Magnets and Electricity
... increases the strength of the electromagnet. • 8. A changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor. • 9. A charged particle experiences no magnetic force when moving parallel to a magnetic field, but when it is moving perpendicular to the field it experiences a force perpendicula ...
... increases the strength of the electromagnet. • 8. A changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor. • 9. A charged particle experiences no magnetic force when moving parallel to a magnetic field, but when it is moving perpendicular to the field it experiences a force perpendicula ...
Magnetism guided reading
... 26. When using the right hand rule, you should point your thumb in which direction? ...
... 26. When using the right hand rule, you should point your thumb in which direction? ...
Magnetism guided reading
... 26. When using the right hand rule, you should point your thumb in which direction? ...
... 26. When using the right hand rule, you should point your thumb in which direction? ...
Chapter 15 Lesson 2 How are Electricity and Magnetism Related
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
The Motor Effect
... Magnets and Magnetic fields •Magnets have a north and a south pole •Like poles repel, opposite poles attract ...
... Magnets and Magnetic fields •Magnets have a north and a south pole •Like poles repel, opposite poles attract ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... • These charged particles can be at rest (“static electricity”) • or they may be moving (“current electricity”) ...
... • These charged particles can be at rest (“static electricity”) • or they may be moving (“current electricity”) ...
What is magnetism?
... • But if you try to bring two of the same poles (two norths or two souths) together they will repel each other. ...
... • But if you try to bring two of the same poles (two norths or two souths) together they will repel each other. ...
Magnets and Electricity
... atoms that line up based on their poles If a magnet is cut, each piece will still have two poles ...
... atoms that line up based on their poles If a magnet is cut, each piece will still have two poles ...
solenoid
... discovery. While investigating other aspects of electricity and magnetism, he took two parallel wires and demonstrated that their respective magnetic fields can interact to cause a force when currents were sent through them. If the respective currents flow in opposing directions, the magnetic field ...
... discovery. While investigating other aspects of electricity and magnetism, he took two parallel wires and demonstrated that their respective magnetic fields can interact to cause a force when currents were sent through them. If the respective currents flow in opposing directions, the magnetic field ...
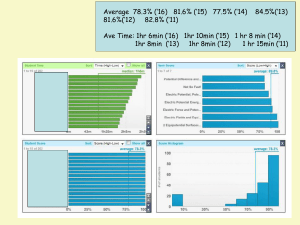
Average 78.3% (`16) 81.6% (`15) 77.5% (`14) 84.5%(`13) 81.6%(`12
... André-Marie Ampère in 1820 was able to devise through experimentation the formula for the angular dependence of the force between two current elements. In all these descriptions, the force was always given in terms of the properties of the objects involved and the distances between them rather than ...
... André-Marie Ampère in 1820 was able to devise through experimentation the formula for the angular dependence of the force between two current elements. In all these descriptions, the force was always given in terms of the properties of the objects involved and the distances between them rather than ...
are conductors (metals). Insulators (rubber,
... (The manipulated variable could be the number of coils of wire and the responding variable could be the number of paperclips the magnet ...
... (The manipulated variable could be the number of coils of wire and the responding variable could be the number of paperclips the magnet ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.