Physics 121 Lab: Finding the horizontal component of the magnetic
... Because the magnetic field at your lab station is mainly from the earth, you should expect that a compass needle points roughly north. Check that it does so. You may have to raise the compass a few inches above the surface of the table to avoid the effect of steel screws. Place the compass carefully ...
... Because the magnetic field at your lab station is mainly from the earth, you should expect that a compass needle points roughly north. Check that it does so. You may have to raise the compass a few inches above the surface of the table to avoid the effect of steel screws. Place the compass carefully ...
Magnetism f08
... energy is wasted in hysteresis loop. Soft magnetic materials are desirable in transformer cores and other applications where residual magnetization is undesirable Defects, such as nonmagnetic phases and voids restrict easy movement of domain walls and are to be avoided in soft magnetic materials. So ...
... energy is wasted in hysteresis loop. Soft magnetic materials are desirable in transformer cores and other applications where residual magnetization is undesirable Defects, such as nonmagnetic phases and voids restrict easy movement of domain walls and are to be avoided in soft magnetic materials. So ...
Lunar Magnetic Anomalies
... • Unlike Earth, the moon now has no global magnetic field • However, small spot-like magnetic fields are detected by lunar satellites – lunar magnetic anomalies • Anomalies suggest remanent magnetisation of lunar crust à Possibly caused by an ancient dipolar magnetic field 3-4 billion years ago ...
... • Unlike Earth, the moon now has no global magnetic field • However, small spot-like magnetic fields are detected by lunar satellites – lunar magnetic anomalies • Anomalies suggest remanent magnetisation of lunar crust à Possibly caused by an ancient dipolar magnetic field 3-4 billion years ago ...
Magnetostriction vs. Magnetoelastic Effects
... all ferromagnetic materials. It couples elastic, electric, magnetic and in some situations also thermal fields and is of great industrial interest for use in sensors, actuators, adaptive or functional structures, robotics, transducers and MEMS. A magnetostrictive material develops large mechanical d ...
... all ferromagnetic materials. It couples elastic, electric, magnetic and in some situations also thermal fields and is of great industrial interest for use in sensors, actuators, adaptive or functional structures, robotics, transducers and MEMS. A magnetostrictive material develops large mechanical d ...
Slide 1
... The emf is proportional to the number of loops times the rate of change of the magnetic field in the loops ...
... The emf is proportional to the number of loops times the rate of change of the magnetic field in the loops ...
Magma Supply Vs Magma Plumbing
... were developed in the 2nd World War as a way to detect submarines (and later mines) Measurements of the magnetic field were first made with a fluxgate magnetometer. Such instruments are still in use today ...
... were developed in the 2nd World War as a way to detect submarines (and later mines) Measurements of the magnetic field were first made with a fluxgate magnetometer. Such instruments are still in use today ...
Magma Supply Vs Magma Plumbing
... were developed in the 2nd World War as a way to detect submarines (and later mines) Measurements of the magnetic field were first made with a fluxgate magnetometer. Such instruments are still in use today ...
... were developed in the 2nd World War as a way to detect submarines (and later mines) Measurements of the magnetic field were first made with a fluxgate magnetometer. Such instruments are still in use today ...
Lesson 16 - Magnetic Fields III
... magnetic field was no longer aligned with the external magnetic field. If we release the current loop, the external magnetic field will do work on our current loop to realign the fields. Thus, magnetic potential energy was stored in turning the loop to the unaligned position and given up when the lo ...
... magnetic field was no longer aligned with the external magnetic field. If we release the current loop, the external magnetic field will do work on our current loop to realign the fields. Thus, magnetic potential energy was stored in turning the loop to the unaligned position and given up when the lo ...
EE 333 Electricity and Magnetism
... 1. Basic understanding of the origin of Maxwell’s equations. 2. Physical intuitive understanding for electromagnetic theory. 3. Intimate understanding of Maxwell’s equations. 4. Ability to use differential vector mathematics to solve electromagnetic problems. 5. Knowledge of analytical and numerical ...
... 1. Basic understanding of the origin of Maxwell’s equations. 2. Physical intuitive understanding for electromagnetic theory. 3. Intimate understanding of Maxwell’s equations. 4. Ability to use differential vector mathematics to solve electromagnetic problems. 5. Knowledge of analytical and numerical ...
numerical code balmer-szdyn for spectroscopy of hydrogen isotopes
... crossed magnetic and electric fields using the four-dimensional symmetry of the hydrogen atom; calculation of the static broadening of these lines with the help of a fast procedure of averaging over direction and amplitude of the electric microfield produced by the plasma ions; 2) description of the ...
... crossed magnetic and electric fields using the four-dimensional symmetry of the hydrogen atom; calculation of the static broadening of these lines with the help of a fast procedure of averaging over direction and amplitude of the electric microfield produced by the plasma ions; 2) description of the ...
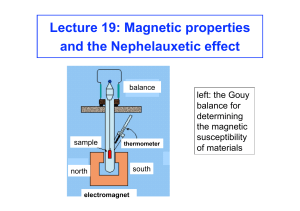
Lecture 19: Magnetic properties and the Nephelauxetic effect
... The value of λ is negligible for very light atoms, but increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row anal ...
... The value of λ is negligible for very light atoms, but increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row anal ...
Using Magnetism to Induce an Electric Current
... a solenoid will create a magnetic field in the solenoid. The magnetic field creates a repulsive force against the permanent magnet. Holding the right hand with the fingers curled and the thumb extended will determine the ...
... a solenoid will create a magnetic field in the solenoid. The magnetic field creates a repulsive force against the permanent magnet. Holding the right hand with the fingers curled and the thumb extended will determine the ...
Reading Comprehension Worksheet - 9th Grade
... An object that attracts metals, especially iron, is called a magnet. The area near the magnet where it has enough power to attract things is called its magnetic field. The farther away from the magnet an item is, the weaker the magnetic field is. When it is weak, it is less likely an object will becom ...
... An object that attracts metals, especially iron, is called a magnet. The area near the magnet where it has enough power to attract things is called its magnetic field. The farther away from the magnet an item is, the weaker the magnetic field is. When it is weak, it is less likely an object will becom ...
Magnetism
... magnets by bringing them close to a magnet; magnetism is induced by aligning areas called domains within a magnetic field Domains strong coupling between neighboring atoms of ferromagnetic materials to form large groups of atoms whose net spins are aligned Unmagnetized substance domains randomly ...
... magnets by bringing them close to a magnet; magnetism is induced by aligning areas called domains within a magnetic field Domains strong coupling between neighboring atoms of ferromagnetic materials to form large groups of atoms whose net spins are aligned Unmagnetized substance domains randomly ...
1 Basics of magnetic materials Definitions in SI
... the total energy cost is U ≈ NJS 2 (π / N ) 2 For lattice spacing a, energy density per domain wall area for N atom thick wall ~ π 2 JS 2 /( Na 2 ) ...
... the total energy cost is U ≈ NJS 2 (π / N ) 2 For lattice spacing a, energy density per domain wall area for N atom thick wall ~ π 2 JS 2 /( Na 2 ) ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.