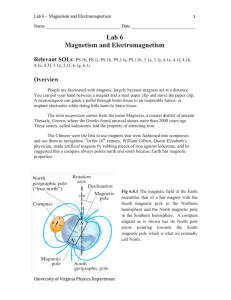
Maxwell`s electromagnetic theory and special relativity
... sense, the first electroscope (called, by Gilbert, the versorium); a fine needle of metal (or certain other substances) delicately balanced on a sharp point and which could rotate freely upon it. A rubbed material could then be brought close to it and even very small attractions between material and n ...
... sense, the first electroscope (called, by Gilbert, the versorium); a fine needle of metal (or certain other substances) delicately balanced on a sharp point and which could rotate freely upon it. A rubbed material could then be brought close to it and even very small attractions between material and n ...
Jiles problem 2 - Studentportalen
... of the coercive field for a modern hard disk and explain why even smaller bit-size will require even larger coercive field you will obtain two bonus points. (1p + 2p bonus) d) Describe briefly the function of an MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory): Describe the memory element; describe the ...
... of the coercive field for a modern hard disk and explain why even smaller bit-size will require even larger coercive field you will obtain two bonus points. (1p + 2p bonus) d) Describe briefly the function of an MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory): Describe the memory element; describe the ...
16-2 Extending our Model of Charge
... orders of magnitude larger than the conductivities of materials like rubber and plastic – those materials we call insulators. The major difference between these two classes of materials is that, in an insulator, each electron is closely tied to its molecule, while some fraction of the electrons in a ...
... orders of magnitude larger than the conductivities of materials like rubber and plastic – those materials we call insulators. The major difference between these two classes of materials is that, in an insulator, each electron is closely tied to its molecule, while some fraction of the electrons in a ...
Power Is Generated By Using Magnetic Rotor
... includes forces exerted by magnets on other magnets. It has its origin in electric currents and the fundamental magnetic moment of elementary particles. These give rise to a magnetic field that acts on other currents and movements. All materials are influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The ...
... includes forces exerted by magnets on other magnets. It has its origin in electric currents and the fundamental magnetic moment of elementary particles. These give rise to a magnetic field that acts on other currents and movements. All materials are influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The ...
PHY 142L Spr 2016 Lab 4
... of predictions is to examine your own understanding of physics; there are no right or wrong answers, but you are graded on the basis of giving due thought. ...
... of predictions is to examine your own understanding of physics; there are no right or wrong answers, but you are graded on the basis of giving due thought. ...
Analyzing Magnetic Fields with Solenoids - Physics
... of unwrapped wire at both ends of the solenoid so that there is enough room to press the stripped sections of wire to the battery terminals. Now that the solenoid is complete I have my students connect the two ends to a D-Cell battery to the stripped sections of wire to send a current through the wi ...
... of unwrapped wire at both ends of the solenoid so that there is enough room to press the stripped sections of wire to the battery terminals. Now that the solenoid is complete I have my students connect the two ends to a D-Cell battery to the stripped sections of wire to send a current through the wi ...
St_Pierre_2002 - Scientific and Clinical Applications of Magnetic
... • Response of superparamagnets to applied field described by Langevin model • Qualitatively similar to paramagnets • At room temperature superparamagnetic materials have a much greater magnetic susceptibility per atom than paramagnetic materials ...
... • Response of superparamagnets to applied field described by Langevin model • Qualitatively similar to paramagnets • At room temperature superparamagnetic materials have a much greater magnetic susceptibility per atom than paramagnetic materials ...
Module 8 Electromagnetism
... talking at the other end. Electric motors also contain magnets to function. Particle accelerators like cyclotron contain thousand of magnets as well. Electricity and magnetism cannot be separated. Magnetism plays an important role in the study of electricity. Whenever electric current appears, there ...
... talking at the other end. Electric motors also contain magnets to function. Particle accelerators like cyclotron contain thousand of magnets as well. Electricity and magnetism cannot be separated. Magnetism plays an important role in the study of electricity. Whenever electric current appears, there ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... You may never have seen such a floating ring, but the physical principle that explains why it is levitated also explains how the modern electrical distribution system works. ...
... You may never have seen such a floating ring, but the physical principle that explains why it is levitated also explains how the modern electrical distribution system works. ...
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
... In India Domestic power supply is at 220 V, 50 Hz; while in USA it is 110 V, 50 Hz. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of 220 V supply over 110 supply. A coil of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and resistor of resistance R all put in series with an alternating source of emd E = E0 si ...
... In India Domestic power supply is at 220 V, 50 Hz; while in USA it is 110 V, 50 Hz. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of 220 V supply over 110 supply. A coil of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and resistor of resistance R all put in series with an alternating source of emd E = E0 si ...
The effect of radial acceleration on the electric and
... fields associated with radial acceleration of the charges forming the circular currents and with radial acceleration of the charges comprising the rotating charge distributions. These fields are computed for several types of rotating charge distributions and for several types of circular currents. O ...
... fields associated with radial acceleration of the charges forming the circular currents and with radial acceleration of the charges comprising the rotating charge distributions. These fields are computed for several types of rotating charge distributions and for several types of circular currents. O ...
The Power of Magnets
... magnets can be found everywhere, including your hard disk, ATM and credit cards, speakers and microphones, electric motors, and toys. Electric motors work through an interaction between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet. Every permanent magnet generates a magnetic field, just like any other ma ...
... magnets can be found everywhere, including your hard disk, ATM and credit cards, speakers and microphones, electric motors, and toys. Electric motors work through an interaction between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet. Every permanent magnet generates a magnetic field, just like any other ma ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.