Magnetism_and_Electromagnetism_Review
... If they come close enough to Earth, they interact with the atmosphere This causes the bright colors An aurora is only seen near the poles because that is the only place where the magnetic field lines come close to Earth ...
... If they come close enough to Earth, they interact with the atmosphere This causes the bright colors An aurora is only seen near the poles because that is the only place where the magnetic field lines come close to Earth ...
Lesson 5 Magnetism and Electricity Notes
... By adding a metal core, you can make the strongest magnetic field of all. ...
... By adding a metal core, you can make the strongest magnetic field of all. ...
Magnetism
... magnets too, although this effect dies away once the object has been moved from the magnetic field. You can create a magnet yourself by magnetizing something metal (such as a needle or a paper clip.) Rub it with a strong magnet in the same direction 30 or 40 times. Some metals are magnetized easily ...
... magnets too, although this effect dies away once the object has been moved from the magnetic field. You can create a magnet yourself by magnetizing something metal (such as a needle or a paper clip.) Rub it with a strong magnet in the same direction 30 or 40 times. Some metals are magnetized easily ...
Fundamental nuclear symmetries meet classical electrodynamic
... • extends to quantum field theories • field is everywhere always E (x, t) • differentiable, integrable • field lines, equipotentials • powerful techniques for solving complex problems ...
... • extends to quantum field theories • field is everywhere always E (x, t) • differentiable, integrable • field lines, equipotentials • powerful techniques for solving complex problems ...
Winter wk 3 – Thus.20.Jan.05
... p.16: The 2 May 1994 event dumped 4600 GW-hr of electricity into Earth’s upper atmosphere. How much energy is that in Joules? p.16: If the Earth’s mean magnetic field is B0=0.5 Gauss, and one Tesla=104 Gauss, by what percent does 2000 nanoTesla change Earth’s field? p.54: For the CME of 1 Sept 1859: ...
... p.16: The 2 May 1994 event dumped 4600 GW-hr of electricity into Earth’s upper atmosphere. How much energy is that in Joules? p.16: If the Earth’s mean magnetic field is B0=0.5 Gauss, and one Tesla=104 Gauss, by what percent does 2000 nanoTesla change Earth’s field? p.54: For the CME of 1 Sept 1859: ...
Chapter 16 Study Guide
... 3.) How are a magnetic field and a moving electrical charge related? 4.) What is the core of an electromagnet usually made of? Memorize the following formula for transformers: Input coils/output coils = input voltage/ output voltage For example, a transformer has an input voltage of 5,000 V and 1,00 ...
... 3.) How are a magnetic field and a moving electrical charge related? 4.) What is the core of an electromagnet usually made of? Memorize the following formula for transformers: Input coils/output coils = input voltage/ output voltage For example, a transformer has an input voltage of 5,000 V and 1,00 ...
Electricity and Magnetism Test Review
... What is an electrical insulator? What does it have? If like repel, what do opposites do? What does the strength of an electrical field depend on? What happens to magnetic force if the distance between magnets increases? Describe the behavior of magnetic poles. Like poles / Opposite poles. What do el ...
... What is an electrical insulator? What does it have? If like repel, what do opposites do? What does the strength of an electrical field depend on? What happens to magnetic force if the distance between magnets increases? Describe the behavior of magnetic poles. Like poles / Opposite poles. What do el ...
Non-KAM dynamical chaos in semiconductor superlattices Arkadii Krokhin, UNT
... I will present our new results concerning electron dynamics in semiconductor superlattices in the presence of non-parallel electric and magnetic field. In this geometry the electrons in the superlattice miniband turn out to form a non-KAM dynamical system that exhibits a non-traditional chaotic beha ...
... I will present our new results concerning electron dynamics in semiconductor superlattices in the presence of non-parallel electric and magnetic field. In this geometry the electrons in the superlattice miniband turn out to form a non-KAM dynamical system that exhibits a non-traditional chaotic beha ...
Homework-Force
... A Hall probe is a device for measuring magnetic fields. In a typical device a current I flows in a ribbon of n-type doped semiconductor located in the magnetic field. In an ntype doped semiconductor the charge caries are electrons. In the steady state there is a voltage difference VH between the edg ...
... A Hall probe is a device for measuring magnetic fields. In a typical device a current I flows in a ribbon of n-type doped semiconductor located in the magnetic field. In an ntype doped semiconductor the charge caries are electrons. In the steady state there is a voltage difference VH between the edg ...
ELECTROMAGNETISM
... interactions as physicists understood around the year 1800. There appear to be three fundamentally different types of interactions: gravitational, electrical, and magnetic. Many types of interactions that appear superficially to be distinct --stickiness, chemical interactions, the energy an archer s ...
... interactions as physicists understood around the year 1800. There appear to be three fundamentally different types of interactions: gravitational, electrical, and magnetic. Many types of interactions that appear superficially to be distinct --stickiness, chemical interactions, the energy an archer s ...
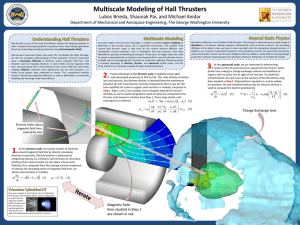
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.