Document
... Here we find the solution by using an analogous method based on the results of static fields. The scalar potential caused by a point charge is obtained first, then use superposition principle to obtain the solution of the scalar potential due to a distribution of time-varying charge. If the source i ...
... Here we find the solution by using an analogous method based on the results of static fields. The scalar potential caused by a point charge is obtained first, then use superposition principle to obtain the solution of the scalar potential due to a distribution of time-varying charge. If the source i ...
B. dA - Rutgers Physics
... seconds. Set the pickup coil horizontal. Observe pictures below. Using a small refrigerator magnet, quickly start and stop data acquisition (Enter, Enter) then quickly pull the magnet up from the pickup coil. (The Off will not become effective until completion of the sweep time.) Double click, if ne ...
... seconds. Set the pickup coil horizontal. Observe pictures below. Using a small refrigerator magnet, quickly start and stop data acquisition (Enter, Enter) then quickly pull the magnet up from the pickup coil. (The Off will not become effective until completion of the sweep time.) Double click, if ne ...
CHAPTER – 14 Electric current and its Effects
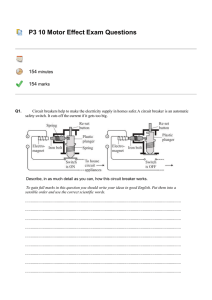
... Switch on the current. After a few seconds touch the wire. The wire feels hot. Then switch off the current. After a few seconds touch the wire again. It does not feel hot. This shows that when electric current flows through a wire, it Nichrome wire gets heated. Nail ...
... Switch on the current. After a few seconds touch the wire. The wire feels hot. Then switch off the current. After a few seconds touch the wire again. It does not feel hot. This shows that when electric current flows through a wire, it Nichrome wire gets heated. Nail ...
Some Aspects of Mean Field Dynamo Theory - Indico
... A dynamo can be thought of as a mechanism for “closing the loop” between poloidal and toroidal fields. Velocity shear (differential rotation) naturally generates toroidal from poloidal field. The α-effect of mean field electrodynamics can complete the cycle and regenerate poloidal from toroidal fiel ...
... A dynamo can be thought of as a mechanism for “closing the loop” between poloidal and toroidal fields. Velocity shear (differential rotation) naturally generates toroidal from poloidal field. The α-effect of mean field electrodynamics can complete the cycle and regenerate poloidal from toroidal fiel ...
Ch 18 ppt: Electromagnetism
... • A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current. • An electromagnet is made up of a solenoid wrapped around an iron core. • Turning Electromagnets On and Off Electromagnets are very useful because they can be turned on and off as needed. The solenoid h ...
... • A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current. • An electromagnet is made up of a solenoid wrapped around an iron core. • Turning Electromagnets On and Off Electromagnets are very useful because they can be turned on and off as needed. The solenoid h ...
Understanding and using the minus sign in Faraday`s law
... where B is the magnetic flux density and dS is an increment of area, part of any surface bounded by C; see figure 2. The directions of E and B follow the usual conventions for electric fields and magnetic fields respectively. The direction of dS may be chosen arbitrarily, either outwards from the su ...
... where B is the magnetic flux density and dS is an increment of area, part of any surface bounded by C; see figure 2. The directions of E and B follow the usual conventions for electric fields and magnetic fields respectively. The direction of dS may be chosen arbitrarily, either outwards from the su ...
File S1.
... minimal when the neurite is aligned with the y-axis and steeply increases if the alignment deviates from this optimal orientation (horizontal dashed straight lines). In contrast, stimulation with the cloverleaf coil results in a threshold that changes by less than 50% for all possible orientations o ...
... minimal when the neurite is aligned with the y-axis and steeply increases if the alignment deviates from this optimal orientation (horizontal dashed straight lines). In contrast, stimulation with the cloverleaf coil results in a threshold that changes by less than 50% for all possible orientations o ...
The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor at absolute zero of
... At absolute zero temperature, in insulators and semiconductors The valence band is full and conduction band is empty The valence band and conduction band are separated by Forbidden band gap Materials which show negligible conductivity at 0K but exhibit significant Conductivity at normal temperatures ...
... At absolute zero temperature, in insulators and semiconductors The valence band is full and conduction band is empty The valence band and conduction band are separated by Forbidden band gap Materials which show negligible conductivity at 0K but exhibit significant Conductivity at normal temperatures ...
Questions - Chemactive
... (a) To avoid cutting through cables, a gas company uses a device to detect their position before digging holes. The magnetic field produced by the cable induces a voltage across the coil. This is registered on a meter attached to the device. Y X ...
... (a) To avoid cutting through cables, a gas company uses a device to detect their position before digging holes. The magnetic field produced by the cable induces a voltage across the coil. This is registered on a meter attached to the device. Y X ...
Magnetism
... iron, can be made into magnets that are surrounded by a magnetic field. How are magnetic fields made? A moving electric charge, such as a moving electron, creates a magnetic field. Inside every magnet are moving charges. All atoms contain negatively charged particles called electrons. Not only do th ...
... iron, can be made into magnets that are surrounded by a magnetic field. How are magnetic fields made? A moving electric charge, such as a moving electron, creates a magnetic field. Inside every magnet are moving charges. All atoms contain negatively charged particles called electrons. Not only do th ...
Magnetic properties of materials Part 2. Types of magnetism
... this may be negligible compared to a positive magnetic susceptibility arising from the magnetic moments of unpaired electrons aligning themselves with the applied field. This is known as paramagnetism. Consider the behaviour of magnetic moments, possessed by certain atoms and ions, in an applied mag ...
... this may be negligible compared to a positive magnetic susceptibility arising from the magnetic moments of unpaired electrons aligning themselves with the applied field. This is known as paramagnetism. Consider the behaviour of magnetic moments, possessed by certain atoms and ions, in an applied mag ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.