Electromagnetic induction
... • What must happen to a conductor (or to the magnetic field in which it’s placed) for electricity to be generated? • What factors would cause the induced emf to be greater? • What is Lenz’s law and what are the applications of this law? ...
... • What must happen to a conductor (or to the magnetic field in which it’s placed) for electricity to be generated? • What factors would cause the induced emf to be greater? • What is Lenz’s law and what are the applications of this law? ...
Magnet Notes
... • Shape is shown with lines drawn from the north pole of the magnet to the south pole, called magnetic field lines • The closer together the magnetic field lines are the stronger the magnetic force is • What part of the magnet has the strongest magnetic force? How can you tell? • AT THE POLES – magn ...
... • Shape is shown with lines drawn from the north pole of the magnet to the south pole, called magnetic field lines • The closer together the magnetic field lines are the stronger the magnetic force is • What part of the magnet has the strongest magnetic force? How can you tell? • AT THE POLES – magn ...
1] How will you show the directive property of a magnet? Suspend a
... A] A magnetic compass: It is a small magnetic needle pivoted at the centre of a brass box having a glass top. The needle is free to move about its centre. The end of the needle, which indicates its north pole, is painted red. B] Magnetic field: The space around the magnet where its influence can be ...
... A] A magnetic compass: It is a small magnetic needle pivoted at the centre of a brass box having a glass top. The needle is free to move about its centre. The end of the needle, which indicates its north pole, is painted red. B] Magnetic field: The space around the magnet where its influence can be ...
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM The magnetic field created by an
... Atoms become positively charged when they have fewer electrons than protons. They are then called CATIONS. ...
... Atoms become positively charged when they have fewer electrons than protons. They are then called CATIONS. ...
Heat Capacity Studies of NdNi4Si Compound
... The study of the heat capacity of the intermetallic compound NdNi4 Si including the effect of the magnetic field is reported. This compound crystallizes in the hexagonal CaCu5 -type structure, space group P 6/mmm. NdNi4 Si is ferromagnetic with TC = 8 K and the saturation magnetic moment of 1.5 µB / ...
... The study of the heat capacity of the intermetallic compound NdNi4 Si including the effect of the magnetic field is reported. This compound crystallizes in the hexagonal CaCu5 -type structure, space group P 6/mmm. NdNi4 Si is ferromagnetic with TC = 8 K and the saturation magnetic moment of 1.5 µB / ...
Electromagnetism Unit 2014
... • The buildup of charges on an object is called static electricity • Static discharge is the movement of charges from one object to another. – Think of this like shocking yourself when you drag your feet on the carpet and touch a door handle. – You feel the “shock.” – What you really experienced is ...
... • The buildup of charges on an object is called static electricity • Static discharge is the movement of charges from one object to another. – Think of this like shocking yourself when you drag your feet on the carpet and touch a door handle. – You feel the “shock.” – What you really experienced is ...
Document
... The supercurrent density has a limit: JC When the superconductor is applied with a magnetic field, a supercurrent is generated so as to maintain the perfect diamagnetism. If the current density needed to screen the field exceeds JC, the superconductor will lose its superconductivity. This limit of t ...
... The supercurrent density has a limit: JC When the superconductor is applied with a magnetic field, a supercurrent is generated so as to maintain the perfect diamagnetism. If the current density needed to screen the field exceeds JC, the superconductor will lose its superconductivity. This limit of t ...
Particle Accelerators - University of Birmingham
... The particles move around in a spiral shaped path. The force which keeps them moving this way is provided by a static magnetic field. This is the Centripetal Force (a force that causes circular motion). ...
... The particles move around in a spiral shaped path. The force which keeps them moving this way is provided by a static magnetic field. This is the Centripetal Force (a force that causes circular motion). ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... – Light inconsistent with longitudinal waves in an ethereal medium – Still an excellent approximation when feature sizes are large compared with the wavelength of light ...
... – Light inconsistent with longitudinal waves in an ethereal medium – Still an excellent approximation when feature sizes are large compared with the wavelength of light ...
PlasmaTech_SinglePar..
... that all of the charged particles in a local area respond to this motion. This is a collective behavior that is a requirement for our system to be in the plasma state. In general it is the collective behavior that is most important to understanding how a plasma operates. Unfortunately it also is fai ...
... that all of the charged particles in a local area respond to this motion. This is a collective behavior that is a requirement for our system to be in the plasma state. In general it is the collective behavior that is most important to understanding how a plasma operates. Unfortunately it also is fai ...
Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action
... • At the northern pole, the compass needle would point straight down • At the southern pole, it would point straight up • Earth’s magnetic field has changed direction throughout geologic time (at least 20 reversals in the past 5 million years) ...
... • At the northern pole, the compass needle would point straight down • At the southern pole, it would point straight up • Earth’s magnetic field has changed direction throughout geologic time (at least 20 reversals in the past 5 million years) ...
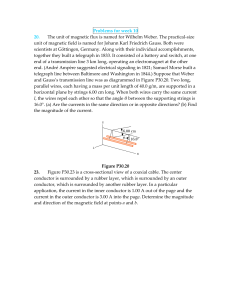
Section 11: GRAPHIC STIMULUS
... 25. B. The opposite poles of each magnet will be drawn together and the two ends will stick to each other. 26. C. The Northern lights 27. A. It ensures that the compass needle always points to the north pole ...
... 25. B. The opposite poles of each magnet will be drawn together and the two ends will stick to each other. 26. C. The Northern lights 27. A. It ensures that the compass needle always points to the north pole ...
Pendahuluan Mesin Elektrik / Mesin Elektrik Secara Am
... Electric motors are used to operate washing machines, elevators, cranes etc while electric generators are used to generate electricity for power generation and alternator for charging car battery. ...
... Electric motors are used to operate washing machines, elevators, cranes etc while electric generators are used to generate electricity for power generation and alternator for charging car battery. ...
SA Power Networks 1 Electric and Magnetic Fields
... appliance is plugged into an active power outlet, it emits an electric field. The appliance doesn’t need to be running. Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found where current is present. The field strength increases with current, so a stronger magnetic field exists near appliances running on ‘high’ ...
... appliance is plugged into an active power outlet, it emits an electric field. The appliance doesn’t need to be running. Magnetic fields Magnetic fields are found where current is present. The field strength increases with current, so a stronger magnetic field exists near appliances running on ‘high’ ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.




![1] How will you show the directive property of a magnet? Suspend a](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001625610_1-56f6c1434741143a0c22f345e56fb644-300x300.png)