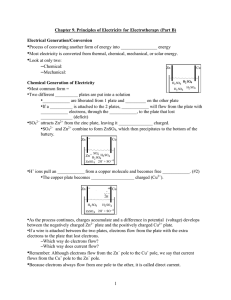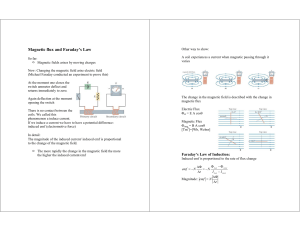
Magnetic flux and Faraday`s Law
... Magnetic flux in a primary coil induces a voltage in a secondary coil. ...
... Magnetic flux in a primary coil induces a voltage in a secondary coil. ...
Ch. 29 and 30 notes
... small magnets, like on the previous page. They tend to be randomly oriented. So iron is not normally a magnet. (E.g, a normal nail doesn't stick to the fridge). But if you put iron into a strong external B field, this will tend to line up all those little domains, and you can magnetize iron this way ...
... small magnets, like on the previous page. They tend to be randomly oriented. So iron is not normally a magnet. (E.g, a normal nail doesn't stick to the fridge). But if you put iron into a strong external B field, this will tend to line up all those little domains, and you can magnetize iron this way ...
Electromagnetic knots and the magnetic flux in superconductors
... equivalent to Maxwell’s standard theory but implies some topological quantization conditions with physical meaning [2, 3, 4]. The model makes use of two fundamental complex scalar fields, the level curves of which are the magnetic and electric lines, respectively. In Section 2, we will see how from ...
... equivalent to Maxwell’s standard theory but implies some topological quantization conditions with physical meaning [2, 3, 4]. The model makes use of two fundamental complex scalar fields, the level curves of which are the magnetic and electric lines, respectively. In Section 2, we will see how from ...
Inductance Motors Generators
... the contacts to the rotating loop are made by a split ring, or commutator. ...
... the contacts to the rotating loop are made by a split ring, or commutator. ...
answer sheet - Mrs. Polay`s Class
... batteries need to be facing a certain direction? The electrons flow through circuits from the negative side of the battery, through all of the components, and back to the positive side of the battery. If two batteries are in a series circuit, they need to be facing in the same direction for current ...
... batteries need to be facing a certain direction? The electrons flow through circuits from the negative side of the battery, through all of the components, and back to the positive side of the battery. If two batteries are in a series circuit, they need to be facing in the same direction for current ...
Lecture5-Phys4
... Gauss’ Law The more charge enclosed, the greater the flux through the surface. The net flux is positive if the net charge enclosed is positive, and negative if the net charge enclosed is ...
... Gauss’ Law The more charge enclosed, the greater the flux through the surface. The net flux is positive if the net charge enclosed is positive, and negative if the net charge enclosed is ...
File - Electric Circuit Analysis
... Magnetic flux lines, do not have origins or terminating points and exist in continuous loops and radiate from north to south pole returning to the north pole through the metallic bar ...
... Magnetic flux lines, do not have origins or terminating points and exist in continuous loops and radiate from north to south pole returning to the north pole through the metallic bar ...
The Magnetic Field
... • In a direct current (DC) electrons flow in one direction. • In an alternating current, electrons change their direction of movement many times each second. • Some generators are built to produce direct current instead of alternating current. ...
... • In a direct current (DC) electrons flow in one direction. • In an alternating current, electrons change their direction of movement many times each second. • Some generators are built to produce direct current instead of alternating current. ...
Electricity and Magnetism – Ch 1 “Magnetism”
... __________ surrounding it and two magnetic ____________. • The magnetic poles are located on Earth’s _______________ where the magnetic force is _______________________. • They are located close to the ___________ poles but not exactly at them (about ______________ km off) • Because of this, a _____ ...
... __________ surrounding it and two magnetic ____________. • The magnetic poles are located on Earth’s _______________ where the magnetic force is _______________________. • They are located close to the ___________ poles but not exactly at them (about ______________ km off) • Because of this, a _____ ...
PHYSICS 6 - The Nature of Light
... current flow through the coil of wire - a solenoid. If the current is constant the magnetic field will be constant as well. (Try to see how this constancy is a result of Maxwell's formulation of Ampere's law.) However, suppose the current is increasing. Then the induced magnetic field will also be i ...
... current flow through the coil of wire - a solenoid. If the current is constant the magnetic field will be constant as well. (Try to see how this constancy is a result of Maxwell's formulation of Ampere's law.) However, suppose the current is increasing. Then the induced magnetic field will also be i ...
introduction
... telecommunication, electronic industries, due to their interesting electrical and magnetic properties. In the past few years, several researchers have studied the electric and magnetic properties of ferrite materials in view of their importance in the application within the range of frequency up to ...
... telecommunication, electronic industries, due to their interesting electrical and magnetic properties. In the past few years, several researchers have studied the electric and magnetic properties of ferrite materials in view of their importance in the application within the range of frequency up to ...
View/Open - Earth
... presence of magnetic sources [13]. In fact, if we postulate the existence of magnetic monopoles m (and currents J m ), Lorentz equation must be symmetrized (adding the terms that include magnetic forces m H (r , t ) J m (r , t ) D(r , t ) ) but the total momentum is still a conserved qu ...
... presence of magnetic sources [13]. In fact, if we postulate the existence of magnetic monopoles m (and currents J m ), Lorentz equation must be symmetrized (adding the terms that include magnetic forces m H (r , t ) J m (r , t ) D(r , t ) ) but the total momentum is still a conserved qu ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.