Magnetic Effects of Electric current
... When a proton enters in a region of magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. As a result of the force, the path of the proton becomes circular. Hence, its velocity and momentum change. Question 11: State Fleming’s left-hand rule. Answer: Fleming’s left hand rule states that if we arrange the ...
... When a proton enters in a region of magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. As a result of the force, the path of the proton becomes circular. Hence, its velocity and momentum change. Question 11: State Fleming’s left-hand rule. Answer: Fleming’s left hand rule states that if we arrange the ...
B - LSU Physics
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
Lecture 1
... Heinrich Hertz verified Maxwell’s predictions He produced electromagnetic waves Æ radio, TV, satellite communication, cell phones, etc ...
... Heinrich Hertz verified Maxwell’s predictions He produced electromagnetic waves Æ radio, TV, satellite communication, cell phones, etc ...
LAB COURSE: 255B Fall 2015
... circumstances are beyond our control, we ask that you become familiar with the SIUC Emergency Response Plan and Building Emergency Response Team (BERT) program. Emergency response information is available on posters in buildings on campus, available on BERT's website at www.bert.siu.edu, Department ...
... circumstances are beyond our control, we ask that you become familiar with the SIUC Emergency Response Plan and Building Emergency Response Team (BERT) program. Emergency response information is available on posters in buildings on campus, available on BERT's website at www.bert.siu.edu, Department ...
Effective Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert Equation for a Conducting
... The Landau-Lifshitz (LL) equation [1] and its modification, the Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert (LLG) equation [2,3], are the basic equations for studying the magnetization dynamics in ferromagnetic materials. Though these equations are equivalent from the mathematical point of view [4] (specifically, the L ...
... The Landau-Lifshitz (LL) equation [1] and its modification, the Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert (LLG) equation [2,3], are the basic equations for studying the magnetization dynamics in ferromagnetic materials. Though these equations are equivalent from the mathematical point of view [4] (specifically, the L ...
Fundamentals of magnetic field
... The flux change occurs either because the magnetic field is changing with time (transformer inductance) or because the wire loop is moving relative to a magnetic field (motional inductance). The Faraday's induction law describes both phenomena. a) If a wire loop is fixed and the flux is varying with ...
... The flux change occurs either because the magnetic field is changing with time (transformer inductance) or because the wire loop is moving relative to a magnetic field (motional inductance). The Faraday's induction law describes both phenomena. a) If a wire loop is fixed and the flux is varying with ...
Electric and Magnetic Power - Everything You Need to Succeed 4th
... Charged particles can move from one object to another. When the positive and negative particles do not balance, it is called static electricity. The word static means “not moving.” When we talk about static electricity, we usually talk about one thing with a positive charge and one thing with a nega ...
... Charged particles can move from one object to another. When the positive and negative particles do not balance, it is called static electricity. The word static means “not moving.” When we talk about static electricity, we usually talk about one thing with a positive charge and one thing with a nega ...
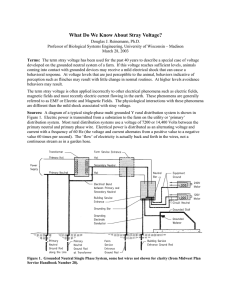
What Do We Know About Stray Voltage?
... transformer. The farm wiring system carries 240 Volt on 2 ‘hot’ or phase wires and 120 Volts electrical power on one ‘hot’ or phase wire and one neutral wire. The neutral is also referred to as a grounded conductor (white colored insulation). The National Electric Code also requires the use of a gro ...
... transformer. The farm wiring system carries 240 Volt on 2 ‘hot’ or phase wires and 120 Volts electrical power on one ‘hot’ or phase wire and one neutral wire. The neutral is also referred to as a grounded conductor (white colored insulation). The National Electric Code also requires the use of a gro ...
magnet and magnetism
... is strong enough to influence surrounding atoms. In iron, for example, four electrons are unpaired. These four electrons line up to form a strong atomic magnet. Under the influence of this atomic magnet adjacent atomic magnets line up in the same direction, and the fields of all the aligned atoms co ...
... is strong enough to influence surrounding atoms. In iron, for example, four electrons are unpaired. These four electrons line up to form a strong atomic magnet. Under the influence of this atomic magnet adjacent atomic magnets line up in the same direction, and the fields of all the aligned atoms co ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.