Magnetism
... end of a piece of metal If you touch a magnet to a piece of metal the piece of metal will become a magnet If you pull away the magnet, the piece of metal’s magnetism disappears ...
... end of a piece of metal If you touch a magnet to a piece of metal the piece of metal will become a magnet If you pull away the magnet, the piece of metal’s magnetism disappears ...
Sea Floor Spreading
... – Youngest rock near the ridge (where magma cooled and hardened most recently) – Oldest rock near shore (where magma cooled and hardened ~180 million years ago ...
... – Youngest rock near the ridge (where magma cooled and hardened most recently) – Oldest rock near shore (where magma cooled and hardened ~180 million years ago ...
Continental Drift Continental Drift Continental Drift
... will be horizontal – Anywhere in-between, the orientation will be at some angle ...
... will be horizontal – Anywhere in-between, the orientation will be at some angle ...
Magnetism Concepts
... ____The polarity of an electromagnet can be determined using the second right-hand rule. ____Current passing through a conductor is increased from 10 A to 15 A. This decreases the strength of the magnetic field produced by the conductor. ____The speed of an electric motor can be controlled by varyin ...
... ____The polarity of an electromagnet can be determined using the second right-hand rule. ____Current passing through a conductor is increased from 10 A to 15 A. This decreases the strength of the magnetic field produced by the conductor. ____The speed of an electric motor can be controlled by varyin ...
Biot-Savart law
... where Jf is the free current density only. Furthermore • is the closed line integral around the closed curve C, • denotes a 2d surface integral over S enclosed by C •dℓ is an infinitesimal element of the curve C (i.e. a vector with magnitude equal to the length of the infinitesimal line element, an ...
... where Jf is the free current density only. Furthermore • is the closed line integral around the closed curve C, • denotes a 2d surface integral over S enclosed by C •dℓ is an infinitesimal element of the curve C (i.e. a vector with magnitude equal to the length of the infinitesimal line element, an ...
Unit 13 Electromagnetic Fields
... P. 5G Investigate and describe the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in applications such as generators, motors and transformers See Instructional Focus Document (IFD) for TEK Specificity ...
... P. 5G Investigate and describe the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in applications such as generators, motors and transformers See Instructional Focus Document (IFD) for TEK Specificity ...
Slide 1
... Methods of Magnetization • Magnetization using an electric current – A solenoid (a length of copper wire wound into a long coil) is connected to a battery in series. – A iron bar is then placed inside the solenoid – The polarities depend no the direction of the flow of the current A magnet created ...
... Methods of Magnetization • Magnetization using an electric current – A solenoid (a length of copper wire wound into a long coil) is connected to a battery in series. – A iron bar is then placed inside the solenoid – The polarities depend no the direction of the flow of the current A magnet created ...
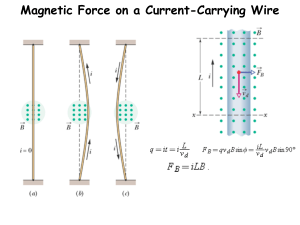
F = BIL (f=force, b=magnetic field, i=current, l
... -Magnetic Field- is a field of force produced by moving electric charges, by electric fields that vary in time, and by the 'intrinsic' magnetic field of elementary particles associated with the spin of the particle. -Magnetic Flux- is a measure of the amount of magnetic B field passing through a giv ...
... -Magnetic Field- is a field of force produced by moving electric charges, by electric fields that vary in time, and by the 'intrinsic' magnetic field of elementary particles associated with the spin of the particle. -Magnetic Flux- is a measure of the amount of magnetic B field passing through a giv ...
Starter
... Worksheet 8Jd/9 (on the website) provides material for a ‘spot the mistake’ exercise. The worksheet provides pictures of a bar magnet with its magnetic field and a starter motor circuit which can be copied onto acetate for use with an OHP. The mistakes on the bar magnet are: the shape of the field ...
... Worksheet 8Jd/9 (on the website) provides material for a ‘spot the mistake’ exercise. The worksheet provides pictures of a bar magnet with its magnetic field and a starter motor circuit which can be copied onto acetate for use with an OHP. The mistakes on the bar magnet are: the shape of the field ...
Magnetism Quiz Review
... A. There is an electric repulsive force between the broken pieces. B. There is an electric attractive force between the broken pieces. C. There is a magnetic repulsive force between the broken pieces. D. There is a magnetic attractive force between the broken pieces. E. There is no force between the ...
... A. There is an electric repulsive force between the broken pieces. B. There is an electric attractive force between the broken pieces. C. There is a magnetic repulsive force between the broken pieces. D. There is a magnetic attractive force between the broken pieces. E. There is no force between the ...
Induced Voltage - Shenendehowa Central Schools
... Changing magnetic fields can create a potential difference (and thus cause current flow) in a conductor. This is the principle behind generators, transformers, induction coils, and magnetic levitation (superconductors, trains). ...
... Changing magnetic fields can create a potential difference (and thus cause current flow) in a conductor. This is the principle behind generators, transformers, induction coils, and magnetic levitation (superconductors, trains). ...
Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Wire - Easy Peasy All-in
... 1. A charged particle, passing through a certain region of space, has a velocity whose magnitude and direction remain constant. (a) If it is known that the external magnetic field is zero everywhere in this region, can you conclude that the external electric field is also zero? Explain. (b) If it is ...
... 1. A charged particle, passing through a certain region of space, has a velocity whose magnitude and direction remain constant. (a) If it is known that the external magnetic field is zero everywhere in this region, can you conclude that the external electric field is also zero? Explain. (b) If it is ...
Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging
... supporting reason if you decide that one is incorrect: a. Nuclear paramagnetism means the nuclear spins align along the magnetic field and generate a macroscopic magnetization. b. The nuclear magnetization of a sample disappears when the applied magnetic field is removed (turned off), or the sample ...
... supporting reason if you decide that one is incorrect: a. Nuclear paramagnetism means the nuclear spins align along the magnetic field and generate a macroscopic magnetization. b. The nuclear magnetization of a sample disappears when the applied magnetic field is removed (turned off), or the sample ...
Transformers and Generators - juan
... strength of the magnetic field through the wire produces a force which drives the electric charges around the wire. AS the loop spins, the direction of the force changes, so too then does the direction of the current The changing direction of the force after every 180 degrees of rotation gives the a ...
... strength of the magnetic field through the wire produces a force which drives the electric charges around the wire. AS the loop spins, the direction of the force changes, so too then does the direction of the current The changing direction of the force after every 180 degrees of rotation gives the a ...
Ancolor Magnetic Inspection Powders
... The Rapid Response Premix Facility for the Powdered Metal Industry ...
... The Rapid Response Premix Facility for the Powdered Metal Industry ...
B v Q l - Rowan County Schools
... • A proton moving east experiences a force of 8.8 x 1019 N upward due to the Earth’s magnetic field. At this location, the field has a magnitude of 5.5 x 10-5 T to the north. Find the velocity of the ...
... • A proton moving east experiences a force of 8.8 x 1019 N upward due to the Earth’s magnetic field. At this location, the field has a magnitude of 5.5 x 10-5 T to the north. Find the velocity of the ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.