FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Content
... What’s the difference between motional emf and induced emf ? “Induced emf” is the more general term. By Faraday’s Law, you get an induced emf whenever there’s a changing magnetic flux through a loop. If the changing emf is due to some kind motion of a conductor in a magnetic field, you would call it ...
... What’s the difference between motional emf and induced emf ? “Induced emf” is the more general term. By Faraday’s Law, you get an induced emf whenever there’s a changing magnetic flux through a loop. If the changing emf is due to some kind motion of a conductor in a magnetic field, you would call it ...
Click here for experiment - Environmental Learning Center
... different directions they cancel each other out. Most materials are not magnetic because the electrons spin constantly in many directions and cancel each-other out. Magnets have two polls; a north and a south pole. The magnetic field travels from north to south. An electromagnet is a magnet that is ...
... different directions they cancel each other out. Most materials are not magnetic because the electrons spin constantly in many directions and cancel each-other out. Magnets have two polls; a north and a south pole. The magnetic field travels from north to south. An electromagnet is a magnet that is ...
THE EFFECT OF ELECTRIC FIELD ON
... human organs or body parts (brain, lungs, digestive organs, etc.) based on their electromagnetic features (conductivity, electric and magnetic permittivity). The distribution of the electric field surrounding humans will be given, as well as the values of the field which penetrates humans. Likewise, ...
... human organs or body parts (brain, lungs, digestive organs, etc.) based on their electromagnetic features (conductivity, electric and magnetic permittivity). The distribution of the electric field surrounding humans will be given, as well as the values of the field which penetrates humans. Likewise, ...
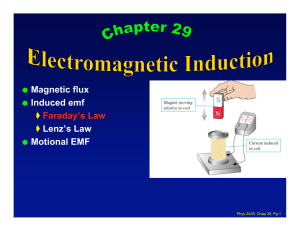
Magnetic flux Induced emf Faraday`s Law Lenz`s Law Motional EMF
... A square coil of wire with side 5.00 cm contains 100 loops and is positioned perpendicular to an uniform 0.60-T magnetic field as shown. It is quickly and uniformly pulled from the field (moving perpendicular to B) to a region where B drops abruptly to zero. At t=0, the right edge of the coil is the ...
... A square coil of wire with side 5.00 cm contains 100 loops and is positioned perpendicular to an uniform 0.60-T magnetic field as shown. It is quickly and uniformly pulled from the field (moving perpendicular to B) to a region where B drops abruptly to zero. At t=0, the right edge of the coil is the ...
PHY481 - Lecture 5: Electrostatics
... where qencl is the total charge inside the closed surface S, and usually we will replace it by q, with the fact that it is the enclosed charge taken implicitly. This law follows from Coulomb’s law and superposition in combination with the properties of electric field lines. The proof of Gauss’s law ...
... where qencl is the total charge inside the closed surface S, and usually we will replace it by q, with the fact that it is the enclosed charge taken implicitly. This law follows from Coulomb’s law and superposition in combination with the properties of electric field lines. The proof of Gauss’s law ...
Advancements in Electromagnetic Material Properties
... rather than occupying any space. It has been calculated that if the model were accurate (that the electron is a sphere of spinning charge), in order to produce the moments that have been recorded in experimentation, electrons would need to spin faster than the speed of light [1]. It has been assumed ...
... rather than occupying any space. It has been calculated that if the model were accurate (that the electron is a sphere of spinning charge), in order to produce the moments that have been recorded in experimentation, electrons would need to spin faster than the speed of light [1]. It has been assumed ...
Physics 2102 Lecture 4
... More Properties of conductors We know the field inside the conductor is zero, and the excess charges are all on the surface. The charges produce an electric field outside the conductor. On the surface of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium, the electric field is always perpendicular to the surf ...
... More Properties of conductors We know the field inside the conductor is zero, and the excess charges are all on the surface. The charges produce an electric field outside the conductor. On the surface of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium, the electric field is always perpendicular to the surf ...
Electromagnetism
... video camera. The other device he’s holding is an electromagnetic field detector. Ghost hunters often use detectors like this one because they believe that ghosts cause changes in electromagnetic fields. The problem for ghost hunters is that electromagnetic fields can be produced by many devices. Yo ...
... video camera. The other device he’s holding is an electromagnetic field detector. Ghost hunters often use detectors like this one because they believe that ghosts cause changes in electromagnetic fields. The problem for ghost hunters is that electromagnetic fields can be produced by many devices. Yo ...
Section 17.2
... 17.2 Electromagnets in Toasters By changing the amount of current, you can easily change the strength of an electromagnet or even turn its magnetism on and off. ...
... 17.2 Electromagnets in Toasters By changing the amount of current, you can easily change the strength of an electromagnet or even turn its magnetism on and off. ...
Chapter 7. Electrodynamics 7.1. Electromotive Force
... fraction of space, and therefore definitely will not intercept all field lines outside the square loop. Therefore, there will be more field lines pointing into the page then there are field lines pointing out of the page. Consequently, the net magnetic flux will be pointing into the page. When the c ...
... fraction of space, and therefore definitely will not intercept all field lines outside the square loop. Therefore, there will be more field lines pointing into the page then there are field lines pointing out of the page. Consequently, the net magnetic flux will be pointing into the page. When the c ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.