iron-cont ...
Activity Lesson Plan
... explain that like poles repel each other while opposite poles attract each other describe magnetism as a force with force lines extending from an object into space recognize that most magnetic objects contain iron (some other less common elements are also magnetic) demonstrate that iron-cont ...
... explain that like poles repel each other while opposite poles attract each other describe magnetism as a force with force lines extending from an object into space recognize that most magnetic objects contain iron (some other less common elements are also magnetic) demonstrate that iron-cont ...
Magnetism - Hoover Elementary School
... Magnetically attract- If two objects magnetically attract to each other, they are pulled toward each other. Iron and steel objects are magnetically attracted to magnets. When two unlike poles of magnets are placed near each other, they are magnetically attracted. Magnetically repel- If two objects m ...
... Magnetically attract- If two objects magnetically attract to each other, they are pulled toward each other. Iron and steel objects are magnetically attracted to magnets. When two unlike poles of magnets are placed near each other, they are magnetically attracted. Magnetically repel- If two objects m ...
Magnetism - Cloudfront.net
... Computers use them to read and write data Your speakers and headphones use them Credit cards and ATM cards store data on ...
... Computers use them to read and write data Your speakers and headphones use them Credit cards and ATM cards store data on ...
Magnetic Fields - Purdue Physics
... Magnetic Properties of Materials • Atoms in many materials act like magnetic dipoles. • Magnetization is the net dipole moment per unit ...
... Magnetic Properties of Materials • Atoms in many materials act like magnetic dipoles. • Magnetization is the net dipole moment per unit ...
Physical Science
... Magnet – an object that attracts certain materials (iron or steel) Magnetic poles – ends of a magnet (north- or southseeking pole) Magnetic field – space all around a magnet where the force of the magnet can act (strongest at the poles) – North and south poles attract (field strongest #15) – North-n ...
... Magnet – an object that attracts certain materials (iron or steel) Magnetic poles – ends of a magnet (north- or southseeking pole) Magnetic field – space all around a magnet where the force of the magnet can act (strongest at the poles) – North and south poles attract (field strongest #15) – North-n ...
Magnetic Fields - Purdue Physics
... Magnetic Properties of Materials • Atoms in many materials act like magnetic dipoles. • Magnetization is the net dipole moment per unit ...
... Magnetic Properties of Materials • Atoms in many materials act like magnetic dipoles. • Magnetization is the net dipole moment per unit ...
Electric and Magnetic Fields
... Electric fields are produced by the presence of voltage or an electrical charge: the higher the voltage, the greater the electric field. The earth’s magnetic field is the force that causes a compass to always point north. Magnetic fields also result from current or the flow of electricity in a wire; ...
... Electric fields are produced by the presence of voltage or an electrical charge: the higher the voltage, the greater the electric field. The earth’s magnetic field is the force that causes a compass to always point north. Magnetic fields also result from current or the flow of electricity in a wire; ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.