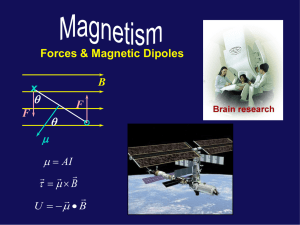
Magnets
... • You can change the strength of a magnetic field produced by a current… • How can you change the strength? • Simply by looping, or winding, the wire of the wire! • The strength will increase as the number of loops or coils ...
... • You can change the strength of a magnetic field produced by a current… • How can you change the strength? • Simply by looping, or winding, the wire of the wire! • The strength will increase as the number of loops or coils ...
What is Light - edhs2dscience
... Mechanical Waves vs Electromagnetic Wave • water wave: energy moves ahead by vibrating water • Sound wave: energy moves ahead by vibrating air • Wave in a rope: rope twists to send energy impulse ahead • Electromagnetic wave does not need medium. It can travel through vacuum, a space free of matter ...
... Mechanical Waves vs Electromagnetic Wave • water wave: energy moves ahead by vibrating water • Sound wave: energy moves ahead by vibrating air • Wave in a rope: rope twists to send energy impulse ahead • Electromagnetic wave does not need medium. It can travel through vacuum, a space free of matter ...
What Is Sea-Floor Spreading?
... • In sea-floor spreading, the sea floor spreads apart along both sides of a mid-ocean ridge as new crust is added. As a result, the ocean floors move like conveyor belts, carrying the continents along with them. ...
... • In sea-floor spreading, the sea floor spreads apart along both sides of a mid-ocean ridge as new crust is added. As a result, the ocean floors move like conveyor belts, carrying the continents along with them. ...
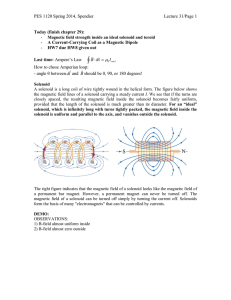
magnetic field
... In most atoms the magnetic effect of the electrons cancel each other out In ferromagnetic materials the magnetic effects of the electrons do not fully cancel each other out, atoms then are like tiny magnets. Ferromagnetic materials consists of small regions (called domains) in which all the N magnet ...
... In most atoms the magnetic effect of the electrons cancel each other out In ferromagnetic materials the magnetic effects of the electrons do not fully cancel each other out, atoms then are like tiny magnets. Ferromagnetic materials consists of small regions (called domains) in which all the N magnet ...
Magnetic Levitation
... any help. But, if I flip one of the magnets over and I try and push the two south poles together, they resist and push apart. They never connect to each other, no matter how hard I push. Take a look at the levitating pencil again. I lined up all the south poles so they would repel each other, which ...
... any help. But, if I flip one of the magnets over and I try and push the two south poles together, they resist and push apart. They never connect to each other, no matter how hard I push. Take a look at the levitating pencil again. I lined up all the south poles so they would repel each other, which ...
PWE 19-3: Magnetic Levitation
... You set up a uniform horizontal magnetic field that points from south to north and has magnitude 2.00 * 1022 T. (This is about 400 times stronger than Earth’s magnetic field, but easily achievable with common magnets.) You want to place a straight copper wire of diameter 0.812 mm in this field, then ...
... You set up a uniform horizontal magnetic field that points from south to north and has magnitude 2.00 * 1022 T. (This is about 400 times stronger than Earth’s magnetic field, but easily achievable with common magnets.) You want to place a straight copper wire of diameter 0.812 mm in this field, then ...
1. A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane... as shown in Figure. In which plane should a straight... X- Guess Questions solved SA-1: Magnetic effects of currents
... magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of field concept. Answer: Current carrying loops behave like bar magnets and both have their associated lines of field. This modifies the already existing earth’s ma ...
... magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of field concept. Answer: Current carrying loops behave like bar magnets and both have their associated lines of field. This modifies the already existing earth’s ma ...
In lecture demonstrations and in the laboratory class
... suspended and still maintain an extremely small restoring constant. When the restoring constant approaches zero the low axial friction makes the device suitable for demonstrating the conservation of angular momentum. If the iron core of the solenoid is removed, the suspension may be used as an accur ...
... suspended and still maintain an extremely small restoring constant. When the restoring constant approaches zero the low axial friction makes the device suitable for demonstrating the conservation of angular momentum. If the iron core of the solenoid is removed, the suspension may be used as an accur ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.